Simplicity is key to understanding and achieving goals
Our minds favour simple explanations and efficient actions, according to a new study
2024-11-22
(Press-News.org)
People’s preference for simple explanations of any situation is connected to their desire to execute tasks efficiently, finds a new study from the University of Waterloo.
"These findings show that our preference for simpler explanations mirrors how we evaluate actions. Simplicity isn't just valued in explanations—it's part of how we think about achieving results efficiently," said Claudia Sehl, lead author and a PhD candidate in developmental psychology at Waterloo.
Sehl collaborated with Waterloo developmental psychology professors Ori Friedman and Stephanie Denison on this study. They conducted seven experiments involving 2,820 participants who were presented with simple and complex ways to explain an outcome or achieve a goal. Participants consistently favoured the simpler options.
The study found that people are more attracted to explanations that involve common and reliable causes. If a cause seemed rare or unreliable, it was viewed as less helpful. In other words, the simpler and more dependable the cause, the more appealing it was both for understanding an event and for achieving results in the future.
"Essentially, the more common and reliable a cause, the more appealing it became as both an explanation and a method for achieving outcomes,” Sehl said. “Additionally, whether describing causes or seeking outcomes, using fewer causes seems both faster and more effective, pointing to a shared mental process behind both preferences."
Overall, the findings suggest that efficiency is valued both in explanations and when achieving goals.
"Our research suggests that people care a lot about efficiency—the idea of doing more with less—and that this focus on efficiency affects how people think about both explanations and accomplishments," Friedman said.
This study, Doing things efficiently: Testing an account of why simple explanations are satisfying, by Sehl, Friedman, and Denison, is published in Cognitive Psychology.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-22
Most ants have two morphologically differentiated adult castes - queens and workers - each irreversibly specialized for either reproduction or nonreproductive altruism such as foraging, defense and care of maternal brood. Adult gynes (virgin queens) normally have higher body mass, wings and frontal eyes, as well as enlarged ovaries and a sperm storage organ. In contrast, workers are wingless females with smaller body size and degenerated reproductive tracts, usually without a sperm storage organ. In 1910, the American entomologist ...
2024-11-22
Expectant mothers who maintain a diet that meets USDA dietary guidelines during pregnancy may be more likely to have infants with healthy birthweights, steadier growth patterns, and potentially a reduced risk of obesity later in childhood, according to a new study funded by the Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program at the National Institutes of Health.
The research, involving more than 2,800 mother-child pairs across eight ECHO Cohort Study Sites, suggests that following a healthy ...
2024-11-22
Dynamic, reversible modifications of DNA and RNA regulate how genes are expressed and transcribed, which can influence cellular processes, disease development, and overall organismal health. Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a common but overlooked group of guide RNA molecules that steer chemical modifications to cellular ribosomal RNA (rRNA) targets, like an usher showing someone to their seat in a theater.
Researchers from the University of Chicago recently developed a new approach for identifying new cellular RNA targets of snoRNAs. ...
2024-11-22
About The Study: In this cohort study, racial and ethnic disparities in early-onset (before 50 years of age) colorectal cancer mortality were evident, with the highest burden among Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander and non-Hispanic Black individuals. These results provide evidence of the role of social determinants of health in explaining these differences.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Maria Elena Martinez, PhD, email e8martinez@health.ucsd.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.46820)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
2024-11-22
About The Study: This serial cross-sectional study observed a significant decrease in positive reviews for health care facilities post-COVID. These findings underscore a disparity in patient experience, particularly in rural areas and areas with the highest proportions of Black and white residents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Neil K. R. Sehgal, ME, email neilsehgal99@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.46890)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for ...
2024-11-22
Tsukuba, Japan—Physical inactivity is the fourth leading mortality risk factor, following hypertension, smoking, and hyperglycemia. Therefore, acquiring an exercise habit is crucial to maintain and improve health. In Japan, Specific Health Guidance is provided to support the improvement of lifestyle habits, including exercise habits. To develop more efficient health guidance, it is important to identify factors that influence its effectiveness (e.g., characteristics and lifestyle of the target ...
2024-11-22
Hydrogen is becoming an increasingly popular choice as we shift towards cleaner energy. It can be burned like traditional fuels, producing only water as a byproduct, and can generate electricity when used in fuel cells. However, as hydrogen production, use, and transportation increase, so do safety concerns. Hydrogen is highly flammable at concentrations as low as 4% and is odorless and colorless, making leaks challenging to detect.
To address these concerns, researchers led by Professor Yutaka Majima from Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) have developed a sensor that detects hydrogen at ultra-low concentrations ...
2024-11-22
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) developed a smart monitoring system that applies digital sensing technology to maintain and manage small- and medium-sized aging bridges. This study was conducted as an international matching joint research funded by KICT, and established a foundation for technology diffusion to ASEAN countries through joint research with University of Transport and Communications (UTC) in Vietnam.
In general, bridge maintenance monitoring technology is applied to long-span bridges such as cable-stayed bridges and suspension bridges. This monitoring system consumes a lot of resources for design and installation, ...
2024-11-22
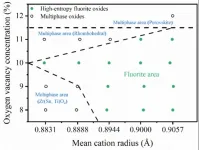
Current researches show that the standard deviation of the cationic radii, configuration entropy, or maintenance of Ce4+ have a certain impact on the formation of single-phase HEFOs, but the discovered rules are only applicable to partially synthesized material systems and have significant limitations. Furthermore, the range of elements used in the synthesized materials is relatively narrow, which restricts the potential to fully exploit the advantages of high-entropy materials and their vast compositional space.
“Inspired by the synthesized HEFOs and the stabilization mechanism ...
2024-11-22
A research team at the University of Vienna, led by medicinal chemist Markus Muttenthaler, has developed a new class of oral peptide therapeutic leads for treating chronic abdominal pain. This groundbreaking innovation offers a safe, non-opioid-based solution for conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which affect millions of people worldwide. The research results were recently published in the international edition of the renowned journal Angewandte Chemie.
An Innovative Approach to Pain Management
Current medications used to treat chronic abdominal pain often rely on opioids. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Simplicity is key to understanding and achieving goals
Our minds favour simple explanations and efficient actions, according to a new study