Shaking it up: An innovative method for culturing microbes in static liquid medium
Researchers use a thin, gas-permeable bag to provide aeration to microorganisms cultured in a liquid medium instead of shaking
2024-11-08
(Press-News.org)
Culturing, a term for growing microorganisms in the laboratory, is a basic yet indispensable method in microbiology research. Microorganisms are often cultured in a liquid medium that provides essential nutrients, and this process is both simple and highly effective. In addition to nutrients, oxygen availability is also critical for the growth of aerobic microorganisms. However, oxygen does not dissolve easily in the liquid medium. As a result, the medium needs to be forcibly aerated, usually by shaking.
Several techniques have been developed for better aeration of “shake” cultures, including “baffled” shake flasks, which have indentations designed to improve oxygen transfer, and supplying air bubbles to bioreactors. However, these conventional shake cultures pose a significant issue by subjecting microorganisms to physical (shear) stress.
Now, in a study published online on October 10, 2024 in Scientific Reports, a team of researchers from Kindai University in Japan, led by Professor Motomu Akita and Dr. Kenji Ito (also affiliated with Cell Film Lab. Co. Ltd.), have demonstrated a novel method for “static” culturing of bacteria in a liquid medium. To achieve this, they utilized a polymer called TPX which is highly permeable to small molecular weight gases, including oxygen. A bag made of TPX film was filled with a small amount of liquid medium, inoculated with bacteria, and was kept on a flat surface to enable the formation of a thin layer of medium that could be used for culturing.
Using this method, the researchers successfully cultured Escherichia coli, which showed similar growth in the film bag and in liquid shake cultures. To test whether this method ensured sufficient oxygen availability, they also cultured Komagataella phaffi, which requires high amounts of oxygen for its growth. They observed that the growth of K. phaffi was slightly lower in the film bag than in the conventional shake cultures.
Using a film bag has several advantages over conventional culturing methods. “Our method enables easy observation of biological phenomena that were previously unobservable,” explains Prof. Akita. “Until now, microorganisms have not been cultured in liquid conditions where sufficient oxygen was supplied and physical stress was absent.” With this method, researchers now have the opportunity to closely examine how microorganisms behave when they are not subjected to shear stress.
One observable phenomenon in this regard is the growth of “biofilms,” gel-like layer formation resulting from microorganisms adhering to a surface. Normally, biofilms cannot form in liquid cultures that are subjected to shaking. However, the present study demonstrated that static culturing of Bacillus species resulted in “biofilm” formation along the bottom of the film bag.
“The possibilities for this new culturing method are enormous. For starters, reducing the space, energy and resources needed to culture bacteria could promote more sustainable research activities,” says Prof. Akita. “This means experiments could be conducted even in limited physical spaces, or when culturing equipment is constrained.”
The new method could have potential applications in science, medicine, and industry research, spanning diverse fields that include education, healthcare, food production, and space exploration. For example, it could be used to conduct experiments in remote locations such as the polar regions or even space stations. Other potential applications include advancing research in laboratories with limited budgets, simplifying procedures in medical centers, enabling on-site culturing during field research, and facilitating educational experiments in schools.
It certainly looks like the team’s findings will bring about significant advancements in biotechnology and related disciplines!
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-08
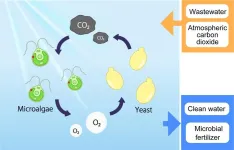
Bakeries and wineries can’t do without yeast, but they have no need for green algae. Wastewater treatment facilities, however, might just want to have these microorganisms team up. Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have discovered that these simple organisms form the best combination in terms of boosting wastewater treatment efficiency.
The active sludge method of wastewater treatment requires electricity to ensure the flow of oxygen that feeds bacteria and other organisms that process the water. Adding microalgae ...
2024-11-08
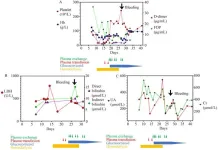
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted the rapid development and administration of various vaccines worldwide, with some reports linking these vaccines to immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). This report presents two cases of TTP occurring after the administration of the inactivated vaccine CoronaVac from Sinovac Biotech, highlighting the potential association between this type of vaccine and TTP. The article also provides an analysis of TTP incidence in the Nanjing area of China, suggesting a possible correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and the occurrence of TTP.
The first case details a 23-year-old female who developed symptoms of TTP three days ...
2024-11-08
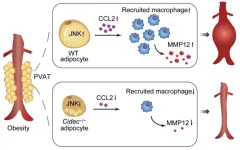
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a degenerative lesion characterized by structural disruption of the abdominal aortic wall and progressive dilatation into a pulsatile mass. AAA is strongly associated with obesity, partly due to abnormal dilatation of perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) in the abdomen, however, direct evidence is still lacking.
Cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor-like effector C (CIDEC), also known as fat-specific protein 27 (FSP27) in rodents, is a lipid droplet (LD)-associated protein that plays an important role in lipid storage. It has been reported that CIDEC/FSP27 promotes the growth of LDs by mediating the exchange and transfer of lipids ...
2024-11-08
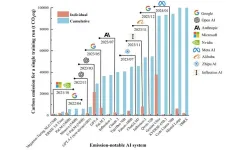
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology progresses, the energy demands of training complex models have surged, raising widespread concerns about associated carbon emissions. This rapid growth is fueled by global demand across industries and academia, leading to exponential increases in computing power that carry significant environmental consequences. Given these challenges, in-depth research is essential to fully understand AI's carbon footprint and develop strategies for mitigating its environmental impact.
In a view (DOI: 10.1007/s11783-024-1918-y) by ...
2024-11-08
Tsukuba, Japan—Students often appear for high-stakes tests that hold significant weight in determining their futures. One such examination, the Common Test for University Admissions, currently allows examinees using braille an extended examination time of 1.5 times the standard duration. However, with the recent increase in complex questions and questions involving charts and diagrams in such tests, it is necessary to review whether the current accommodations remain adequate.
The researchers assessed the validity of the current time extension for examination questions containing complex tables by measuring the time required to read the text and complex tables. The results showed that ...
2024-11-08
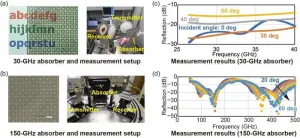
5G wireless communication services have rapidly expanded worldwide, leveraging millimeter-wave (mmW) frequencies in the 24 GHz to 71 GHz range (referred to as frequency range 2, or FR2). Looking ahead, Beyond 5G and 6G services, projected to offer ultra-fast connectivity exceeding 100 Gbit/s, are expected to be introduced in the 2030s. Frequencies in the 150-GHz to 300-GHz range are being considered as potential candidates for these future networks. However, critical components such as radio-wave absorbers, essential for packaging and modularization, still need to be developed. These absorbers play a key role in reducing ...
2024-11-08
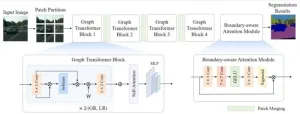
The transformer-based semantic segmentation approaches, which divide the image into different regions by sliding windows and model the relation inside each window, have achieved outstanding success. However, since the relation modeling between windows was not the primary emphasis of previous work, it was not fully utilized.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zizhang Wu published their new research on 15 October 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer ...
2024-11-08
TUCSON, Ariz., November 7, 2024 — Critical Path Institute® (C-Path) today announced key leadership appointments: Diane Stephenson, Ph.D., has been promoted to Vice President of Neurology, and Nadine Tatton, Ph.D., has been welcomed as the new Executive Director of C-Path’s Critical Path for Alzheimer’s Disease (CPAD) Consortium.
With over 30 years of specialized research in neuroscience and drug development and having served as the Executive Director of the Critical Path for Parkinson’s Consortium (CPP) for nearly 15 years, Dr. Stephenson has been an extraordinary partner in advancing our understanding ...
2024-11-08
First-of-its-kind analysis of US national data reveals significant disparities in individual well-being as measured by lifespan, education, and income.
White males make up largest share of the group with lowest well-being while American Indian and Alaska Native individuals, and Black males, face the most significant challenges to overall well-being.
Populations at the lowest levels of well-being across the US are especially concentrated in the Deep South, Appalachia, and the Rust Belt.
The ...
2024-11-08
Exercise-only programmes help cut the severity of the ‘baby blues’ and the risk of major clinical depression in new mums, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
But at least 80 weekly minutes of moderate intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, water aerobics, stationary cycling, and resistance training with bands, weights, or body weight are needed to achieve the effects, the findings show.
Maternal depression and anxiety are relatively common after giving birth and associated with reduced self-care and compromised infant caregiving and bonding, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Shaking it up: An innovative method for culturing microbes in static liquid medium
Researchers use a thin, gas-permeable bag to provide aeration to microorganisms cultured in a liquid medium instead of shaking