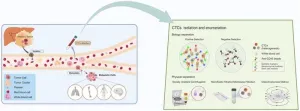
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant global health concern, particularly in regions like the Asia-Pacific, where chronic viral hepatitis and liver diseases contribute to its high incidence and mortality. Despite medical advancements, the late-stage diagnosis of HCC remains a major challenge, which underscores the need for more effective early detection strategies. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which are tumor cells released into the bloodstream from primary neoplastic sites, offer a promising avenue for non-invasive cancer diagnostics. This review provides a comprehensive overview of CTC detection methods, their association with HCC progression, and their role in prognostication and treatment monitoring.
CTC Detection and Enrichment Methods
The detection of CTCs can be broadly classified into two main approaches: biological property-based and physical property-based separations.
Biological Property-Based Methods: These techniques rely on the expression of specific biomarkers on the surface of CTCs, such as EpCAM, CK8/18/19, and mesenchymal markers. Antibodies targeting these markers are used for positive selection, allowing for the isolation of CTCs. Systems like CellSearch, Canpatrol, and NanoVelcro are widely used for this purpose. However, heterogeneity in CTC surface markers and the downregulation of these markers during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) present challenges to their detection.
Physical Property-Based Methods: These methods exploit differences in size, density, or deformability between CTCs and blood cells. Techniques like density gradient centrifugation, membrane filtration, microfluidic filtration, and dielectrophoresis have been developed for this purpose. While these approaches do not rely on surface markers, they face limitations when CTCs share similar physical properties with blood cells, such as in hematologic malignancies.
Role and Impact of CTCs in HCC
CTCs hold significant potential for early diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment evaluation in HCC patients. Studies show that the number of CTCs correlates with tumor size, grade, and overall cancer severity. Patients with high CTC counts typically present with more advanced disease stages and exhibit poorer outcomes. Furthermore, CTCs are particularly useful in monitoring minimal residual disease and predicting recurrence after surgical interventions, including liver transplantation and tumor resection.
Research also suggests that CTCs can act as indicators for extrahepatic metastasis. Mesenchymal CTCs (M-CTCs), which are involved in the metastatic process, are particularly associated with larger tumors and more aggressive HCC phenotypes.
CTCs and Surgical Outcomes
CTC analysis has revealed insights into the effects of surgical interventions on tumor recurrence and patient survival. Preoperative CTC counts can predict disease-free survival, while postoperative monitoring helps assess the risk of recurrence. Interestingly, surgery itself does not seem to increase CTC counts, though persistent CTC presence after surgery correlates with poorer outcomes. Studies comparing open surgery with laparoscopic techniques have shown differences in the postoperative inflammatory response but minimal variation in CTC dynamics, suggesting the robustness of CTC monitoring as a prognostic tool.
Integration with Other Biomarkers
CTCs can be integrated with other biochemical markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and microvascular invasion (MVI), to enhance prognostic accuracy. Combining CTC counts with AFP levels has been shown to improve prediction models for patient outcomes, especially in detecting early-stage HCC and monitoring recurrence. This highlights the importance of a multi-modal approach to cancer diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
Limitations and Future Directions
While CTC detection holds great promise, challenges remain in terms of standardization and sensitivity. The heterogeneity of CTCs, their low concentration in peripheral blood, and technical difficulties in isolation and identification pose significant hurdles. More sophisticated technologies, along with improved biomarker panels, are needed to overcome these limitations. Standardization of detection protocols across clinical settings will be crucial for integrating CTC analysis into routine cancer care.
Conclusions
CTCs offer a unique and promising tool for non-invasive cancer diagnostics and personalized medicine in HCC. As detection technologies advance and more is understood about the molecular biology of CTCs, their role in early diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and treatment monitoring will likely expand. This review underscores the need for continued research and technological development to fully integrate CTCs into clinical practice, thus enhancing precision oncology for HCC patients.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2024-00230
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END