A “chemical ChatGPT” for new medications
Study by the University of Bonn with promising results
2024-10-23
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from the University of Bonn have trained an AI process to predict potential active ingredients with special properties. Therefore, they derived a chemical language model – a kind of ChatGPT for molecules. Following a training phase, the AI was able to exactly reproduce the chemical structures of compounds with known dual-target activity that may be particularly effective medications. The study has now been published in Cell Reports Physical Science. Do not publish before Wednesday, October 23rd, 5:00 pm CEST!
Anyone who wants to delight their granny with a poem on her 90th birthday doesn’t need to be a poet nowadays: A short prompt in ChatGPT is all it takes, and within a few seconds the AI spits out a long list of words that rhyme with the birthday girl’s name. It can even produce a sonnet to go with it if you like.
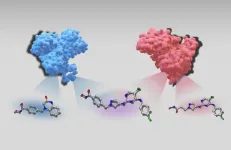
Researchers at the University of Bonn have implemented a similar model in their study – known as a chemical language model. This does not, however, produce rhymes. Instead, the AI displays the structural formulas of chemical compounds that may have a particularly desirable property: They are able to bind to two different target proteins. In the organism, this means, for example, they can inhibit two enzymes at once.
Wanted: Active ingredients with a double effect
“In pharmaceutical research, these types of active compounds are highly desirable due to their polypharmacology,” explains Prof. Dr. Jürgen Bajorath. The computational chemistry expert heads the AI in Life Sciences area at the Lamarr Institute for Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence and the Life Science Informatics program at b-it (Bonn-Aachen International Center for Information Technology) at Uni Bonn. “Because compounds with desirable multi-target activity influence several intracellular processes and signaling pathways at the same time, they are often particularly effective – such as in the fight against cancer.” In principle, this effect can also be achieved by co-administration of different drugs. However, there is a risk of unwanted drug-drug interactions and different compounds are also often broken down at different rates in the body, making it difficult to administer them together.
Finding a molecule that specifically influences the effect of a single target protein is no easy task. Designing compounds that have a predefined double effect is even more complicated. Chemical language models may help here in the future. ChatGPT is trained with billions of pages of written text and learns to formulate sentences itself. Chemical language models work in a similar way, but only have comparably very small amounts of data available for learning. However, in principle, they are also fed with texts, such as what are known as SMILES strings, which show organic molecules and their structure as a sequence of letters and symbols. “We have now trained our chemical language model with pairs of strings,” says Sanjana Srinivasan from Bajorath’s research group. “One of the strings described a molecule that we know only acts against one target protein. The other represented a compound that, in addition to this protein, also influences a second target protein.”
AI learns chemical connections
The model was fed with more than 70,000 of these pairs. This allowed it to acquire an implicit knowledge of how the normal active compounds differed from those with the double effect. “When we then fed it with a compound against a target protein, it suggested molecules on this basis that would act not only against this protein but also against another,” explains Bajorath.
The training compounds with the double effect often target proteins that are similar and thus perform a similar function in the body. In pharmaceutical research, however, people are also looking for active ingredients that influence completely different classes of enzymes or receptors. To prepare the AI for this task, fine-tuning took place after the general learning phase. The researchers used several dozen special training pairs to teach the algorithm which different classes of proteins the suggested compounds should target. This is a bit like instructing ChatGPT not to create a sonnet this time, but instead a limerick.
After the fine-tuning, the model actually spat out molecules that have already been shown to act against the desired combinations of target proteins. “This shows that the process works,” says Bajorath. In his opinion, however, the strength of the approach is not that new compounds exceeding the effect of available pharmaceuticals can immediately be found. “It is more interesting, from my point of view, that the AI often suggests chemical structures that most chemists would not even think of right away,” he explains. “To a certain extent, it triggers ‘out of the box’ ideas and comes up with original solutions that can lead to new design hypotheses and approaches.”
Participating institutions and funding:
The study was conducted at the University of Bonn at the Lamarr Institute and b-it.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-23
PHOENIX, AZ (Oct. 23, 2024) — Soteria Precision Medicine Foundation, a non-profit organization dedicated to providing leading-edge patient precision medicine navigation services to individuals with cancer diagnoses, today announced a partnership with the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), part of City of Hope, to provide precision medicine navigation for Special Operation Forces in their battle against cancer.
Through the strategic agreement with TGen, Soteria will deploy, and scale precision medicine navigation capabilities tailored to meet the unique needs of Special Operation Forces (SOF) members ...
2024-10-23
Capturing and storing the carbon dioxide humans produce is key to lowering atmospheric greenhouse gases and slowing global warming, but today's carbon capture technologies work well only for concentrated sources of carbon, such as power plant exhaust. The same methods cannot efficiently capture carbon dioxide from ambient air, where concentrations are hundreds of times lower than in flue gases.
Yet direct air capture, or DAC, is being counted on to reverse the rise of CO2 levels, which have reached 426 parts per million (ppm), 50% higher than ...
2024-10-23
Spectrometers are technology for reading light that date back to the era of famed 17th-century physicist Isaac Newton. They work by breaking down light waves into their different colors — or spectra — to provide information about the makeup of the objects being measured.
UC Santa Cruz researchers are designing new ways to make spectrometers that are ultra-small but still very powerful, to be used for anything from detecting disease to observing stars in distant galaxies. Their inexpensive production cost makes them more accessible and customizable for specific applications.
The team of researchers, led by an interdisciplinary ...
2024-10-23
Since its launch in late 2021, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has raised the possibility that we could detect signs of life on exoplanets, or planets outside our solar system.
Top candidates in this search are rocky, rather than gaseous, planets orbiting low-mass stars called M-dwarfs — easily the most common stars in the universe. One nearby M-dwarf is TRAPPIST-1, a star about 40 light years away that hosts a system of orbiting planets under intense scrutiny in the search for life on planets orbiting stars other than the sun.
Previous research questioned the habitability of planets orbiting TRAPPIST-1, finding that intense UV rays would burn away their ...
2024-10-23
In certain parts of the United States, especially Appalachia, New England and the Northwest, the ability of residents to prepare for and respond to flooding is being undercut on three different levels.
This is according to a new study from the University of Michigan's School for Environment and Sustainability.
"It's a very worrying confluence that does keep me up," said Joshua Newell, a professor with the school's Center for Sustainable Systems and senior author of the study. "The communities that are most at risk of catastrophic flooding ...
2024-10-23
Saving the bats: Researchers find bacteria, fungi on bat wings that could help fight deadly white-nose syndrome
Hamilton, ON, Oct. 23, 2024 – Bacteria and fungi from the wings of bats could play a significant role in saving them from white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fungal disease affecting the skin of wings and muzzle, which has nearly wiped out vulnerable bat populations across North America.
Researchers at McMaster University have gathered and analyzed samples from the community of microorganisms, or microbiome, on the wings of several bat species ...
2024-10-23
Washington, D.C. – October 23, 2024 – Project Cure CRC, the breakthrough research fund of the leading nonprofit Colorectal Cancer Alliance (Alliance), has announced five new awardees of funds to advance urgent science in the colorectal cancer space. To date, 10 research grants have been awarded for a grand total of almost $5 million in critically needed funding.
Recipients of the most recent grants totaling almost $1 million include investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, Indiana University, University of Saskatchewan, Georgetown University, and Anglia Ruskin University. ...
2024-10-23
California’s Channel Islands are home to the Channel Island fox (Urocyon littoralis), one of the smallest and most cherished species of island fox in the United States. Although no longer on the Endangered Species List, they remain a species of special concern due to their ecological importance.
In the 1990s, the San Miguel Island fox nearly went extinct, dropping to just 15 individuals. A recovery program restored their numbers by 2010. However, from 2014 to 2018, the population fell to 30% of its peak right after a new acanthocephalan parasite, commonly known as thorny-headed worms, was identified on the island. This also occurred while a multi-year draught heated San ...
2024-10-23
ATLANTA, Oct. 23, 2024 -- Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes has joined with UL Standards and Engagement to release new guidance for communities at risk for fires in wildland-urban interface (WUI) areas. An estimated 70,000 communities and 45 million residential buildings are at risk of destruction caused by wildfires. Additionally, WUI fires pose significant health risks. The smoke emitted by WUI fires likely contains a mixture of contaminants such as combustion gases, organic and inorganic metal complexes, volatile organic compounds and numerous reaction products. WUI wildfire plumes carry the risks of ...
2024-10-23
(Boston, MA) — Concussion researchers have recognized a new concussion sign that could identify up to 33% of undiagnosed concussions. After a hit to the head, individuals sometimes quickly shake their head back and forth. Although it has been depicted in movies, television, and even cartoons for decades, this motion has never been studied, named, and does not appear on any medical or sports organization’s list of potential concussion signs. A new study, led by Concussion Legacy Foundation (CLF) CEO and co-founder Chris Nowinski, PhD, says it should.
The study, published today in Diagnostics, reveals that when athletes exhibit this movement, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A “chemical ChatGPT” for new medications
Study by the University of Bonn with promising results