(Press-News.org) Wrist-based activity sensors worn by individuals with depression and those without over the course of two weeks provided evidence for the relationship between daily sunlight exposure and physical activity, according to a study published September 25, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS Mental Health by Oleg Kovtun and Sandra Rosenthal from Vanderbilt University, U.S.
Mood disorders are the leading cause of ‘disability’ worldwide. Up to 30 percent of individuals with major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder display a seasonal pattern of symptoms. This phenomenon is now recognized in official diagnostic manuals. Yet very little is known about the influence of day length (i.e., photoperiod) and sunlight intensity (i.e., solar insolation) on seasonal patterns in major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder.
In their new study, Kovtun and Rosenthal used a quantitative approach to examine the relationship between sunlight measures and objectively measured movement activity patterns to begin to understand the environmental factors driving seasonality in major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder. They used motor-activity recordings collected via accelerometers (which measure the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time) from 23 individuals with unipolar or bipolar depression and 32 individuals without depression. Participants were recruited at the University of Bergen, Norway.
The findings revealed relationships between daytime physical activity, depressed state, photoperiod and solar insolation. In particular, more depressed states were associated with lower daytime activity, whilst daytime activity increased with photoperiod and solar insolation. Additional results suggest that the impact of solar insolation on physical activity may differ between depressed individuals and those who are not. This finding could indicate that depressed individuals exhibit an altered physiological link between energy input (i.e., solar insolation) and physical activity. On the other hand, it is also possible that increased sedentary behavior results in reduced time spent outdoors and does not allow depressed people to capitalize on the benefits of sunlight exposure.
According to the authors, the study presents a generalizable strategy to understand the complex interplay between sunlight, physical activity, and depressed state using open-source digital tools. The ability to identify mood disturbances, particularly in seasonally susceptible individuals, using passive digital biomarker data offers promise in informing next-generation predictive, personalized diagnostics in mental health.
Specifically, a digital biomarker, such as accelerometer-derived motor activity patterns, could form the basis of an early warning system that alerts a clinician to initiate a timely intervention. Incorporating objectively measured sunlight exposure markers (i.e., NASA-collected solar insolation data or accelerometer-measured light exposure) could further enhance the predictive power of such tools and lay the foundation for personalized models aimed at individuals susceptible to mood disturbances with seasonal patterns.
Rosenthal and Kovtun add, "Individuals with seasonal mood disorders may not yet recognize the pattern of their illness. One of the goals of our study is to motivate the development of digital tools to assist clinicians and help affected individuals with self management of their symptoms”.
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Mental Health: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000124
Video Caption: Rate of Change: Sandra Rosenthal & the Patterns of Bipolar Disorder (Dr Rosenthal talking about her lived experience and the rate of change in solar insolation)
Video Credit: Vanderbilt University
Video Link: https://youtu.be/F8TYzvDNNT8?si=f5pSJmanyALi95JR
Citation: Kovtun O, Rosenthal SJ (2024) Seasonality in mood disorders: Probing association of accelerometer-derived physical activity with daylength and solar insolation. PLOS Ment Health 1(4): e0000124. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000124
Author Countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by Velux Stiftung (grant No. 1821 to SJR and OK). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Digital biomarkers shedding light on seasonality in mood disorders
Physical activity is linked to depressed state, daylength and sunlight intensity
2024-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US politicians support climate action when linked to certain other issues
2024-09-25
The US House of Representatives is more likely to vote on climate action when it is linked with certain other environmental issues, according to a study published September 25, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Kayla Morton of the University of Washington, Seattle and colleagues.
Climate change is a very polarizing issue in US politics. While Congress has not passed many climate-related bills over the past two decades, the House of Representatives has voted on many bills and resolutions related to climate issues, thus providing an opportunity to examine the factors that motivate ...
Mars’ missing atmosphere could be hiding in plain sight
2024-09-25
Mars wasn’t always the cold desert we see today. There’s increasing evidence that water once flowed on the Red Planet’s surface, billions of years ago. And if there was water, there must also have been a thick atmosphere to keep that water from freezing. But sometime around 3.5 billion years ago, the water dried up, and the air, once heavy with carbon dioxide, dramatically thinned, leaving only the wisp of an atmosphere that clings to the planet today.
Where exactly did Mars’ ...
Pitt study identifies potential new treatment for liver fibrosis
2024-09-25
New research from the University of Pittsburgh School of Pharmacy sheds light on the processes that lead to liver fibrosis and suggests a novel treatment approach for this common and serious condition.
Led by senior author Wen Xie, M.D., Ph.D., professor and Joseph Koslow endowed chair of the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and co-first authors Hung-Chun Tung, graduate student, and Jong-Won Kim, Ph.D., postdoctoral fellow, the study published today in Science Translational Medicine.
In this Q&A, Xie elaborates ...
Hardest hit by heat
2024-09-25
Each passing year, climate change drives summer temperatures to new extremes, with heat records being shattered one after another. In a new study, scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) have examined how extreme temperatures in the US affect the mortality of people from different racial groups. Risto Conte Keivabu, Ugofilippo Basellini, and Emilio Zagheni (director of MPIDR) analyzed data from 1993 to 2005 and examined racial differences in temperature-related deaths. The study found that both extreme cold (temperatures in the coldest 5%) and extreme heat (temperatures in the hottest 5%) increase mortality rates, with heat disproportionate impacting ...
Pigs may be transmission route of rat hepatitis E to humans
2024-09-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that pigs may function as a transmission vehicle for a strain of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) common in rats that has recently been found to infect humans.
The Rocahepevirus ratti strain is called “rat HEV” because rats are the primary reservoir of the virus. Since the first human case was reported in a person with a suppressed immune system in Hong Kong in 2018, at least 20 total human cases have been reported – including in people with normal immune function.
People infected with rat HEV did not report exposure to rats, leaving the cause of infection undefined. ...
The Foundation of Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (FCMSC) receives $100,000 gift for the June Halper MS Nursing Scholarship Fund
2024-09-25
(Hackensack, NJ, September 2024) The Foundation of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (FCMSC) recently received a generous donation of $100,000 from EMD Serono Inc., in honor of June Halper, MSN, APN-C, FAAN, MSCN. Ms. Halper a longtime pioneer in the comprehensive care movement for multiple sclerosis (MS), and leading nurse practitioner and MS advocate, passed away on July 24, 2024, at the age of 86, working until her final days as CEO of the CMSC, FCMSC and IOMSN (International Organization of MS Nurses).
Since 1978, Ms. ...
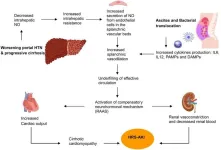
Effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on renal and pulmonary function in hepatic decompensation with and without hepatorenal and hepatopulmonary syndromes
2024-09-25
Cirrhosis is one of the leading causes of mortality from non-communicable diseases, with complications arising as liver function deteriorates. HRS and HPS represent the most severe outcomes of cirrhosis, associated with systemic vasodilation driven by elevated levels of vasodilators like nitric oxide (NO). These complications significantly impair renal and pulmonary functions, leading to high mortality rates. TIPS, by shunting blood from the portal to systemic circulation, can potentially improve renal function by increasing systemic blood volume. However, the diversion of NO through TIPS could exacerbate systemic hypotension, posing a risk to renal ...
Encoding human experience: Study reveals how brain cells compute the flow of time
2024-09-25
A landmark study led by UCLA Health has begun to unravel one of the fundamental mysteries in neuroscience – how the human brain encodes and makes sense of the flow of time and experiences.
The study, published in the journal Nature, directly recorded the activity of individual neurons in humans and found specific types of brain cells fired in a way that mostly mirrored the order and structure of a person’s experience. They found the brain retains these unique firing patterns after the experience is concluded and can rapidly replay them while at rest. Furthermore, the brain is also able to utilize these learned patterns to ready itself for future stimuli following that experience. ...
New study: Deep-sea discovery shines light on life in the twilight zone
2024-09-25
TAMPA, Fla. (Sept. 23, 2024) – The ocean’s twilight zone is deep, dark, and — according to new research — iron deficient.
No sunlight reaches this region 200 to 1,000 meters below the sea surface, where levels of iron, a key micronutrient, are so low that the growth of bacteria is restricted. To compensate, these bacteria produce molecules called siderophores, which help the bacteria scavenge trace amounts of iron from the surrounding seawater.
The paper detailing these unexpected findings from the Pacific Ocean will publish on Wednesday, Sept. 25, at 11 a.m. ET (4 p.m. London Time) in Nature, and will be viewable at that time at this link. The ...
Brazilian fossils reveal jaw-dropping discovery in mammal evolution
2024-09-25
These fossils, belonging to the mammal-precursor species Brasilodon quadrangularis and Riograndia guaibensis, offer critical insights into the development of the mammalian jaw and middle ear, revealing evolutionary experiments that occurred millions of years earlier than previously thought.
Mammals stand out among vertebrates for their distinct jaw structure and the presence of three middle ear bones. This transition from earlier vertebrates, which had a single middle ear bone, has long fascinated scientists. The new study explores how mammal ancestors, known as cynodonts, evolved these features ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
[Press-News.org] Digital biomarkers shedding light on seasonality in mood disordersPhysical activity is linked to depressed state, daylength and sunlight intensity