(Press-News.org)
As demand surges for electric vehicles and energy storage systems, lithium-ion batteries need to deliver higher energy densities at lower costs. While conventional cathode materials like LiFePO4 and Li-Ni-Co-Mn-O are widely used, they often fail to balance performance with affordability. Lithium-rich manganese oxides (LRMOs) have emerged as a potential alternative due to their high capacity and cobalt-free composition. However, their low initial Coulombic efficiency and rapid voltage decay have limited their broader application. Addressing these challenges requires deeper research to stabilize LRMOs for widespread commercial use.
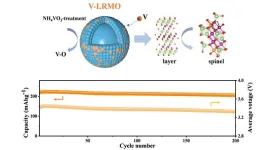
In September, 2024, a team from Guangdong University of Technology, led by Dong Luo and Chenyu Liu, published a study (DOI: 10.26599/EMD.2024.9370039) in Energy Materials and Devices. that marks a significant advancement in lithium-ion battery technology. Their research demonstrates how treating lithium-rich cathode materials with NH4VO3 results in a vanadium-doped spinel-layered structure that enhances both initial Coulombic efficiency and voltage stability. This simple yet effective modification represents a major step toward improving the sustainability and performance of high-energy lithium-ion batteries.
The study addresses two long-standing issues in LRMO cathodes: low initial Coulombic efficiency (ICE) and rapid voltage decay. The research team employed a hydrothermal treatment using NH4VO3, which introduced vanadium to the cathode surface, forming a V-doped spinel-layered structure. This innovative structure improved lithium-ion diffusion and reduced surface interface reactions, thereby stabilizing the oxygen redox process. Notably, the ICE jumped from 74.4% to 91.6%, surpassing the threshold required for commercialization. In addition to the significant boost in efficiency, the cathode also demonstrated impressive voltage stability, with a minimal decay of only 0.47 mV per cycle over 200 cycles. This improvement is linked to the suppression of irreversible oxygen release and the formation of strong V-O bonds, which reinforce the material’s structural stability. By addressing these critical challenges, the study highlights a promising approach to enhancing the performance and lifespan of LRMO cathodes, making them more suitable for high-energy applications.
Commenting on the research, lead scientist Professor Dong Luo stated, "Our findings offer a practical and highly effective method for tackling the persistent challenges of low Coulombic efficiency and voltage decay in lithium-rich cathodes. By incorporating vanadium, we’ve significantly improved redox stability and voltage performance, paving the way for next-generation lithium-ion batteries to meet the growing energy needs of sectors like electric vehicles and renewable energy storage."
The V-doped lithium-rich cathode holds strong potential for applications in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and consumer electronics, where battery efficiency and longevity are paramount. The improved efficiency and stability not only promise to lower costs by eliminating cobalt but also enhance overall battery performance. As this technology scales, it could lead to more affordable and sustainable energy solutions, accelerating the global shift towards cleaner, more efficient power sources.
About Energy Materials and Devices
Energy Materials and Devices is launched by Tsinghua University, published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, exclusively available via SciOpen, aiming at being an international, single-blind peer-reviewed, open-access and interdisciplinary journal in the cutting-edge field of energy materials and devices. It focuses on the innovation research of the whole chain of basic research, technological innovation, achievement transformation and industrialization in the field of energy materials and devices, and publishes original, leading and forward-looking research results, including but not limited to the materials design, synthesis, integration, assembly and characterization of devices for energy storage and conversion etc.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is an open access resource of scientific and technical content published by Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, identity management, and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
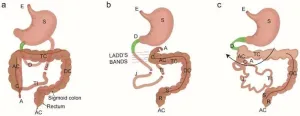
Gastroschisis, a congenital abdominal wall defect, has transformed from a uniformly fatal condition to one with a 95% survival rate through surgical advancements over the past six decades. The primary goal of managing gastroschisis is to mitigate fetal and postnatal risks, including damage from herniated bowel loops and ensuring effective decompression of the gastrointestinal tract during recovery. This review focuses on both preventative and corrective aspects of gastroschisis management, highlighting innovations in neonatal surgery that improve quality of life and long-term health outcomes.
Definition ...
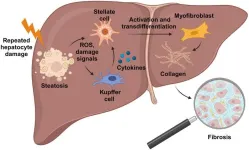
Liver fibrosis is a progressive and potentially reversible condition that results from chronic liver damage, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), alcohol abuse, and viral hepatitis. MASLD affects a significant portion of the global population and can progress to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), leading to liver cirrhosis if left untreated. Given the prevalence of MASLD and its related conditions, the study of fibrosis and its regression ...
From November 11 to 12, the Fortune Global Forum 2024, an invite-only premier event of Fortune, is set to gathers the leaders of the world’s biggest multinational companies on the dynamic frontiers of global business in New York, where business leaders from around the globe come together to create a modern roadmap for success.
Insilico Medicine(“Insilico”), a global leading generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven biotechnology company, announces that Alex Zhavoronkov PhD, founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine will be attending the Fortune ...
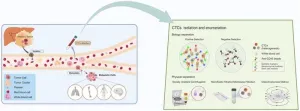
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant global health concern, particularly in regions like the Asia-Pacific, where chronic viral hepatitis and liver diseases contribute to its high incidence and mortality. Despite medical advancements, the late-stage diagnosis of HCC remains a major challenge, which underscores the need for more effective early detection strategies. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which are tumor cells released into the bloodstream from primary neoplastic sites, offer a promising avenue for non-invasive cancer diagnostics. This review provides a comprehensive overview of CTC detection methods, ...
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (11/08/2024) — Researchers at the University of Minnesota have achieved a new material that will be pivotal in making the next generation of high-power electronics faster, transparent and more efficient. This artificially designed material allows electrons to move faster while remaining transparent to both visible and ultraviolet light, breaking the previous record.
The research, published in Science Advances, a peer-reviewed scientific journal, marks a significant leap forward in semiconductor ...
As air temperatures stay elevated through fall months, people may still want clothes that cool them down while outside, especially if they live in cities that stay warmer than rural landscapes. Researchers who previously demonstrated a cooling fabric coating now report on additional tests of a treated polyester fabric in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Fabric treated with the team’s chalk-based coating kept the air underneath up to 6 degrees Fahrenheit cooler in warmer urban environments.
Researchers Evan D. Patamia, Megan K. Yee and Trisha L. ...
As cancer cells grow, they pump out metabolic byproducts such as lactic acid into the tumor microenvironment. Exhausted T cells — which have lost their cancer-fighting oomph — consume this lactic acid, which further saps their energy, according to new research from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC Hillman Cancer Center.
When the researchers blocked the protein that imports lactic acid into cells, exhausted T cells gained a new lease on life, which led to improved tumor control in mouse models of cancer. The findings are published today in Nature Immunology.
“Blocking access to inhibitory metabolites is a completely new take on how we can reinvigorate ...
Only a few weeks ago, massive precipitation produced by the storm “Boris” led to chaos and flooding in Central and Eastern Europe. An analysis conducted by the Alfred Wegener Institute shows that in a world without the current level of global warming Boris would have deposited roughly nine percent less rain. Such conclusions can be drawn thanks to a new modelling approach called ‘storylines’. How it can be used in near-real-time was just presented in the Nature journal Communications Earth & Environment. At the same time, the AWI team released a freely available online tool that ...
Researchers today (Nov. 8, 2024) are releasing the flagship dataset from an ambitious study of biomarkers and environmental factors that might influence the development of type 2 diabetes. Because the study participants include people with no diabetes and others with various stages of the condition, the early findings hint at a tapestry of information distinct from previous research.
For instance, data from a customized environmental sensor in participants’ homes show a clear association between disease state and exposure to tiny particulates of pollution. ...
Culturing, a term for growing microorganisms in the laboratory, is a basic yet indispensable method in microbiology research. Microorganisms are often cultured in a liquid medium that provides essential nutrients, and this process is both simple and highly effective. In addition to nutrients, oxygen availability is also critical for the growth of aerobic microorganisms. However, oxygen does not dissolve easily in the liquid medium. As a result, the medium needs to be forcibly aerated, usually by shaking.
Several techniques have been developed for better aeration of “shake” cultures, including “baffled” shake flasks, which have indentations designed to improve oxygen ...