(Press-News.org) Children who grow up with pets or on farms may develop allergies at lower rates because their gut microbiome develops with more anaerobic commensals, per fecal analysis in small cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0313078
Article Title: Gut microbiota markers in early childhood are linked to farm living, pets in household and allergy
Author Countries: Sweden
Funding: This work was supported by the Region Västra Götaland (agreement concerning medical research and education – ALF), https://www.alfvastragotaland.se [ALFGBG966243] [ALFGBG720181] (IA); the Swedish Medical Research Council (Vetenskapsrådet), https://www.vr.se/ [K98-06X-12612-01A] (AW); and the Health & Medical Care Committee of the Region Västra Götaland (Regional Research & Development funds Västra Götaland region) https://www.researchweb.org/is/vgregion/ [grant no. VGFOUREG-12007] (IA). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Children who grow up with pets or on farms may develop allergies at lower rates because their gut microbiome develops with more anaerobic commensals, per fecal analysis in small cohort study
2024-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
North American Early Paleoindians almost 13,000 years ago used the bones of canids, felids, and hares to create needles in modern-day Wyoming, potentially to make the tailored fur garments which enabl
2024-11-27
North American Early Paleoindians almost 13,000 years ago used the bones of canids, felids, and hares to create needles in modern-day Wyoming, potentially to make the tailored fur garments which enabled their dispersal into these colder climates
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0313610
Article Title: Early Paleoindian use of canids, felids, and hares for bone needle production at the La Prele site, Wyoming, USA
Contact: Spencer Pelton, spencer.pelton@wyo.gov, Ph. +1 307 399 2827
Author Countries: U.S.
Funding: Funding for this project includes the National Science Foundation (award #1947297), the ...
Higher levels of democracy and lower levels of corruption are associated with more doctors, independent of healthcare spending, per cross-sectional study of 134 countries
2024-11-27
Higher levels of democracy and lower levels of corruption are associated with more doctors, independent of healthcare spending, per cross-sectional study of 134 countries.
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal. pgph.0003656
Article Title: The relationship between democracy and corruption and the global physician workforce
Author Countries: Canada
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
In major materials breakthrough, UVA team solves a nearly 200-year-old challenge in polymers
2024-11-27
Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science have developed a new polymer design that appears to rewrite the textbook on polymer engineering. No longer is it dogma that the stiffer a polymeric material is, the less stretchable it has to be.
“We are addressing a fundamental challenge that has been thought to be impossible to solve since the invention of vulcanized rubber in 1839,” said Liheng Cai, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering, and chemical engineering.
That’s when Charles Goodyear accidentally discovered that heating natural rubber with sulfur ...
Wyoming research shows early North Americans made needles from fur-bearers
2024-11-27
A Wyoming archaeological site where people killed or scavenged a Columbian mammoth nearly 13,000 years ago has produced yet another discovery that sheds light on the life of these early inhabitants of North America.
Wyoming State Archaeologist Spencer Pelton and colleagues at the University of Wyoming and other institutions have found that these Paleolithic humans made needles from the bones of fur-bearers -- including foxes; hares or rabbits; and cats such as bobcats, mountain lions, lynx and possibly even the now-extinct ...
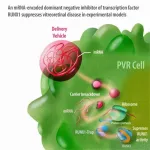
Preclinical tests show mRNA-based treatments effective for blinding condition
2024-11-27
A new preclinical study by Mass Eye and Ear investigators showed that a novel mRNA-based therapy may be able to prevent blindness and scarring from proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) following a retinal detachment repair or traumatic injury to the eye. There is no current treatment for PVR other than surgery, which itself carries a high risk of causing or exacerbating PVR. Their results, published in Science Translational Medicine, show the promise that mRNA-based therapies may one day offer patients with PVR and other retinal conditions.
“This ...
Velcro DNA helps build nanorobotic Meccano
2024-11-27
Researchers at the University of Sydney Nano Institute have made a significant advance in the field of molecular robotics by developing custom-designed and programmable nanostructures using DNA origami.
This innovative approach has potential across a range of applications, from targeted drug delivery systems to responsive materials and energy-efficient optical signal processing. The method uses ‘DNA origami’, so-called as it uses the natural folding power of DNA, the building blocks of human life, to create new and useful biological structures.
As a proof-of-concept, the researchers made more than 50 nanoscale objects, including a ‘nano-dinosaur’, ...
Oceans emit sulfur and cool the climate more than previously thought
2024-11-27
Researchers have quantified for the first time the global emissions of a sulfur gas produced by marine life, revealing it cools the climate more than previously thought, especially over the Southern Ocean.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, shows that the oceans not only capture and redistribute the sun's heat, but produce gases that make particles with immediate climatic effects, for example through the brightening of clouds that reflect this heat.
It broadens the climatic impact of marine sulfur because it adds a new compound, methanethiol, that had previously gone unnoticed. Researchers only detected the gas recently, because ...
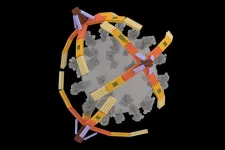
Nanorobot hand made of DNA grabs viruses for diagnostics and blocks cell entry
2024-11-27
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A tiny, four-fingered “hand” folded from a single piece of DNA can pick up the virus that causes COVID-19 for highly sensitive rapid detection and can even block viral particles from entering cells to infect them, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers report. Dubbed the NanoGripper, the nanorobotic hand also could be programmed to interact with other viruses or to recognize cell surface markers for targeted drug delivery, such as for cancer treatment.
Led by Xing Wang, a professor of bioengineering and of chemistry at the ...
Rare, mysterious brain malformations in children linked to protein misfolding, study finds
2024-11-27
In 1992, Judith Frydman, PhD, discovered a molecular complex with an essential purpose in all of our cells: folding proteins correctly.
The complex, a type of “protein chaperone” known as TRiC, helps fold thousands of human proteins: It was later found that about 10% of all our proteins pass through its barrel structure.
All animals have several different kinds of protein chaperones, each with its own job of helping fold proteins in the cell. TRiC binds to newborn proteins and shapes these strings of amino acids into the correct 3D structures, ...
Newly designed nanomaterial shows promise as antimicrobial agent
2024-11-27
HOUSTON – (Nov. 27, 2024) – Newly developed halide perovskite nanocrystals (HPNCs) show potential as antimicrobial agents that are stable, effective and easy to produce. After almost three years, Rice University scientist Yifan Zhu and colleagues have developed a new HPNC that is effective at killing bacteria in a biofluid under visible light without experiencing light- and moisture-driven degradation common in HPNCs.
A new method using two layers of silicon dioxide that Zhu and colleagues developed over years of work was used in experiments with lead-based and bismuth-based HPNCs to test their antimicrobial efficacy and stability in water. ...