(Press-News.org) About The Study: This retrospective cohort study with an extended follow-up period found associations between COVID-19 and the long-term risk of various autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders. Long-term monitoring and care of patients is crucial after COVID-19, considering demographic factors, disease severity, and vaccination status, to mitigate these risks.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Solam Lee, MD, PhD, email solam@yonsei.ac.kr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.4233)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.4233?guestAccessKey=c58e0ba8-9aa0-457e-a4e7-c043439b3e52&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=110624
END
Long-term risk of autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders following COVID-19
JAMA Dermatology
2024-11-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mount Sinai researchers have uncovered the mechanism in the brain that constantly refreshes memory
2024-11-06
Mount Sinai researchers have discovered for the first time a neural mechanism for memory integration that stretches across both time and personal experience. These findings, reported in Nature, demonstrate how memories stored in neural ensembles in the brain are constantly being updated and reorganized with salient information, and represent an important step in deciphering how our memories stay current with the most recently available information. This discovery could have important implications for better understanding adaptive memory processes ...
Breakthrough in energy-efficient avalanche-based amorphization could revolutionize data storage
2024-11-06
The atoms of amorphous solids like glass have no ordered structure; they arrange themselves randomly, like scattered grains of sand on a beach. Normally, making materials amorphous — a process known as amorphization — requires considerable amounts of energy. The most common technique is the melt-quench process, which involves heating a material until it liquifies, then rapidly cooling it so the atoms don’t have time to order themselves in a crystal lattice.
Now, researchers ...
Scientists discover how specific E. coli bacteria drive colon cancer
2024-11-06
Ghent, 7 November 2024 – Scientists have uncovered how certain E. coli bacteria in the gut promote colon cancer by binding to intestinal cells and releasing a DNA-damaging toxin. The study, published in Nature, sheds light on a new approach to potentially reduce cancer risk. The study was performed by the teams of Prof. Lars Vereecke (VIB-UGent Center for Inflammation Research) and Prof. Han Remaut (VIB-VUB Center for Structural Biology).
Bacteria and colon cancer
Colon cancer ranks as the third most prevalent and deadliest type of cancer. Alarmingly, its incidence is rising, particularly ...
Brain acts like music box playing different behaviours
2024-11-06
Neuroscientists have discovered brain cells that form multiple coordinate systems to tell us “where we are” in a sequence of behaviours. These cells can play out different sequences of actions, just like a music box can be configured to play different sequences of tones. The findings help us understand the algorithms used by the brain to flexibly generate complex behaviours, such as planning and reasoning, and might be useful in understanding how such processes go wrong in psychiatric ...
Study reveals how cancer immunotherapy may cause heart inflammation in some patients
2024-11-06
Some patients being treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors, a type of cancer immunotherapy, develop a dangerous form of heart inflammation called myocarditis. Researchers led by physicians and scientists at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, have now uncovered the immune basis of this inflammation. The team identified changes in specific types of immune and stromal cells in the heart that underlie myocarditis and pinpointed factors in the blood that may indicate ...
More families purchased school meals after federal nutrition policies enacted
2024-11-06
Families purchased more school lunches and breakfasts the year after the federal government toughened nutritional standards for school meals. A new University of California, Davis, study suggests that families turned to school lunches after the Obama administration initiative was in effect to save time and money and take advantage of more nutritious options.
Researchers looked at the purchasing habits of nearly 8,000 U.S. households over two years — one year before and after the change in standards. The results have important implications for policymakers and researchers, but also food manufacturers and retailers, researchers said.
The study, ...
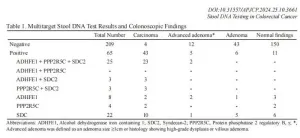
Research proves stool DNA as non-invasive alternative for colorectal cancer screening in Thailand
2024-11-06
A recent prospective cross-sectional study in Thailand demonstrates that multitarget stool DNA testing is highly sensitive and specific for detecting colorectal cancer (CRC) among Thai individuals. Researchers believe that this testing method could serve as a viable non-invasive alternative to colonoscopy, especially in settings where colonoscopy is less accessible or less accepted by patients.
This study was conducted by BGI Genomics in 2023, in collaboration with Professor Varut Lohsiriwat’s team from the Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand. ...
Detecting evidence of lung cancer in exhaled breath
2024-11-06
Exhaled breath contains chemical clues to what’s going on inside the body, including diseases like lung cancer. And devising ways to sense these compounds could help doctors provide early diagnoses — and improve patients’ prospects. In a study in ACS Sensors, researchers report developing ultrasensitive, nanoscale sensors that in small-scale tests distinguished a key change in the chemistry of the breath of people with lung cancer. November is Lung Cancer Awareness Month.
People breathe out many gases, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide, as well as other airborne compounds. Researchers ...
A joint research team of Korea University College of Medicine announced the world's first single-port robotic thymectomy comparative results
2024-11-06
A Joint research team (Prof. Jun-hee Lee, Hyun-koo Kim, Jin-Wook Hwang, Jae-Ho Chung, the Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine) Announced the world's first compartive results of single-port robotic thymectomy using the single-port robotic system.
The team compared and analyzed the perioperative outcomes of 110 cases of robotic thymectomy using the single-port robotic system and conventional video-assisted thoracic surgery(VATS) thymectomy from November 2018 to May 2024. The results showed that all robotic thymectomy performed were successfully ...
National Mental Health Institute awards CAD 45 million to develop mental health treatments
2024-11-06
One out of 100 people will experience a psychotic episode in their lifetime, and these usually appear in late adolescence or early adulthood. A Canada-US team consisting of Sylvain Bouix, from École de technologie supérieure (ÉTS), Martha E. Shenton and Ofer Pasternak, from the Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Harvard University), and René Kahn, from Mount Sinai Hospital (New York) has just received US $33 million in funding—the equivalent of CAD 45 million—over five years from the National Institute of Mental Health ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Long-term risk of autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders following COVID-19JAMA Dermatology