(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (11/08/2024) — Researchers at the University of Minnesota have achieved a new material that will be pivotal in making the next generation of high-power electronics faster, transparent and more efficient. This artificially designed material allows electrons to move faster while remaining transparent to both visible and ultraviolet light, breaking the previous record.
The research, published in Science Advances, a peer-reviewed scientific journal, marks a significant leap forward in semiconductor design, which is crucial to a trillion-dollar global industry expected to continue growing as digital technologies expand.
Semiconductors power nearly all electronics, from smartphones to medical devices. A key to advancing these technologies lies in improving what scientists refer to as "ultra-wide band gap" materials. These materials can conduct electricity efficiently even under extreme conditions. Ultra-wide band gap semiconductors enable high-performance at elevated temperatures, making them essential for more durable and robust electronics.
In this paper, the researchers looked at creating a new class of materials with increased “band gap,” enhancing both transparency and conductivity. This unique achievement supports the development of faster, more efficient devices, paving the way for breakthroughs in computers, smartphones, and potentially even quantum computing.
The new material is a transparent conducting oxide, created with a specialized thin-layered structure that enhances transparency without sacrificing conductivity. As technology and artificial intelligence applications demand ever-more capable materials, this groundbreaking development offers a promising solution.
"This breakthrough is a game-changer for transparent conducting materials, enabling us to overcome limitations that have held back deep ultra-violet device performance for years," said Bharat Jalan, Shell Chair and Professor in the University of Minnesota's Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science.
The work not only demonstrates an unprecedented combination of transparency and conductivity in the deep-ultraviolet spectrum but also paves the way for innovations in high-power and optoelectronic devices that can operate in the most demanding environments, Jalan explained.
The study’s first co-authors Fengdeng Liu and Zhifei Yang, chemical engineering and materials science Ph.D. students working in Jalan’s lab, said they proved that the properties of the material were almost too perfect to believe for these electronic applications. They ran multiple experiments and eliminated defects in the material to increase its performance.
“Through detailed electron microscopy, we saw this material was clean with no obvious defects, revealing just how powerful oxide-based perovskites can be as semiconductors if defects are controlled,” said Andre Mkhoyan, a senior author on the paper and Ray D. and Mary T. Johnson Chair and Professor in the University of Minnesota Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science.
In addition to Jalan, Liu, Yang, and Mkhoyan, the team included Silo Guo from the University of Minnesota’s Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science and David Abramovitch and Marco Bernardi from the California Institute of Technology’s Department of Applied Physics and Materials Science.
This work was funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), the National Science Foundation, and the University of Minnesota Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC). The work was completed in collaboration with the University of Minnesota Characterization Facility and the Minnesota Nano Center.
To read the full paper titled, “Deep-ultraviolet transparent conducting SrSnO3 via heterostructure design,” visit the Science Advances website.
END
New material to make next generation of electronics faster and more efficient
With the increase of new technology and artificial intelligence, the demand for efficient and powerful semiconductors continues to grow
2024-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research update: Chalk-coated textiles cool in urban environments
2024-11-08
As air temperatures stay elevated through fall months, people may still want clothes that cool them down while outside, especially if they live in cities that stay warmer than rural landscapes. Researchers who previously demonstrated a cooling fabric coating now report on additional tests of a treated polyester fabric in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Fabric treated with the team’s chalk-based coating kept the air underneath up to 6 degrees Fahrenheit cooler in warmer urban environments.
Researchers Evan D. Patamia, Megan K. Yee and Trisha L. ...
New take on immunotherapy reinvigorates T cells by blocking uptake of energy-sapping cancer byproducts
2024-11-08
As cancer cells grow, they pump out metabolic byproducts such as lactic acid into the tumor microenvironment. Exhausted T cells — which have lost their cancer-fighting oomph — consume this lactic acid, which further saps their energy, according to new research from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC Hillman Cancer Center.
When the researchers blocked the protein that imports lactic acid into cells, exhausted T cells gained a new lease on life, which led to improved tumor control in mouse models of cancer. The findings are published today in Nature Immunology.
“Blocking access to inhibitory metabolites is a completely new take on how we can reinvigorate ...
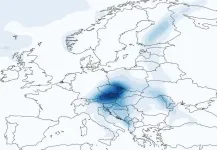
How much climate change is in the weather?
2024-11-08
Only a few weeks ago, massive precipitation produced by the storm “Boris” led to chaos and flooding in Central and Eastern Europe. An analysis conducted by the Alfred Wegener Institute shows that in a world without the current level of global warming Boris would have deposited roughly nine percent less rain. Such conclusions can be drawn thanks to a new modelling approach called ‘storylines’. How it can be used in near-real-time was just presented in the Nature journal Communications Earth & Environment. At the same time, the AWI team released a freely available online tool that ...
Flagship AI-ready dataset released in type 2 diabetes study
2024-11-08
Researchers today (Nov. 8, 2024) are releasing the flagship dataset from an ambitious study of biomarkers and environmental factors that might influence the development of type 2 diabetes. Because the study participants include people with no diabetes and others with various stages of the condition, the early findings hint at a tapestry of information distinct from previous research.
For instance, data from a customized environmental sensor in participants’ homes show a clear association between disease state and exposure to tiny particulates of pollution. ...
Shaking it up: An innovative method for culturing microbes in static liquid medium
2024-11-08
Culturing, a term for growing microorganisms in the laboratory, is a basic yet indispensable method in microbiology research. Microorganisms are often cultured in a liquid medium that provides essential nutrients, and this process is both simple and highly effective. In addition to nutrients, oxygen availability is also critical for the growth of aerobic microorganisms. However, oxygen does not dissolve easily in the liquid medium. As a result, the medium needs to be forcibly aerated, usually by shaking.
Several techniques have been developed for better aeration of “shake” cultures, including “baffled” shake flasks, which have indentations designed to improve oxygen ...
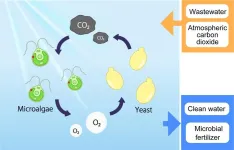
Greener and cleaner: Yeast-green algae mix improves water treatment
2024-11-08
Bakeries and wineries can’t do without yeast, but they have no need for green algae. Wastewater treatment facilities, however, might just want to have these microorganisms team up. Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have discovered that these simple organisms form the best combination in terms of boosting wastewater treatment efficiency.
The active sludge method of wastewater treatment requires electricity to ensure the flow of oxygen that feeds bacteria and other organisms that process the water. Adding microalgae ...
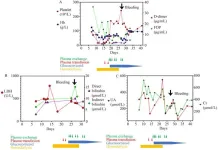
Acquired immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) associated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine CoronaVac
2024-11-08
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted the rapid development and administration of various vaccines worldwide, with some reports linking these vaccines to immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). This report presents two cases of TTP occurring after the administration of the inactivated vaccine CoronaVac from Sinovac Biotech, highlighting the potential association between this type of vaccine and TTP. The article also provides an analysis of TTP incidence in the Nanjing area of China, suggesting a possible correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and the occurrence of TTP.
The first case details a 23-year-old female who developed symptoms of TTP three days ...
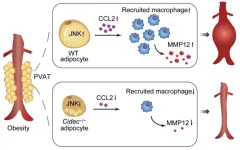
CIDEC as a novel player in abdominal aortic aneurysm formation
2024-11-08
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a degenerative lesion characterized by structural disruption of the abdominal aortic wall and progressive dilatation into a pulsatile mass. AAA is strongly associated with obesity, partly due to abnormal dilatation of perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) in the abdomen, however, direct evidence is still lacking.
Cell death-inducing DNA fragmentation factor-like effector C (CIDEC), also known as fat-specific protein 27 (FSP27) in rodents, is a lipid droplet (LD)-associated protein that plays an important role in lipid storage. It has been reported that CIDEC/FSP27 promotes the growth of LDs by mediating the exchange and transfer of lipids ...
Artificial intelligence: a double-edged sword for the environment?
2024-11-08
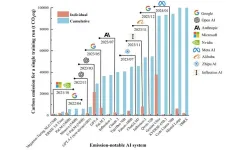
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology progresses, the energy demands of training complex models have surged, raising widespread concerns about associated carbon emissions. This rapid growth is fueled by global demand across industries and academia, leading to exponential increases in computing power that carry significant environmental consequences. Given these challenges, in-depth research is essential to fully understand AI's carbon footprint and develop strategies for mitigating its environmental impact.
In a view (DOI: 10.1007/s11783-024-1918-y) by ...
Current test accommodations for students with blindness do not fully address their needs
2024-11-08
Tsukuba, Japan—Students often appear for high-stakes tests that hold significant weight in determining their futures. One such examination, the Common Test for University Admissions, currently allows examinees using braille an extended examination time of 1.5 times the standard duration. However, with the recent increase in complex questions and questions involving charts and diagrams in such tests, it is necessary to review whether the current accommodations remain adequate.
The researchers assessed the validity of the current time extension for examination questions containing complex tables by measuring the time required to read the text and complex tables. The results showed that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
[Press-News.org] New material to make next generation of electronics faster and more efficientWith the increase of new technology and artificial intelligence, the demand for efficient and powerful semiconductors continues to grow