(Press-News.org) Background and Goal: The participatory research approach is an important tool of family medicine and primary health care research. However, standard consensus methods like the Delphi and nominal group techniques can be time consuming and may not represent a broad range of opinions. To address these issues, researchers developed an adapted nominal group technique (aNGT) to efficiently build consensus among stakeholders with diverse perspectives.
Approach: This study focused on shaping care trajectories for adults aged 65 and older, aiming to prioritize key domains and identify new care indicators. Researchers used four main strategies: (1) recruiting four diverse stakeholder groups (older adults, clinicians, managers, and decision makers); (2) using remote tools to maximize participation; (3) adding a pre-elicitation activity so participants could individually review study materials and rank domains before group discussions; and (4) tailoring discussions to each group’s needs, including scheduling meetings around lunch for clinicians and avoiding jargon.
Main Results: Of 28 participants who completed the questionnaire, 20 joined a group discussion. Through the pre-elicitation activity and one round of discussions, participants reached a consensus on prioritizing “symptoms, functioning, and quality of care.” Tailored discussions and remote tools were the most effective strategies.
Why It Matters: By addressing traditional consensus-building challenges, the aNGT fosters inclusivity, efficiency, and relevance, making it a valuable approach for research that informs care standards.
Building Timely Consensus Among Diverse Stakeholders: An Adapted Nominal Group Technique
Deniz Cetin-Sahin, MD, PhD, et al
Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Department of Family Medicine, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
PERMANENT LINK
END
Adapted nominal group technique effectively builds consensus on health care priorities for older adults
Building timely consensus among diverse stakeholders: an adapted nominal group technique
2024-11-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Single-visit first-trimester care with point-of-care ultrasound cuts emergency visits by 81% for non-miscarrying patients
2024-11-25
The Bethesda Family Medicine Clinic in St. Paul, Minnesota, established a bi-monthly Early Pregnancy Dating & Risk Assessment Clinic in September 2022. The clinic introduced an integrated approach, combining point-of-care ultrasound with immediate, multidisciplinary first-trimester care. This integration allowed the clinic to quickly identify high-risk cases and offer timely intervention for issues such as miscarriage or abnormal pregnancies, reducing emergency visits, urgent clinic appointments, and first-trimester phone inquiries by 81% for non-miscarrying patients. Clinic implementation ...
Study reveals impact of trauma on health care professionals in Israel following 2023 terror attack
2024-11-25
Research Brief
Background and Goal: The October 7, 2023, terrorist attack in southern Israel forced the evacuation of countless individuals, placing intense demands on health care personnel. Primary care clinicians, who are at the forefront of treating severely traumatized evacuees, are often exposed to secondary trauma, which can affect their mental health and job performance. This study investigated the levels of burnout, well-being, and resilience among health care staff working in primary care clinics in Israel during the aftermath of the attack.
Study Approach: This cross-sectional ...
Primary care settings face barriers to screening for early detection of cognitive impairment
2024-11-25
Background and Goal: Early detection of cognitive impairment is essential for improving patient outcomes, but primary care settings face significant challenges in screening. This special report summarizes key points and gaps in knowledge about methods for detecting cognitive impairment in primary care clinics.
Key Insights: The report highlights the importance of addressing the rising incidence of cognitive impairment as the population ages, particularly with new treatments for early Alzheimer’s disease now available. It advocates for creative solutions to manage the increased workload, such as partnering with community health workers and leveraging telehealth. ...
November/December Annals of Family Medicine Tip Sheet
2024-11-25
Editorial
War Takes a Toll on Family Doctors Trying to Care for Patients
Background: This issue of Annals of Family Medicine includes four articles discussing the impact of the Israeli/Palestinian conflict on family doctors and patients in the region. These articles offer perspectives from academic family doctors who have firsthand experience living and working in the region to reveal the complexity and impact of this conflict.
Editorial Stance: The decision to publish these articles was ...
Antibiotics initiated for suspected community-acquired pneumonia even when chest radiography results are negative
2024-11-25
Original Research
Background and Goal: This study explored how chest X-ray results influence antibiotic initiation by general practitioners in France when managing patients with suspected pneumonia.
Study Approach: A prospective cross-sectional study was conducted with adult patients with suspected pneumonia who received chest X-rays as part of their evaluation. To analyze factors associated with antibiotic initiation, patients’ characteristics were compared at inclusion and at 28 days between patients with positive chest X-rays (indicating pneumonia) and patients with negative chest X-ray results.
Main Results: The sample included 259 ...
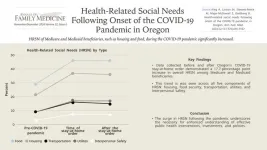
COVID-19 stay-at-home order increased reporting of food, housing, and other health-related social needs in Oregon
2024-11-25
Background and Goal: Efforts to address the health-related social needs (HRSN) of Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries, such as housing and food, during the COVID-19 pandemic were insufficient. This research examined HRSN data from the Accountable Health Communities (AHC) study collected in Oregon to understand changes in HRSN for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries at the onset and during the first two years of the pandemic.
Study Approach: The study sample included 21,522 Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries screened for overall health-related social needs between ...
UW-led research links wildfire smoke exposure with increased dementia risk
2024-11-25
As Baby Boomers hit retirement, about 1 in 6 Americans is now over the age of 65. The number of Americans living with dementia is projected to skyrocket — but the proportion of older Americans who develop dementia has actually decreased. The exact reason why is uncertain, but various lifestyle and environmental factors can influence a person’s risk of cognitive decline.
One recently discovered risk is air pollution. Studies have linked exposure to a type of air pollution called fine particulate matter, or PM2.5, with an increased risk of developing dementia, and researchers suspect ...
Most U.S. adults surveyed trust store-bought turkey is free of contaminants, despite research finding fecal bacteria in ground turkey
2024-11-25
WASHINGTON, D.C. ؚ— More than six out of 10 U.S. adults who took part in a Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine/Morning Consult survey last week say they wouldn’t eat turkey contaminated with feces, yet consumer research has shown more than half of store-bought packages of ground turkey tested positive for it.
The poll included 2,183 adults interviewed Nov. 18 to Nov. 20, 82% of whom said they plan to eat turkey for Thanksgiving this year. Of those, 87% said they trust it’ll be free from contaminants, but 65% said if they knew it was contaminated with fecal bacteria, they’d be unlikely to eat it.
In research conducted by Consumer Reports in ...
New therapy from UI Health offers FDA-approved treatment option for brittle type 1 diabetes
2024-11-25
A new therapy for brittle type 1 diabetes, the only treatment currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, is available exclusively at UI Health in Chicago.
Pancreatic islet cell therapy is a treatment approved by the FDA only for adults with type 1 diabetes who struggle to control their blood sugar levels due to frequent episodes of severe low blood sugar and hypoglycemia unawareness, a condition that occurs when patients can’t detect that their blood sugar is dropping. This new therapy, called Lantidra, is derived from a deceased donor pancreas. To regulate blood glucose, the drug is infused into the patient’s liver where insulin is produced. ...
Alzheimer's: A new strategy to prevent neurodegeneration
2024-11-25
A future treatment for Alzheimer disease may involve a nasal spray. Researchers at Università Cattolica and Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS have discovered that by inhibiting the brain enzyme S-acyltransferase (zDHHC) through a nasal-spray drug, they can counteract the cognitive decline and brain damage typical of the disease. The study has been led by Professor Claudio Grassi, Director of the Neuroscience Department, and Professor Salvatore Fusco, with the collaboration of the University of Catania.
The researchers observed that the post-mortem brains of Alzheimer patients contained an excess of S-acyltransferase, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Adapted nominal group technique effectively builds consensus on health care priorities for older adultsBuilding timely consensus among diverse stakeholders: an adapted nominal group technique