(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS – People whose diet more closely resembles the MIND diet may have a lower risk of cognitive impairment, according to a study published in the September 18, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Results were similar for Black and white participants. These results do not prove that the MIND diet prevents cognitive impairment, they only show an association.
The MIND diet is a combination of the Mediterranean and DASH diets. It includes green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale and collard greens along with other vegetables. It recommends whole grains, olive oil, poultry, fish, beans and nuts. It prioritizes berries over other fruits and recommends one or more servings of fish per week.
“With the number of people with dementia increasing with the aging population, it’s critical to find changes that we can make to delay or slow down the development of cognitive problems,” said study author Russell P. Sawyer, MD, of the University of Cincinnati in Ohio and member of the American Academy of Neurology. “We were especially interested to see whether diet affects the risk of cognitive impairment in both Black and white study participants.”
The study involved 14,145 people with an average age of 64. Of participants, 70% were white and 30% were Black. They were followed for an average of 10 years.
Participants filled out a questionnaire on their diet over the past year. Researchers looked at how closely the foods people were eating matched the MIND diet.
One point was given for each of the following: three or more daily servings of whole grains; six or more weekly servings of green leafy vegetables; one or more daily servings of other vegetables; two or more weekly servings of berries; one or more weekly servings of fish; two or more weekly servings of poultry; three weekly servings of beans; five daily servings of nuts; four or fewer weekly servings of red meat; one or fewer weekly servings of fast or fried foods; one or more weekly servings of olive oil; and one or fewer tablespoons of butter or margarine daily; five or fewer weekly servings of pastries and sweets; and one glass per day of wine. The total points possible was 12.
Researchers then divided participants into three groups. The low group had an average diet score of five, the middle group had an average score of seven and the high group had an average score of nine.
Thinking and memory skills were measured at the beginning and end of the study.
During the study, cognitive impairment developed in 532 people, or 12% of 4,456 people in the low diet group; in 617 people, or 11% of 5,602 people in the middle group; and in 402 people, or 10% of the 4,086 people in the high group.
After adjusting for factors such as age, high blood pressure and diabetes, researchers found people in the high group had a 4% decreased risk of cognitive impairment compared to those in the low group.
When looking at male and female participants, researchers found a 6% decreased risk of cognitive impairment for female participants who most closely followed the diet but no decreased risk for male participants.
Researchers also looked at how quickly people’s thinking skills declined as they developed problems. They found that people who more closely followed the MIND diet declined more slowly than those who did not, and that association was stronger in Black participants than in white participants.
“These findings warrant further study, especially to examine these varying impacts among men and women and Black and white people, but it’s exciting to consider that people could make some simple changes to their diet and potentially reduce or delay their risk of cognitive issues,” said Sawyer.
A limitation of the study was it included only older Black and white people so results may not be the same for other populations.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging.
Learn more about dementia at BrainandLife.org home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, X and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world's largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN’s mission is to enhance member career fulfillment and promote brain health for all. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, concussion, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, headache and migraine.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, X, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
Can the MIND diet lower the risk of memory problems later in life?
2024-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Some diabetes drugs tied to lower risk of dementia, Parkinson’s disease
2024-09-18
MINNEAPOLIS – A class of drugs for diabetes may be associated with a lower risk of dementia and Parkinson’s disease, according to a study published in the September 18, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
The study looked at sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which are also known as gliflozins. They lower blood sugar by causing the kidneys to remove sugar from the body through urine.
“We know that these neurodegenerative diseases like dementia and Parkinson’s disease are common and the number of cases is growing as the ...
Propagated corals reveal increased resistance to bleaching across the Caribbean during the fatal heatwave of 2023
2024-09-18
SECORE International’s Coral Seeding approach utilizes assisted reproduction, the breeding of corals, for reef restoration. This approach is realized within a training and partner network throughout the Caribbean. Now, a peer-reviewed study shows that all the effort was worthwhile: during the devastating heatwave in the Caribbean in 2023, the young, bred corals out on the reef stayed healthy while most of the remaining wild corals bleached and many died in the aftermath.
The summer of 2023 was deadly for many corals in the Caribbean Basin. An unprecedented heatwave, in intensity as well as in duration, hit the Caribbean with catastrophic ...
South African rock art possibly inspired by long-extinct species
2024-09-18
A mysterious tusked animal depicted in South African rock art might portray an ancient species preserved as fossils in the same region, according to a study published September 18, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Julien Benoit of the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa.
The Horned Serpent panel is a section of rock wall featuring artwork of animals and other cultural elements associated with the San people of South Africa, originally painted between 1821 and 1835. Among the painted figures is ...
Even marine animals in untouched habitats are at risk from human impacts
2024-09-18
Climate change and a range of other human impacts are putting marine animals at risk of extinction – even those living in almost pristine marine habitats and diverse coastal regions – reports a new study by Casey O'Hara of the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis at the University of California, Santa Barbara, USA, and colleagues, published September 18, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Human activities on land and sea, in combination with climate change, are degrading coastal ...
Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules shape-shift into versatile robots
2024-09-18
Stuttgart – Scientists at the Max-Planck-Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) have developed hexagon-shaped robotic components, called modules, that can be snapped together LEGO-style into high-speed robots that can be rearranged for different capabilities. The team of researchers from the Robotic Materials Department at MPI-IS, led by Christoph Keplinger, integrated artificial muscles into hexagonal exoskeletons that are embedded with magnets, allowing for quick mechanical and electrical connections. The team’s work, “Hexagonal electrohydraulic modules for rapidly reconfigurable high-speed robots” will be published in Science ...
Flexible circuits made with silk and graphene on the horizon
2024-09-18
RICHLAND, Wash.—After thousands of years as a highly valuable commodity, silk continues to surprise. Now it may help usher in a whole new direction for microelectronics and computing.
While silk protein has been deployed in designer electronics, its use is currently limited in part because silk fibers are a messy tangle of spaghetti-like strands.
Now, a research team led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has tamed the tangle. They report in the journal ...
Scott Emr and Wesley Sundquist awarded 2024 Horwitz Prize for discovering the ESCRT pathway
2024-09-18
NEW YORK, NY (September 18, 2024)—Columbia University will award the 2024 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize to Scott Emr and Wesley Sundquist for discovering the ESCRT (Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport) pathway and revealing how it works.
ESCRT (pronounced “escort”) complexes deform the cell membrane and bend parts of it away from the cytoplasm, the space that houses all material inside a cell. This unique process plays an essential role in keeping cells healthy by packaging and sorting molecules, removing waste, and regulating important functions such as cell division, neuron remodeling, ...
Versatile knee exo for safer lifting
2024-09-18
Images
A set of knee exoskeletons, built with commercially available knee braces and drone motors at the University of Michigan, has been shown to help counteract fatigue in lifting and carrying tasks. They helped users maintain better lifting posture even when tired, a key factor in defending against on-the-job injuries, the researchers say.
"Rather than directly bracing the back and giving up on proper lifting form, we strengthen the legs to maintain it," said Robert Gregg, U-M professor of robotics and corresponding author of the study in Science Robotics. "This differs from what's more commonly done in industry."
Already ...
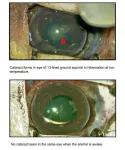
NIH-led studies point to potential development of a cataract drug
2024-09-18
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators have identified a protein, known as RNF114, that reverses cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens that occurs commonly in people as they age. The study, which was conducted in the 13-lined ground squirrel and rats, may represent a possible surgery-free strategy for managing cataracts, a common cause of vision loss. The study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“Scientists have long searched for an alternative to cataract surgery, which is effective, but not without risk. Lack of access to cataract surgery is a barrier to care in some ...
Artificial intelligence grunt work can be outsourced using a new blockchain-based framework developed by Concordians
2024-09-18
Tomorrow’s workplace will be run on mind-boggling amounts of data. To make sense of it all, businesses, developers and individuals will need better artificial intelligence (AI) systems, better trained AI workers and more efficient number-crunching servers.
While big tech companies have the resources and expertise to meet these demands, they remain beyond the reach of most small and medium-sized enterprises and individuals. To respond to this need, a Concordia-led international team of researchers has developed a new framework to make complex AI tasks more accessible ...