(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 10, 2024)–Recent studies show that women can experience bothersome menopause symptoms, like hot flashes, for longer than originally estimated. As a result, more research is focusing on the long-term effects of hormone therapy. A new study suggests certain estrogen-based hormone therapies have favorable long-term effects on the risk of heart disease. Results of the study will be presented at the 2024 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Chicago September 10-14.
Hormone therapy has been the subject of intense debate for more than 20 years since the results of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) became public. Despite the fact that hormone therapy has proven to be the most effective treatment for managing some of the more common symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, some still have concerns about potential health risks, especially after extended use.
A new study based on data from the WHI suggests that, with regard to heart health, extended use of certain hormone therapies might actually be beneficial. The study specifically evaluated women who were taking conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) alone—the most commonly prescribed oral estrogen treatment—and CEE plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA).
Both CEE-alone and CEE plus MPA were shown to have a favorable influence on all cardiovascular biomarkers, except for triglycerides. In particular, relative to placebo, HDL-C (sometimes referred to as good cholesterol) increased by 13% and 7% for participants randomized to CEE-alone and CEE plus MPA, respectively. The reduction of LDL-C (sometimes referred to as bad cholesterol) was around 11% for both types of therapy. Insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) decreased by 14% and 8% for CEE-alone and CEE plus MPA, respectively. Lipoprotein(a), sometimes referred to as the heart’s quiet killer, decreased by 15% and 20% for CEE-alone and CEE plus MPA, respectively.
“Although we see a few more favorable effects with CEE, both therapies performed well in relation to their impact on biomarkers except for triglycerides,” says Dr. Matthew Nudy, lead author from Penn State Hershey Medical Center. “Future research should assess whether other progestogen formulations may be less likely to attenuate estrogen’s long-term effect on cholesterol.”
More detailed results will be discussed at the 2024 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society as part of the presentation entitled “The Long-Term Effect of Hormone Therapy on Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Women’s Health Initiative.”
“For many years women and healthcare professionals shied away from hormone therapy for fear of the potential adverse health effects, says Dr. Stephanie Faubion, medical director for The Menopause Society. “Studies like this are valuable to help women feel more confident about their decision to use hormone therapy for managing their bothersome menopause symptoms, especially hot flashes.”
Drs. Nudy and Faubion are available for interviews in advance of the Annual Meeting.
For more information about menopause and healthy aging, visit the newly redesigned www.menopause.org.
The Menopause Society (formerly The North American Menopause Society) is dedicated to empowering healthcare professionals and providing them with the tools and resources to improve the health of women during the menopause transition and beyond. As the leading authority on menopause since 1989, the nonprofit, multidisciplinary organization serves as the independent, evidence-based resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, the media, and the public and leads the conversation about improving women’s health and healthcare experiences. To learn more, visit menopause.org.
END
Is hormone therapy good for heart health?
New study based on Women's Health Initiative data suggests estrogen-based hormone therapy has favorable long-term effect on all cardiovascular biomarkers except triglycerides
2024-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mass production of metal nanowires possible by breakthrough technique
2024-09-10
A group from Nagoya University in Japan has created a new technique for growing the tiny metal nanowires (NWs) that are expected to be used in next-generation electronics. Their results suggest a way to mass produce pure metal NWs, which has until now limited their use. The new technique promises to enhance the efficiency of electronics production, including circuitry, LEDs, and solar cells. The study was published in Science.
Mass production of NWs has been challenging because of the difficulties of scaling production while maintaining quality and ...
Methane emissions are rising faster than ever
2024-09-10
The world has not hit the brakes on methane emissions, a powerful driver of climate change. More than 150 nations have pledged to slash by 30% this decade under a global methane pledge, but new research shows global methane emissions over the past five years have risen faster than ever.
The trend “cannot continue if we are to maintain a habitable climate,” the researchers write in a Sept. 10 perspective article in Environmental Research Letters published alongside data in Earth System Science Data. Both papers are the work of the Global ...
New study to explore novel marker in interstitial lung disease prognosis
2024-09-10
Researchers at the University of Exeter and clinical radiopharmaceutical company Serac Healthcare Ltd are researching a new molecular imaging marker which could help to detect disease progression sooner.
The novel imaging agent 99mTc-maraciclatide has been used to scan the first patient with the aim of evaluating the marker’s potential for predicting interstitial lung disease in a Phase II study titled ‘PRospective Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Disease progression with quantitative CT’ ...
Experimenting with different vapes could be crucial to help people quit smoking
2024-09-10
New research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) found that more than a third of quitters who were given a vape in A&E experimented with different devices bought from shops or online
People who smoke and had little experience with vapes were particularly receptive to an opportunistic approach in a medical setting
The study found that some quitters reduced their vaping significantly within a few months, showing that not everyone who uses an e-cigarette becomes dependent on vaping long-term
Peer-reviewed – Observational Study- People
Experimenting with commercially ...
Long-term exercisers have 'healthier' belly fat
2024-09-10
People with obesity who are long-time exercisers have healthier belly fat tissue and can store fat there more effectively than nonexercisers with obesity, according to a new study from a team of researchers at the University of Michigan.
The research team also grew fat tissue in the lab from cells collected from both exercisers and nonexercisers, and cells from the exercisers developed into a tissue that stored fat more effectively.
"Our findings indicate that in addition to being a means to expend calories, exercising regularly for several months to years seems to modify your fat tissue ...
Gene therapy effective in hereditary blindness
2024-09-10
Bothnia dystrophy is a form of hereditary blindness, prevalent in the region Västerbotten in Sweden. A new study at Karolinska Institutet published in Nature Communications shows that gene therapy can improve vision in patients with the disease.
Bothnia dystrophy occurs mainly in the region Västerbotten in Sweden, but the disease has also been identified in other parts of the world. The disease leads to progressive visual impairment due to the destruction of the visual cells in the retina. It is caused by an inherited genetic mutation ...
Report: Conscientiousness, not willpower, is a reliable predictor of success
2024-09-10
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — According to two psychologists, the field of psychological science has a problem with the concept of self-control. It has named self-control both a “trait” — a key facet of personality involving attributes like conscientiousness, grit and the ability to tolerate delayed gratification — and a “state,” a fleeting condition that can best be described as willpower. These two concepts are at odds with one another and are often confused, the authors report.
“Self-control is a cherished quality. People who have lots of it are celebrated and seen as morally righteous,” wrote University of Toronto psychology professor Michael Inzlicht ...
Advancing prison safety
2024-09-10
The lead article in the current issue of The Criminologist, written by Nancy Rodriguez, University of California Irvine professor of criminology, law and society, shines a light on the lack of prison violence metrics that could help advance safety.
“For the 800,000 persons currently confined and the 200,000 state and federal correctional officers who work within U.S. prisons, the threat of violence is a routine feature of daily life,” she writes. “Accounts from incarcerated persons and staff detail the ever-present threats ...
Towards a better understanding of epigenetics and dynamic gene silencing and reactivation
2024-09-10
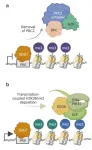
Ikoma, Japan – One of the most fascinating discoveries in biology is that cells have mechanisms for dynamically regulating genetic expression. This ability to promote or restrict the transcription of specific genes without altering the DNA sequences themselves is essential to all forms of life, from single-cell organisms to the most complex plants and animal species.
While our understanding of these so-called epigenetic mechanisms is far from complete, remarkable progress has been made in this field with the understanding of the role of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2). PRC2 is a protein that, in many plants, binds to specific DNA sequences called polycomb ...
Artificial muscles propel a robotic leg to walk and jump
2024-09-09
Inventors and researchers have been developing robots for almost 70 years. To date, all the machines they have built – whether for factories or elsewhere – have had one thing in common: they are powered by motors, a technology that is already 200 years old. Even walking robots feature arms and legs that are powered by motors, not by muscles as in humans and animals. This in part suggests why they lack the mobility and adaptability of living creatures.
A new muscle-powered robotic leg is not only more energy efficient than a conventional one, it can also perform high jumps and fast movements as well as detect and react to obstacles – ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Is hormone therapy good for heart health?New study based on Women's Health Initiative data suggests estrogen-based hormone therapy has favorable long-term effect on all cardiovascular biomarkers except triglycerides