(Press-News.org) Manmade sounds such vehicle traffic can mask the positive impact of nature soundscapes on people’s stress and anxiety, according to a new study published November 27, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Paul Lintott of the University of the West of England, U.K., and Lia Gilmour of the Bat Conservation Trust, U.K.
Existing research shows that natural sounds, like birdsong, can lower blood pressure, heart, and respiratory rates, as well as self-reported stress and anxiety. Conversely, anthropogenic soundscapes, like traffic or aircraft noise, are hypothesized to have negative effects on human health and wellbeing in a variety of ways.
In the new study, 68 student volunteers listened to three 3-minute soundscapes: a nature soundscape recorded at sunrise in West Sussex, U.K., the same soundscape combined with 20 mile per hour road traffic sounds, and the same soundscape with 40 mile per hour traffic sounds. General mood and anxiety were assessed before and after the soundscapes using self-reported scales.
The study found that listening to a natural soundscape reduced self-reported stress and anxiety levels, and also enhanced mood recovery after a stressor. However, the benefits of improved mood associated with the natural soundscape was limited when traffic sounds were included. The natural soundscape alone was associated with the lowest levels of stress and anxiety, with the highest levels reported after the soundscape that included 40 mile per hour traffic.
The authors conclude that reducing traffic speed in urban areas might influence human health and wellbeing not only through its safety impacts, but also through its effect on natural soundscapes.
The authors add: “Our study shows that listening to natural soundscapes can reduce stress and anxiety, and that anthropogenic sounds such as traffic noise can mask potential positive impacts. Reducing traffic speeds in cities is therefore an important step towards more people experiencing the positive effects of nature on their health and wellbeing.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0311487
Citation: Gilmour LRV, Bray I, Alford C, Lintott PR (2024) Natural soundscapes enhance mood recovery amid anthropogenic noise pollution. PLoS ONE 19(11): e0311487. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0311487
Author Countries: U.K., Australia
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
END
The sound of traffic increases stress and anxiety
People experienced less stress and anxiety while listening to nature soundscapes, but the addition of road traffic noise increased their stress and anxiety
2024-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Global food yields have grown steadily during last six decades
2024-11-27
Contrary to widespread concerns that global crop yields have stagnated in recent decades, a comprehensive study of worldwide food production finds yields have continued to grow at roughly the same rate since the 1960s. John Baffes of the World Bank and Xiaoli Etienne of the University of Idaho, U.S., report these findings on November 27, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Almost 10 billion people are expected to inhabit Earth by 2050, so agricultural production will become increasingly critical ...
Children who grow up with pets or on farms may develop allergies at lower rates because their gut microbiome develops with more anaerobic commensals, per fecal analysis in small cohort study
2024-11-27
Children who grow up with pets or on farms may develop allergies at lower rates because their gut microbiome develops with more anaerobic commensals, per fecal analysis in small cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0313078
Article Title: Gut microbiota markers in early childhood are linked to farm living, pets in household and allergy
Author Countries: Sweden
Funding: This work was supported by the Region Västra Götaland (agreement concerning medical research and education – ALF), https://www.alfvastragotaland.se [ALFGBG966243] [ALFGBG720181] ...
North American Early Paleoindians almost 13,000 years ago used the bones of canids, felids, and hares to create needles in modern-day Wyoming, potentially to make the tailored fur garments which enabl
2024-11-27
North American Early Paleoindians almost 13,000 years ago used the bones of canids, felids, and hares to create needles in modern-day Wyoming, potentially to make the tailored fur garments which enabled their dispersal into these colder climates
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0313610
Article Title: Early Paleoindian use of canids, felids, and hares for bone needle production at the La Prele site, Wyoming, USA
Contact: Spencer Pelton, spencer.pelton@wyo.gov, Ph. +1 307 399 2827
Author Countries: U.S.
Funding: Funding for this project includes the National Science Foundation (award #1947297), the ...
Higher levels of democracy and lower levels of corruption are associated with more doctors, independent of healthcare spending, per cross-sectional study of 134 countries
2024-11-27
Higher levels of democracy and lower levels of corruption are associated with more doctors, independent of healthcare spending, per cross-sectional study of 134 countries.
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal. pgph.0003656
Article Title: The relationship between democracy and corruption and the global physician workforce
Author Countries: Canada
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
In major materials breakthrough, UVA team solves a nearly 200-year-old challenge in polymers
2024-11-27
Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science have developed a new polymer design that appears to rewrite the textbook on polymer engineering. No longer is it dogma that the stiffer a polymeric material is, the less stretchable it has to be.
“We are addressing a fundamental challenge that has been thought to be impossible to solve since the invention of vulcanized rubber in 1839,” said Liheng Cai, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering, and chemical engineering.
That’s when Charles Goodyear accidentally discovered that heating natural rubber with sulfur ...
Wyoming research shows early North Americans made needles from fur-bearers
2024-11-27
A Wyoming archaeological site where people killed or scavenged a Columbian mammoth nearly 13,000 years ago has produced yet another discovery that sheds light on the life of these early inhabitants of North America.
Wyoming State Archaeologist Spencer Pelton and colleagues at the University of Wyoming and other institutions have found that these Paleolithic humans made needles from the bones of fur-bearers -- including foxes; hares or rabbits; and cats such as bobcats, mountain lions, lynx and possibly even the now-extinct ...
Preclinical tests show mRNA-based treatments effective for blinding condition
2024-11-27
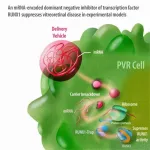
A new preclinical study by Mass Eye and Ear investigators showed that a novel mRNA-based therapy may be able to prevent blindness and scarring from proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) following a retinal detachment repair or traumatic injury to the eye. There is no current treatment for PVR other than surgery, which itself carries a high risk of causing or exacerbating PVR. Their results, published in Science Translational Medicine, show the promise that mRNA-based therapies may one day offer patients with PVR and other retinal conditions.
“This ...
Velcro DNA helps build nanorobotic Meccano
2024-11-27
Researchers at the University of Sydney Nano Institute have made a significant advance in the field of molecular robotics by developing custom-designed and programmable nanostructures using DNA origami.
This innovative approach has potential across a range of applications, from targeted drug delivery systems to responsive materials and energy-efficient optical signal processing. The method uses ‘DNA origami’, so-called as it uses the natural folding power of DNA, the building blocks of human life, to create new and useful biological structures.
As a proof-of-concept, the researchers made more than 50 nanoscale objects, including a ‘nano-dinosaur’, ...
Oceans emit sulfur and cool the climate more than previously thought
2024-11-27
Researchers have quantified for the first time the global emissions of a sulfur gas produced by marine life, revealing it cools the climate more than previously thought, especially over the Southern Ocean.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, shows that the oceans not only capture and redistribute the sun's heat, but produce gases that make particles with immediate climatic effects, for example through the brightening of clouds that reflect this heat.
It broadens the climatic impact of marine sulfur because it adds a new compound, methanethiol, that had previously gone unnoticed. Researchers only detected the gas recently, because ...
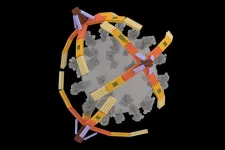
Nanorobot hand made of DNA grabs viruses for diagnostics and blocks cell entry
2024-11-27
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A tiny, four-fingered “hand” folded from a single piece of DNA can pick up the virus that causes COVID-19 for highly sensitive rapid detection and can even block viral particles from entering cells to infect them, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers report. Dubbed the NanoGripper, the nanorobotic hand also could be programmed to interact with other viruses or to recognize cell surface markers for targeted drug delivery, such as for cancer treatment.
Led by Xing Wang, a professor of bioengineering and of chemistry at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
[Press-News.org] The sound of traffic increases stress and anxietyPeople experienced less stress and anxiety while listening to nature soundscapes, but the addition of road traffic noise increased their stress and anxiety