(Press-News.org) A mysterious tusked animal depicted in South African rock art might portray an ancient species preserved as fossils in the same region, according to a study published September 18, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Julien Benoit of the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa.
The Horned Serpent panel is a section of rock wall featuring artwork of animals and other cultural elements associated with the San people of South Africa, originally painted between 1821 and 1835. Among the painted figures is a long-bodied animal with downward-turned tusks which doesn’t match any known modern species in the area. As the San people are known to have included various aspects of their surroundings into art, including fossils, Benoit suggests the tusked creature might have been inspired by an extinct species.
The Karoo Basin of South Africa is famous for abundant well-preserved fossils, including tusked animals called dicynodonts, which are often found eroding out of the ground. Benoit revisited the Horned Serpent panel and found the tusked figure comparable with dicynodont fossils, an interpretation that is also supported by San myths of large animals that once roamed the region but are now extinct. If the tusked figure is in fact an artistic interpretation of a dicynodont, a species which went extinct before dinosaurs appeared and were long extinct when humans appeared in Africa, it would predate the first scientific description of these ancient animals by at least ten years.
There is archaeological evidence that the San people might have collected fossils and incorporated them into their artwork, but the extent of indigenous knowledge of paleontology is poorly understood across Africa. Further research into indigenous cultures might shed more light on how humans around the world have incorporated fossils into their culture.
Julien Benoit adds: “The painting was made in 1835 at the latest, which means this dicynodont was depicted at least ten years before the western scientific discovery and naming of the first dicynodont by Richard Owen in 1845. This work supports that the first inhabitants of southern Africa, the San hunter-gatherers, discovered fossils, interpreted them and integrated them in their rock art and belief system.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0309908
Citation: Benoit J (2024) A possible later stone age painting of a dicynodont (Synapsida) from the South African Karoo. PLoS ONE 19(9): e0309908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0309908
Author Countries: South Africa
Funding: This research was financially supported by the DSI-NRF African Origins Platform (AOP210218587003; UID: 136505). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
South African rock art possibly inspired by long-extinct species
Research compares 1800s painting of tusked animal by San people to local fossils
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Even marine animals in untouched habitats are at risk from human impacts
2024-09-18
Climate change and a range of other human impacts are putting marine animals at risk of extinction – even those living in almost pristine marine habitats and diverse coastal regions – reports a new study by Casey O'Hara of the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis at the University of California, Santa Barbara, USA, and colleagues, published September 18, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Human activities on land and sea, in combination with climate change, are degrading coastal ...
Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules shape-shift into versatile robots
2024-09-18
Stuttgart – Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) have developed hexagon-shaped robotic components, called modules, that can be snapped together LEGO-style into high-speed robots that can be rearranged for different capabilities. The team of researchers from the Robotic Materials Department at MPI-IS, led by Christoph Keplinger, integrated artificial muscles into hexagonal exoskeletons that are embedded with magnets, allowing for quick mechanical and electrical connections. The team’s work, “Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules for rapidly reconfigurable high-speed robots” will be published in Science ...
Flexible circuits made with silk and graphene on the horizon
2024-09-18
RICHLAND, Wash.—After thousands of years as a highly valuable commodity, silk continues to surprise. Now it may help usher in a whole new direction for microelectronics and computing.
While silk protein has been deployed in designer electronics, its use is currently limited in part because silk fibers are a messy tangle of spaghetti-like strands.
Now, a research team led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has tamed the tangle. They report in the journal ...
Scott Emr and Wesley Sundquist awarded 2024 Horwitz Prize for discovering the ESCRT pathway
2024-09-18
NEW YORK, NY (September 18, 2024)—Columbia University will award the 2024 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize to Scott Emr and Wesley Sundquist for discovering the ESCRT (Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport) pathway and revealing how it works.
ESCRT (pronounced “escort”) complexes deform the cell membrane and bend parts of it away from the cytoplasm, the space that houses all material inside a cell. This unique process plays an essential role in keeping cells healthy by packaging and sorting molecules, removing waste, and regulating important functions such as cell division, neuron remodeling, ...
Versatile knee exo for safer lifting
2024-09-18
Images
A set of knee exoskeletons, built with commercially available knee braces and drone motors at the University of Michigan, has been shown to help counteract fatigue in lifting and carrying tasks. They helped users maintain better lifting posture even when tired, a key factor in defending against on-the-job injuries, the researchers say.
"Rather than directly bracing the back and giving up on proper lifting form, we strengthen the legs to maintain it," said Robert Gregg, U-M professor of robotics and corresponding author of the study in Science Robotics. "This differs from what's more commonly done in industry."
Already ...
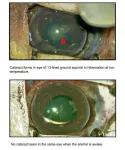
NIH-led studies point to potential development of a cataract drug
2024-09-18
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators have identified a protein, known as RNF114, that reverses cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens that occurs commonly in people as they age. The study, which was conducted in the 13-lined ground squirrel and rats, may represent a possible surgery-free strategy for managing cataracts, a common cause of vision loss. The study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“Scientists have long searched for an alternative to cataract surgery, which is effective, but not without risk. Lack of access to cataract surgery is a barrier to care in some ...
Artificial intelligence grunt work can be outsourced using a new blockchain-based framework developed by Concordians
2024-09-18
Tomorrow’s workplace will be run on mind-boggling amounts of data. To make sense of it all, businesses, developers and individuals will need better artificial intelligence (AI) systems, better trained AI workers and more efficient number-crunching servers.
While big tech companies have the resources and expertise to meet these demands, they remain beyond the reach of most small and medium-sized enterprises and individuals. To respond to this need, a Concordia-led international team of researchers has developed a new framework to make complex AI tasks more accessible ...
Mental health challenges faced by children with cystic fibrosis are the focus of a major, multisite study led by UB
2024-09-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A University at Buffalo psychiatrist who has played a critical role in getting mental health screening and treatment integrated into routine care for adults and adolescents with cystic fibrosis (CF) has been awarded $3 million from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation to focus on the mental health of children with the disease.
Led by UB and launched this summer, the new study is an outgrowth of The International Depression Epidemiological Study (TIDES), which began in 2014 and was the largest study of mental health in adolescents and adults with CF. As a result of TIDES, ...
UC3M and Universia obtain an ENIA Chair in artificial intelligence in data economy
2024-09-18
The Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) is one of 22 institutions that have been selected by the Ministry for Digital Transformation and the Civil Service to create an ENIA Chair to further the development of artificial intelligence (AI)-based applications. The AImpulsa UC3M-Universia Chair, as it is called, will be the only one of its kind in Spain in the area of Data Economy and will collaborate with Universia-Banco Santander, through Santander Universities.
The ENIA Chairs' objectives, which depend on the Secretary of State for Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence of the Ministry for Digital Transformation and ...
Why petting your cat leads to static electricity
2024-09-18
Anyone who has ever pet a cat or shuffled their feet across the carpet knows that rubbing objects together generates static electricity. But an explanation for this phenomenon has eluded researchers for more than two millennia.
Now, Northwestern University scientists have finally uncovered the mechanics at play.
When an object slides, the front and back parts of that object experience different forces, researchers found. This difference in forces causes different electrical charges to build up on the front and back parts of the object. And the difference in electrical charges creates a current, leading to a light zap.
The study was published yesterday (Sept. 17) in the journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
[Press-News.org] South African rock art possibly inspired by long-extinct speciesResearch compares 1800s painting of tusked animal by San people to local fossils