Research update: Chalk-coated textiles cool in urban environments
2024-11-08
(Press-News.org) As air temperatures stay elevated through fall months, people may still want clothes that cool them down while outside, especially if they live in cities that stay warmer than rural landscapes. Researchers who previously demonstrated a cooling fabric coating now report on additional tests of a treated polyester fabric in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Fabric treated with the team’s chalk-based coating kept the air underneath up to 6 degrees Fahrenheit cooler in warmer urban environments.
Researchers Evan D. Patamia, Megan K. Yee and Trisha L. Andrew created a polymer-mineral coating for commercial fabrics and presented preliminary assessments of the coating’s cooling effect at ACS Fall 2024, a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Now, the researchers confirm that their treated polyester poplin fabric could keep a person up to 15 F cooler than untreated polyester. Additionally, they have expanded the testing environments to four outdoor urban settings, including areas with materials that absorb and emit the sun’s heat. Observations made during hot, cloudless days indicate that treated polyester cooled the air underneath the fabric regardless of the environment:
Open grass field: averaging 6 F below ambient air temperature.
Concrete-paved alley between buildings: averaging 3 F below ambient.
Asphalt-paved parking lot: averaging 1 F below ambient.
Open concrete veranda: averaging 3 F below ambient.
The researchers say their expanded results show the potential of their coated fabrics to provide energy-free cooling for pedestrians and cyclists in urban environments.
The authors acknowledge support from an Interdisciplinary Research Grant from the College of Natural Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, e-books and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Registered journalists can subscribe to the ACS journalist news portal on EurekAlert! to access embargoed and public science press releases. For media inquiries, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-08
As cancer cells grow, they pump out metabolic byproducts such as lactic acid into the tumor microenvironment. Exhausted T cells — which have lost their cancer-fighting oomph — consume this lactic acid, which further saps their energy, according to new research from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC Hillman Cancer Center.
When the researchers blocked the protein that imports lactic acid into cells, exhausted T cells gained a new lease on life, which led to improved tumor control in mouse models of cancer. The findings are published today in Nature Immunology.
“Blocking access to inhibitory metabolites is a completely new take on how we can reinvigorate ...
2024-11-08
Only a few weeks ago, massive precipitation produced by the storm “Boris” led to chaos and flooding in Central and Eastern Europe. An analysis conducted by the Alfred Wegener Institute shows that in a world without the current level of global warming Boris would have deposited roughly nine percent less rain. Such conclusions can be drawn thanks to a new modelling approach called ‘storylines’. How it can be used in near-real-time was just presented in the Nature journal Communications Earth & Environment. At the same time, the AWI team released a freely available online tool that ...
2024-11-08
Researchers today (Nov. 8, 2024) are releasing the flagship dataset from an ambitious study of biomarkers and environmental factors that might influence the development of type 2 diabetes. Because the study participants include people with no diabetes and others with various stages of the condition, the early findings hint at a tapestry of information distinct from previous research.
For instance, data from a customized environmental sensor in participants’ homes show a clear association between disease state and exposure to tiny particulates of pollution. ...
2024-11-08
Culturing, a term for growing microorganisms in the laboratory, is a basic yet indispensable method in microbiology research. Microorganisms are often cultured in a liquid medium that provides essential nutrients, and this process is both simple and highly effective. In addition to nutrients, oxygen availability is also critical for the growth of aerobic microorganisms. However, oxygen does not dissolve easily in the liquid medium. As a result, the medium needs to be forcibly aerated, usually by shaking.
Several techniques have been developed for better aeration of “shake” cultures, including “baffled” shake flasks, which have indentations designed to improve oxygen ...
2024-11-08
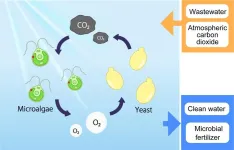
Bakeries and wineries can’t do without yeast, but they have no need for green algae. Wastewater treatment facilities, however, might just want to have these microorganisms team up. Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have discovered that these simple organisms form the best combination in terms of boosting wastewater treatment efficiency.
The active sludge method of wastewater treatment requires electricity to ensure the flow of oxygen that feeds bacteria and other organisms that process the water. Adding microalgae ...
2024-11-08
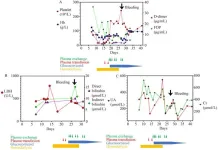
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted the rapid development and administration of various vaccines worldwide, with some reports linking these vaccines to immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). This report presents two cases of TTP occurring after the administration of the inactivated vaccine CoronaVac from Sinovac Biotech, highlighting the potential association between this type of vaccine and TTP. The article also provides an analysis of TTP incidence in the Nanjing area of China, suggesting a possible correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and the occurrence of TTP.
The first case details a 23-year-old female who developed symptoms of TTP three days ...
2024-11-08
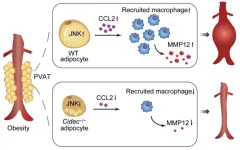
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a degenerative lesion characterized by structural disruption of the abdominal aortic wall and progressive dilatation into a pulsatile mass. AAA is strongly associated with obesity, partly due to abnormal dilatation of perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) in the abdomen, however, direct evidence is still lacking.
Cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor-like effector C (CIDEC), also known as fat-specific protein 27 (FSP27) in rodents, is a lipid droplet (LD)-associated protein that plays an important role in lipid storage. It has been reported that CIDEC/FSP27 promotes the growth of LDs by mediating the exchange and transfer of lipids ...
2024-11-08
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology progresses, the energy demands of training complex models have surged, raising widespread concerns about associated carbon emissions. This rapid growth is fueled by global demand across industries and academia, leading to exponential increases in computing power that carry significant environmental consequences. Given these challenges, in-depth research is essential to fully understand AI's carbon footprint and develop strategies for mitigating its environmental impact.
In a view (DOI: 10.1007/s11783-024-1918-y) by ...
2024-11-08
Tsukuba, Japan—Students often appear for high-stakes tests that hold significant weight in determining their futures. One such examination, the Common Test for University Admissions, currently allows examinees using braille an extended examination time of 1.5 times the standard duration. However, with the recent increase in complex questions and questions involving charts and diagrams in such tests, it is necessary to review whether the current accommodations remain adequate.
The researchers assessed the validity of the current time extension for examination questions containing complex tables by measuring the time required to read the text and complex tables. The results showed that ...
2024-11-08
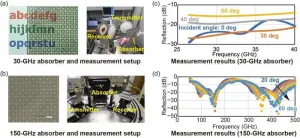
5G wireless communication services have rapidly expanded worldwide, leveraging millimeter-wave (mmW) frequencies in the 24 GHz to 71 GHz range (referred to as frequency range 2, or FR2). Looking ahead, Beyond 5G and 6G services, projected to offer ultra-fast connectivity exceeding 100 Gbit/s, are expected to be introduced in the 2030s. Frequencies in the 150-GHz to 300-GHz range are being considered as potential candidates for these future networks. However, critical components such as radio-wave absorbers, essential for packaging and modularization, still need to be developed. These absorbers play a key role in reducing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research update: Chalk-coated textiles cool in urban environments