Sociodemographic factors associated with depression among people living with human immunodeficiency virus on antiretroviral therapy at a university teaching hospital in a Nigerian cosmopolitan city
2024-10-25
(Press-News.org) Background and objectives
Depression can lead to poor outcomes during antiretroviral therapy, and current evidence suggests high rates of depression among people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLHIV), especially in low-and middle-income countries. This study was designed to investigate the sociodemographic factors associated with depression among PLHIV on antiretroviral therapy in a Nigerian cosmopolitan city.
Methods
A hospital-based, cross-sectional study was conducted among 592 consenting, randomly selected adult PLHIV receiving treatment at a university teaching hospital in Jos, Nigeria, in 2022, using the PHQ-9 questionnaire and an interviewer-administered sociodemographic questionnaire. Associated variables in univariate analysis were used in multivariable binary logistic regression to obtain adjusted odds ratios (AOR) with a significance level set at α = 0.05.
Results
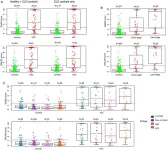
Depression was found to be highly prevalent among study participants, with 44.9% of them affected. Findings revealed that being male [AOR = 0.62; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.42–0.92], being employed (AOR = 0.55; 95%CI: 0.31–0.97), and earning a monthly income of ₦50,000–100,000 ($65–130) (AOR = 0.49; 95% CI: 0.27–0.91) and >₦100,000–200,000(>$130–260) (AOR = 0.33; 95% CI: 0.13–0.77) were significantly associated with reduced odds of depression.
Conclusions
The significant association of being male, having formal employment, and earning a moderate monthly income with reduced odds of depression may have implications for policy and strategies for managing mental health issues among PLHIV in cosmopolitan areas like Jos, which face peculiar challenges such as cultural tensions, traffic congestion, and gentrification. PLHIV categories with a relatively higher likelihood of depression may benefit from targeted mental health support systems, in addition to other mental health management strategies generally available to PLHIV.
Full text:
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2472-0712/ERHM-2024-00018
The study was recently published in the Exploratory Research and Hypothesis in Medicine.
Exploratory Research and Hypothesis in Medicine (ERHM) publishes original exploratory research articles and state-of-the-art reviews that focus on novel findings and the most recent scientific advances that support new hypotheses in medicine. The journal accepts a wide range of topics, including innovative diagnostic and therapeutic modalities as well as insightful theories related to the practice of medicine. The exploratory research published in ERHM does not necessarily need to be comprehensive and conclusive, but the study design must be solid, the methodologies must be reliable, the results must be true, and the hypothesis must be rational and justifiable with evidence.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-10-25
Background and Aims
Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is crucial for improving survival in patients with chronic hepatitis. The GALAD algorithm combines gender (biological sex), age, α-fetoprotein (AFP), Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of AFP (AFP-L3), and protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II (PIVKA-II) for HCC detection. Similarly, the GAAD algorithm incorporates gender (biological sex), age, AFP, and PIVKA-II. This study aimed to assess the clinical utility of AFP-L3 in the GALAD algorithm and its potential synergies with ultrasound. We compared the clinical performance of GALAD with GAAD; AFP; AFP-L3; and PIVKA-II, with ...
2024-10-25
Background and Aims
Data regarding risk factors and long-term outcomes of U.S. patients with biopsy-proven metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) are limited. This study aimed to investigate the role of clinical and histologic risk factors on long-term outcomes in patients with MASLD.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study of 451 adults with biopsy-proven MASLD was conducted at a U.S. academic hospital from 2012 to 2020. An experienced pathologist evaluated the index liver biopsy. Patients with a prior liver transplant or alternative etiologies of chronic liver disease were excluded. The duration ...
2024-10-25
Water is synonymous with life, but the dynamic, multifaceted interaction that brings H2O molecules together – the hydrogen bond – remains mysterious. Hydrogen bonds result when hydrogen and oxygen atoms between water molecules interact, sharing electronic charge in the process. This charge-sharing is a key feature of the three-dimensional ‘H-bond’ network that gives liquid water its unique properties, but quantum phenomena at the heart of such networks have thus far been understood only through theoretical simulations.
Now, researchers led by Sylvie Roke, head of the Laboratory for Fundamental BioPhotonics in EPFL’s School of Engineering, ...
2024-10-25
Subtle temperature differences at the ocean surface allow more carbon dioxide (CO₂) to be absorbed, new research shows.
Scientists studied the “ocean skin” – a sliver less than 2 mm deep at the ocean surface that is fractionally cooler than the rest.
Theoretical and lab work have suggested this temperature difference should increase the amount of CO₂ absorbed by the ocean – but this had never been successfully observed at sea before.
The new study – led by researchers from the University of Exeter’s Penryn Campus in Cornwall – used precision measurements to confirm that the ...
2024-10-25
URBANA, Ill. — Invasive silver carp have been spreading throughout the Mississippi River Basin since their introduction a half-century ago. Yet, try as they might, the fish have not advanced beyond a particular stretch of the Illinois River north of Kankakee. Research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign shows the fish are likely avoiding contaminants from the Chicago Area Waterway, which flows south before petering out around Kankakee.
A new study, published today in Scientific Reports, shows silver carp change their behavior and metabolism when introduced to water from the Illinois River north of Kankakee, representing Chicago-area water.
“When animals ...
2024-10-25
Imagine trying to settle into a new home while constantly being attacked. That’s what the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa faces when it infects the lungs, and it can’t both spread and protect itself from antibiotics at the same time. Nonetheless, it’s one of the top culprits in hospital-acquired infections and it’s notorious for causing long-lasting, antibiotic-resistant infections, causing damage especially in people with lung diseases like cystic fibrosis, COPD, or bronchiectasis.
To survive tough conditions, P. aeruginosa forms colonies ...
2024-10-25
University of Oxford researchers have made a significant step towards realising miniature, soft batteries for use in a variety of biomedical applications, including the defibrillation and pacing of heart tissues. The work has been published today in the journal Nature Chemical Engineering.
The development of tiny smart devices, smaller than a few cubic millimeters, demands equally small power sources. For minimally invasive biomedical devices that interact with biological tissues, these power sources must be fabricated from soft materials. Ideally, these should ...
2024-10-25
FINDINGS
UCLA scientists have identified the protein GPNMB as a critical regulator in the heart’s healing process after a heart attack.
Using animal models, they demonstrate that bone marrow-derived immune cells called macrophages secrete GPNMB, which binds to the receptor GPR39, promoting heart repair. These findings offer a new understanding of how the heart heals itself and could lead to new treatments aimed at improving heart function and preventing the progression to heart failure.
BACKGROUND
Every 40 seconds, ...
2024-10-25
News coverage of the 2024 election season has often centered on how partisan division has affected our politics. But a new analysis shows that political polarization also poses significant health risks—by obstructing the implementation of legislation and policies aimed at keeping Americans healthy, by discouraging individual action to address health needs, such as getting a flu shot, and by boosting the spread of misinformation that can reduce trust in health professionals.
“Compared to other high-income countries, the United States has a disadvantage when it comes to the health of its citizens,” ...
2024-10-25
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL OCT. 25 AT 5 A.M. ET**
A newly described stage of a lymph node-like structure seen in liver tumors after presurgical immunotherapy may be vital to successfully treating patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, according to a study by researchers from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study, published Oct. 25 in Nature Immunology, provides new information about lymph node-like structures called tertiary lymphoid structures. These structures, which are highly organized ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sociodemographic factors associated with depression among people living with human immunodeficiency virus on antiretroviral therapy at a university teaching hospital in a Nigerian cosmopolitan city