(Press-News.org) Medical professionals have a responsibility to lead the fight against climate misinformation to ensure that the public is well informed about the health risks posed by climate change, say experts in The BMJ today.
Misinformation (inaccurate information spread without malicious intent) and disinformation (deliberately deceptive information) in health is not new, write Professor Andy Haines and colleagues.
Just as the rapid spread of false information during the covid-19 pandemic undermined public trust in science and public health interventions, false information also pervades the climate change debate, influencing public perception and policy.
The World Health Organisation has identified climate change as the greatest threat to global health in the 21st century, but the public's understanding of this threat is often clouded by conflicting narratives.
Common myths include the belief that climate change is a hoax designed to push political agendas, a natural phenomenon unaffected by human activity, or that the risks are exaggerated, they explain. “Disinformation activities, often supported by fossil fuel interests, propagate these myths, impeding efforts to mobilise public support for necessary policy changes,” they add.
Social media platforms have also become major conduits for health-related climate disinformation. The covid-19 pandemic showed how quickly misinformation could escalate into a global health crisis. Similar dynamics are at play with climate change, where misinformation can lead to public apathy or resistance towards climate action.
“The amplification of such misinformation by influential figures and networks further entrenches these beliefs, making it challenging to shift public opinion.”
And they note that the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has added a new dimension to the spread of false information, further muddying the waters of public discourse.
“The medical community has a pivotal role in addressing the issue of misinformation around health and climate change,” they conclude.
“By adopting a multifaceted approach that includes robust communication, collaboration with tech companies, education, policy advocacy, and community engagement, the impact of misinformation can be mitigated to ensure that the public is well-informed about the health risks posed by climate change.”
[Ends]
END
Medical professionals must lead the fight against climate misinformation
As trusted voices, the profession can mitigate the impact of falsehoods about the health risks posed by climate change, say experts
2024-10-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Should doctors be suspended for unlawful climate activism?
2024-10-09
Former GP Sarah Benn was suspended by the medical practitioners tribunal service (MPTS) after an arrest for her involvement in climate protests. In The BMJ today, two experts debate the question of when and whether doctors in such cases should be sanctioned.
The recent case of Sarah Benn has sparked debate, partly because of a perception that the GMC referred her to a MPTS tribunal for taking part in peaceful protests, says Andrew Hoyle, assistant director at the GMC.
In reality, he explains ...
Extreme rainfall linked to heightened risk of death
2024-10-09
Extreme rainfall events are associated with an increased risk of death from all causes as well as from heart and lung diseases, finds an analysis of data from 34 countries and regions published by The BMJ today.
The health effects of extreme rainfall varied by local climate and vegetation coverage, providing a global perspective on the effect of extreme rainfall events on health.
Climate change is intensifying the frequency and severity of short term rainfall events, and emerging evidence suggests a compelling link between rainfall events and adverse health outcomes, particularly transmission ...
New research highlights the overlooked dangers of subtle and covert abuse in intimate relationships
2024-10-09
Peer-reviewed – Scoping Review - People
New research from the University of East Anglia has uncovered a significant gap in understanding of a harmful form of domestic abuse known as subtle or covert abuse.
Unlike more obvious forms of physical or verbal abuse, subtle abuse is less visible but can be just as damaging to victims.
The review found that current research on this topic is limited, despite its potentially widespread impact.
The findings suggest that subtle abuse ...
Snowflake dance analysis could improve rain forecasts
2024-10-09
The key to more accurate rainfall predictions may lie in the intricate dance of falling snowflakes, a new study has found.
The research, observing the physical motion of falling ice crystals, will help scientists better estimate where and when these crystals will melt into raindrops, a crucial stage in the formation of many types of rain.
Published today (Thursday 10 October) in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, the study involved scientists watching how fake snowflakes fell in a substance ...
ASPB welcomes Hong Ma as Society President
2024-10-09
ASPB is delighted to welcome its new President, Hong Ma, who was elected in 2023 as President-elect and served in this role starting October 1, 2023. He stepped into his role as ASPB President on October 1, 2024 following the end of now-Past President Leeann Thornton’s term.
“A top priority is to support and train young plant biologists toward becoming members of a community with greater diversity, to amplify the voices of diverse members of our society, and to promote diversity and representation in society leadership and society activities,” ...
Can advanced AI can solve visual puzzles and perform abstract reasoning?
2024-10-09
Artificial Intelligence has learned to master language, generate art, and even beat grandmasters at chess. But can it crack the code of abstract reasoning—those tricky visual puzzles that leave humans scratching their heads? Researchers at USC Viterbi School of Engineering Information Sciences Institute (ISI) are putting AI’s cognitive abilities to the test, pushing the multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to solve visual problems once reserved for human IQ tests. The result? A glimpse into how far AI has come—and where it still stumbles.
USC Viterbi ISI Research ...
West Health-Gallup poll: Healthcare may be sleeper issue in U.S. presidential campaign
2024-10-09
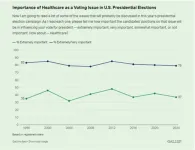
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Oct. 9, 2024 – Though in this year’s presidential election healthcare has seemingly taken a back to other issues including the economy and democracy, nearly eight in 10 registered voters still say the issue that has been critical in nearly every presidential campaign in modern history, remains extremely (37%) or very important (42%) to whom they cast their vote, according to a new a West Health-Gallup poll of voters. This sentiment is consistent with what’s been expressed in most previous elections, although slightly more ...
UC Irvine scientists track and analyze lofted embers that cause spot fires
2024-10-09
Irvine, Calif., Oct. 9, 2024 — In the chaos of a wildfire, heat, wind, flames and fuel interact to produce embers that are lofted into surrounding areas, starting new spot fires and spreading destruction and property loss in California’s wildland-urban interface. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have conducted first-of-their-kind field experiments to better understand the physics of these firebrands, and their results can help authorities better model the outcomes of disasters that are happening with greater frequency in a warming climate.
In a paper published recently in the journal Physics of Fluids, UC Irvine team members describe their ...
Uncovering pandemic inequities
2024-10-09
More than four years after the COVID-19 pandemic caused the world to come to a standstill, lessons in pandemic response are still being learned. What we know: the global pandemic disproportionately affected racial and ethnic minority groups across the U.S., with Black and Hispanic individuals being three to four times more likely to die from COVID compared to white individuals.
Daniel Harris, Assistant Professor of Epidemiology in the University of Delaware's College of Health Sciences (CHS), took a deep dive into rarely obtained COVID-19 ...
Microbiome researcher awarded NIH Transformative Research Award to pursue personalized treatment for gut diseases
2024-10-09
Baylor University researcher Aaron Wright, Ph.D., has earned a $5.6 million National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director’s Transformative Research Award for a project that he and collaborators hope could lead to personalized – and revolutionary – treatments for gut microbiome diseases like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s, Ulcerative Colitis and more. Wright, a nationally recognized microbiome researcher and chemical biologist who serves as The Schofield Endowed Chair in Biomedical Science in Baylor’s Department of Biology, will partner on the project with colleagues from Weill ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Medical professionals must lead the fight against climate misinformationAs trusted voices, the profession can mitigate the impact of falsehoods about the health risks posed by climate change, say experts