(Press-News.org) World-renowned physicians and scientists will gather at the Houston Methodist Research Institute September 17-18 to discuss pioneering research discoveries and technologies in neuroscience that have the potential to transform the field and evolve into innovative treatments for neurological disorders of all kinds.
Hosted by the Houston Methodist and Rice University Center for Neural Systems Restoration, the symposium brings together experts in the field of neural circuits, neural technology and neuro-restoration. Twenty-four speakers will highlight the latest findings in understanding brain mechanisms and treating neurological disorders and will discuss how to translate these findings from the laboratory into novel therapies for patients.
Information on the symposium’s program and speakers, as well as a registration portal for the free event, can be found on the Houston Methodist website. The two-day event is open to all researchers, clinicians, residents, fellows and medical students interested in neuroprosthetics and neural restoration.
CNSR is an interdisciplinary center for neuroscience research and medical treatment innovation that aims to redefine the state of the art in neuroprosthetics and neural restoration through collaborative projects at Houston Methodist and Rice University.
END
Houston Methodist and Rice University Center for Neural Systems Restoration Inaugural Fall Symposium
“NeuroSystems: From Circuits to Restoration”
2024-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Making waves in hurricane prediction
2024-08-28
More accurately predicting periods of increased hurricane activity weeks in advance may become possible due to new research published this month.
The study, led by the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR), shows that twice as many hurricanes form two days after the passing of large-scale atmospheric waves called Kelvin waves than in the days before. This finding may enable forecasters and emergency managers to anticipate clusters of hurricanes days to weeks in advance.
The research team used an innovative ...
Autistic traits, behavioral problems in 7-year-olds linked with gender nonconforming play
2024-08-28
Gender nonconformity in 7-year-olds — as measured by levels of gender-conforming play — may be associated with autistic traits and behavioral difficulties in girls, and with peer relationship problems in boys, according to a new study published August 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marlene Stratmann of Karlstad University, Sweden, and colleagues.
Gender nonconformity (GNC) refers to variations in gender expression from societal and cultural gender norms. In childhood, GNC can manifest itself in several ways, including play behavior, peer relationships, clothing, and body language. Childhood GNC does not directly indicate developing gender ...
Geographic differences in US homicide rates have decreased since the 1970s
2024-08-28
A new study finds that, counter to expectations, geographic disparities in rates of homicides in the US have decreased in recent decades. Richard Boylan of Rice University in Houston, Texas, US, presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 28, 2024.
Since the 1970s, gaps in economic and social wellbeing between Americans living in different regions have grown. Some researchers hypothesize that areas with reduced economic and social well-being would see higher rates of violent crime. For instance, impoverished areas with lower tax bases might receive less police protection, ...
Lackluster prioritization of the health sector in government spending and dwindling donor contributions drive slow growth in health spending in Sub-Saharan Africa
2024-08-28
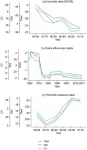
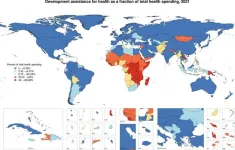
Slow growth in health sector spending is projected in Sub-Saharan Africa as reported in a study published in the open access journal, PLOS Global Public Health. The decline is expected to continue to 2050, according to Angela E Apeagyei and researchers at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, University of Washington, Seattle, and is driven by tepid growth in the share of government spending that is allocated to health and reductions in development assistance for health.
The research analyses data from databases covering development assistance for health, global health spending and gross domestic spending (GDP) per capita ...
People experiencing relatively mild cases of mental ill-health may be perceived differently by others depending on whether or not diagnostic labels are provided
2024-08-28
Diagnostic labels for people experiencing what some consider to be relatively milder forms of mental-ill health may affect how others perceive them for better and worse, according to a study published August 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Mental Health by Nick Haslam from the University of Melbourne, Australia, and colleagues.
In recent years, there’s been a general shift to increased diagnoses of mental ill-health. Here, Haslam and colleagues investigate the implications of diagnosing individuals presenting with ...
Unhealthy commodities—like alcohol and social media—are connected with poor mental health
2024-08-28
“Unhealthy commodities” such as tobacco, alcohol, ultra-processed foods, social media, and fossil fuels, as well as impacts of fossil fuel consumption such as climate change and air pollution are associated with depression, suicide, and self-harm, according to a study published August 28 by Kate Dun-Campbell from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and colleagues.
Globally, around one out of every eight people currently live with a mental health disorder. These disorders—including depression, suicide, anxiety, and other diseases and disorders—can have many underlying causes. ...
Bacterial cells transmit memories to offspring
2024-08-28
Bacterial cells can “remember” brief, temporary changes to their bodies and immediate surroundings, a new Northwestern University and University of Texas-Southwestern study has found.
And, although these changes are not encoded in the cell’s genetics, the cell still passes memories of them to its offspring — for multiple generations.
Not only does this discovery challenge long-held assumptions of how the simplest organisms transmit and inherit physical traits, it also could be leveraged for new medical applications. For example, researchers could circumvent antibiotic resistance by subtly tweaking a pathogenic ...
Dogs understand words from soundboard buttons, study reveals
2024-08-28
If you’ve seen those viral social media videos of dogs using soundboard buttons to “talk,” you’re not alone. These buttons have taken the pet world by storm, leading to impressive and sometimes seemingly miraculous feats shared across platforms like TikTok and Instagram. But are these dogs truly communicating, or are they just responding to cues from their owners?
Now, a new study published in PLOS ONE – by researchers from the University of California San Diego and other institutions – ...
New pancreatic cancer treatment proves effective in shrinking, clearing tumors
2024-08-28
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and UMass Chan Medical School have demonstrated in mice a new method to combat pancreatic cancer. The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, outlines the synergistic effects of a novel nanoparticle drug-delivery system to activate an immune pathway in combination with tumor-targeting agents.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common form of pancreatic cancer. With a dismal,13% five-year survival rate, it is the third leading cause of cancer deaths.
One major ...
Study reveals isolation, endogamy and pathogens in early medieval Spanish community
2024-08-28
An archaeogenetic study sheds new light on the isolated medieval community Las Gobas in northern Spain. Besides isolation and endogamy, the researchers have also identified the variola virus which can offer a new explanation on how smallpox entered Iberia.
Researchers from Sweden and Spain have conducted a comprehensive archaeogenetic study on a community that lived on the border between the northern Christian kingdoms and Al-Andalus during the early Medieval period. This dynamic era, especially ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Houston Methodist and Rice University Center for Neural Systems Restoration Inaugural Fall Symposium“NeuroSystems: From Circuits to Restoration”