(Press-News.org) “Vaccines are 100% safe, and anyone who doubts this is ignorant”: Have you ever come across messages like this during the pandemic crisis a few years ago? If you often feel that certain public debates—such as those on vaccines or the climate crisis—boil down to a black-and-white clash between two sides demanding, with harsh tones, unquestioning allegiance to their view, you're not entirely wrong. We are rightly accustomed to being warned about pseudoscientific misinformation and fake news, and much research has been devoted to identifying the characteristics of such messages in order to debunk them. Yet, even those "on the side of science" sometimes use a form of polarized communication that doesn't align with a genuinely scientific approach, which should foster critical thinking and the ability to evolve over time. A certain type of scientific message, like the example above, often amplifies these forms of polarization by reinforcing extreme viewpoints, deepening divisions between different audience segments. Therefore, it is important to recognize not only scientific misinformation but also polarized scientific information.
A new study just published in the Journal of Science Communication (JCOM) elucidated, based on available scientific literature, the characteristics of polarized scientific digital messages, proposing a system of codification for identifying and characterizing polarized discourses in science communication digital messages.
“Polarized messages in online science communication often present extreme views about a specific scientific topic, which can stir strong emotions, reinforce group loyalty, and deepen divisions in society," explains Thiago Cruvinel, professor at the University of São Paulo, Brazil, and coordinator of the research. “These polarized views can affect various social aspects. For example, to make people feel certain and comfortable, a one-sided message might use terms related to conflict or separation, even when talking about well-known scientific topics like climate change caused by humans.”
As Cruvinel explains, simplifying and polarizing scientific information is not always the best approach, as it can limit critical thinking. Presenting scientific agreement as unquestionable may unite supporters but push away skeptics, making the issue even more divisive. When one dominant view takes over, it can hold back scientific progress by discouraging people from challenging existing ideas, which is a key part of advancing science. Cruvinel and his colleagues' work mapped the scientific literature that examined the syntactic and lexical features of polarized messages in online science communication, as well as studies measuring the effects of these messages on readers' opinions, which also involved more specialized audiences like journalists, scientists, and health professionals. This scoping reviewmapped the available literature, identifying ten studies that allowed Cruvinel and his colleagues to develop a system to identify polarized scientific messages.
“Our codification system is grounded in a framework that encompasses 20 distinct codes, categorized into four key dimensions: sideness, criticism, emphasis, and discordance," explains Cruvinel. “This structured approach enables a nuanced analysis of the underlying elements contributing to polarization within scientific discourse.”
According to Cruvinel, an important contribution of this study is that this coding system can serve as a valuable tool for science researchers and journalists, supporting the systematic identification of polarized materials within the realm of science communication.
END
When science speaks in extremes
Polarizing scientific information can be harmful. A study published in JCOM tries to identify it
2024-10-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Will the ocean suffer an epidemic?
2024-10-28
Written by a team of European experts from the marine sciences, Navigating the Future VI discusses how the biodiversity crisis is being played out in the Ocean. It notes that Ocean species large and small are far less well described than their terrestrial counterparts, making it harder to measure declines and their impacts. This publication provides governments, policymakers and funders with robust, independent scientific advice on future seas and Ocean research. With the COP16 on biodiversity already in full swing in Cali, Colombia, it is timely to reflect further on the need to better understand our Ocean biodiversity.
“Climate change ...
A single thin film perfectly absorbs all electromagnetic waves!
2024-10-28
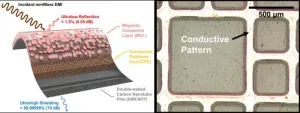
The research team of Dr. Byeongjin Park and Dr. Sang Bok Lee from the Composites & Convergence Materials Research Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), has developed the world's first ultra-thin film composite material capable of absorbing over 99% of electromagnetic waves from various frequency bands (such as 5G/6G, WiFi, and autonomous driving radar) using a single material.
This electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding material is less than 0.5mm thick and is distinguished by its low reflectance ...
Teens who made history with Pythagoras’ theorem discovery publish their first academic paper with new proofs
2024-10-28
In 2022, U.S. high school students Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson astonished teachers when they discovered a new way to prove Pythagoras’ theorem using trigonometry after entering a competition at their local high school. As a result, both students were awarded keys to the city of New Orleans, and even received personal praise from Michelle Obama.
Today they become published authors of a new peer-reviewed paper detailing their discoveries, published in the journal American Mathematical Monthly.
Pythagoras’ famous 2,000-year-old ...
More social species live longer, Oxford study finds
2024-10-28
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01 GMT MONDAY 28 OCTOBER / 20:01 ET SUNDAY 27 OCTOBER 2024
More social species live longer, Oxford study finds
New research published today (28 Oct) from the University of Oxford has revealed that species that are more social live longer and produce offspring for a greater timespan. This is the first study on this topic which spans the animal kingdom, from jellyfish to humans.
What are the benefits and costs of sociality? Social organisms may enjoy benefits such as sharing resources, being better protected from predators, and having support to raise offspring. However, by living in more ...
Magicians don’t mind sharing the secrets behind tricks – if they are their own
2024-10-27
Magic is one of the oldest forms of entertainment, and much of its enchantment is said to rely on the audience not knowing how the tricks are done.
However, while magicians swear to keep their secrets forever when they embark on their profession they are happy to share the tricks of their trade in certain circumstances, a new study shows.
Illusionists who took part in major new research thought it was OK to expose their own techniques, but not those invented by others, and also believe it is acceptable to reveal the secrets behind tricks invented by someone who has since died.
They didn’t think it was right to share the workings of a magic trick just to gain public ...
No incentive for older birds to make new friends
2024-10-27
Like people, birds have fewer friends as they age, but the reasons why are unclear. New research suggests they may just have no drive to.
In humans, it’s often been assumed that older people have fewer friends because they’re pickier about who they spend their time with. There’s also the issue that there are fewer people of their own age around.
But it’s hard to pick apart the various potential causes for humans, so researchers have turned to animals. The team behind the new research, led by Imperial College London, studied an isolated population of sparrows on the island of Lundy, in the Bristol Channel.
By mapping the ...
Development and validation of a new prognostic model for predicting survival outcomes in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure
2024-10-27
Background and Aims
Early determination of prognosis in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is crucial for optimizing treatment options and liver allocation. This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with ACLF and to develop new prognostic models that accurately predict patient outcomes.
Methods
We retrospectively selected 1,952 hospitalized patients diagnosed with ACLF between January 2010 and June 2018. This cohort was used to develop new prognostic scores, which were subsequently validated in external groups.
Results
The study included 1,386 ACLF patients and identified six independent ...
Identification and validation of the Hsa_circ_0001726/miR-140-3p/KRAS axis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on microarray analyses and experiments
2024-10-27
Background and Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most fatal malignancies. Epigenetic mechanisms have revealed that noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs), are involved in HCC progression. This study aimed to construct a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in HCC and validate one axis within the network.
Methods
HCC-related transcriptome data were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus, and HCC-related genes were sourced from GeneCards to identify differentially expressed circRNAs and miRNAs. ...
New study warns that melting Arctic sea-ice could affect global ocean circulation
2024-10-27
“Our finding that enhanced melting of Arctic sea-ice likely resulted in significant cooling in northern Europe in the earth’s past is alarming,” says Mohamed Ezat from the iC3 Polar Research Hub, lead author of the new study. “This reminds us that the planet’s climate is a delicate balance, easily disrupted by changes in temperature and ice cover.”
Ice-free summer conditions are expected to occur in the Arctic Ocean from the year 2050 onwards.
Earlier this ...
Researchers test imlifidase enzyme versus plasma exchange in removing donor-specific antibodies in kidney transplant rejection trial
2024-10-27
San Diego, CA (October 26, 2024) — For kidney transplant recipients experiencing antibody-mediated rejection, the current standard of care involves removing donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) through plasmapheresis (PLEX)—a procedure that removes antibodies from the plasma portion of the blood. Results from a recent clinical trial reveal that an investigational drug called imlifidase, which cleaves and inactivates the type of antibodies that include DSAs, is more effective than PLEX. The research will be presented at ASN Kidney ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] When science speaks in extremesPolarizing scientific information can be harmful. A study published in JCOM tries to identify it