(Press-News.org)
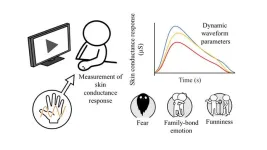
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have used measurements of skin conductance over time to tell emotions apart. Volunteers were shown videos depicting fearful scenes, family bonding, and humor, while their skin conductance trace was recorded. The team’s analysis showed that traces could be used to make good guesses of which emotions were being felt. Advances like this help break down an over-reliance on facial data, bringing emotionally aware technologies closer to home.
A new frontier is being pioneered in consumer electronics: one day, digital devices might be able to offer services depending on your emotional state. While this sounds amazing, this depends on whether devices can correctly tell what people are feeling. The most common methods depend on facial expressions: while these have had some success, such data may not always be available. This has led to researchers looking for different biological signals which could be interpreted to access emotional states, like brain wave measurements or cardiograms.
A team of scientists led by Professor Shogo Okamoto from Tokyo Metropolitan University have been using skin conductance as a doorway to human emotions. When people feel different things, the electrical properties of their skin change drastically due to perspiration, with signals showing up within one to three seconds of the original stimulus. Previous research has already shown that measurements of peak conductance, for example, can be correlated with certain emotions. In their most recent work, the team focused on the dynamics of the response i.e. how quickly the conductance trace following some stimulus reaches a peak, and how it decays back to normal.
In their experiment, volunteers were asked to wear probes on the skin and watch videos which were either scary scenes from horror movies, emotional scenes of family bonding, or funny acts performed by comedians. Importantly, each of the scenes had well-defined points at which a certain emotional stimulus was sought. Analyzing the traces, the team found many interesting and significant trends. For example, they found that the response to fear lasted the longest. This may be a biologically evolved trait, since there are benefits to perceptions of danger lasting longer. Comparing responses to humor and emotional scenes of family bonding, they found responses to family bonding seemed to increase more slowly. The emotions that were evoked were most likely a mixture of sadness and happiness, so it may be that they interfere with each other, leading to a slower change.
Importantly, the team’s statistical analysis revealed that the different numbers extracted from the dynamics of the trace could be used to discriminate the emotional state of an individual. Though they can’t yet tell the emotions apart perfectly, the data could, for example, be used to make statistically significant predictions of whether a subject was experiencing fear or feeling the warmth of a family bond. Combined with other signals, the team believe we are one step closer to devices knowing how we are feeling, with scope for a better understanding of human emotions.
This work was supported in part by an Institutional Research Grant from Tokyo Metropolitan University.
END
Images/videos of capuchin monkeys
ANN ARBOR—The immune performance of wild capuchin monkeys declines when the animals experience higher temperatures, and younger monkeys seem to be particularly vulnerable to heat, according to a University of Michigan study.
U-M anthropology doctoral student Jordan Lucore examined how the immune systems of wild monkeys in Costa Rica were impacted by temperature. Lucore and a team of researchers found that when monkeys experienced about two weeks of warmer temperatures—86 degrees Fahrenheit—their generalized immune system performance declined. This is the part of the immune system that ...
Embargoed for release: Friday, November 29, 2:00 PM ET
Key points:
Exposure to PM2.5 was associated with higher levels of inflammation among pregnant women, potentially leading to adverse birth outcomes.
Study examined PM2.5 and maternal and fetal health on a single-cell level, using an innovative technology to detect how pollution modified the DNA within individual cells.
Findings provide new understanding of the biological pathways through which air pollution affects pregnancy and birth outcomes, ...
Our bodies are remarkably skilled at adapting to changing environments. For example, whether amid summer heat or a winter freeze, our internal temperature remains steady at 37°C, thanks to a process called homeostasis. This hidden balancing act is vital for survival, enabling animals to maintain stable internal conditions even as the external world shifts. But recent research from the Ikmi Group at EMBL Heidelberg shows that homeostasis can extend beyond internal regulation and actively redefine an organism’s shape.
The starlet sea anemone (Nematostella vectensis) possesses remarkable regenerative abilities. Cut off its head ...
Dr. Woohyun Kim's research team from the Hydrogen Research Department at the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has successfully developed an innovative nickel-cobalt composite catalyst that can accelerate the production and commercialization of turquoise hydrogen.*
*Turquoise Hydrogen: A technology that produces hydrogen and carbon by decomposing hydrocarbons such as methane (CH₄) (CH₄ → C + 2H₂). Unlike gray hydrogen, the most widely used hydrogen production technology, ...
Bacteria modify their ribosomes when exposed to widely used antibiotics, according to research published today in Nature Communications. The subtle changes might be enough to alter the binding site of drug targets and constitute a possible new mechanism of antibiotic resistance.
Escherichia coli is a common bacterium which is often harmless but can cause serious infections. The researchers exposed E. coli to streptomycin and kasugamycin, two drugs which treat bacterial infections. Streptomycin has been a staple in treating tuberculosis and other infections since the 1940s, while kasugamycin is less known but crucial in agricultural settings ...
Ghent, 29 November 2024 – We are increasingly confronted with the impacts of climate change, with failed harvests being only one example. Addressing these challenges requires multifaceted approaches, including making plants more resilient. An international research team led by researchers at VIB-UGent has unraveled how the opening and closing of stomata - tiny pores on leaves – is regulated in response to high temperatures and drought. These new insights, published in Nature Plants, pave the way for developing climate change-ready crops.
Global climate change affects more and more people, with extreme weather conditions ...
Water can be a catalyst for peace and security with a critical role in preventing conflicts and promoting cooperation among communities and nations - but only if managed equitably and sustainably, a new study reveals.
Experts have devised a blueprint to ensure safe, equitable and sustainable global access to clean water. The seven-point strategy will allow water challenges to be governed effectively so they do not create conflict when access is restricted or usage unfairly shared.
Publishing ...
Ewing sarcoma is a tumour of the bones and soft tissues that occurs in children and young people. A quarter of patients do not respond well to therapy.
The group led by Ana Losada, at Spain’s National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), has discovered an alteration in the most aggressive cases that affects genes never previously related to this disease.
This finding expands the list of potential prognostic markers and therapeutic targets in the most aggressive cases of Ewing sarcoma.
The new research is published in EMBO Reports.
Ewing sarcoma is a tumour of the bones and soft tissues that occurs in children and young people. ...
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest the NOTCH3-associated small vessel disease (NOTCH3-SVD) staging system will help to better harmonize NOTCH3-SVD and cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) cohort studies and registries; may improve individualized disease counseling, monitoring, and clinical management; and may facilitate patient stratification in clinical trials.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding ...
A new study led by King’s College London has provided further evidence that the deaths of 350 African elephants in Botswana during 2020 were the result of drinking from water holes where toxic algae populations had exploded due to climate change.
The lead author of the report says their analysis shows animals were very likely poisoned by watering holes where toxic blooms of blue-green algae, or cyanobacteria, had developed after a very wet year followed a very dry one.
Davide Lomeo, a PhD student in the Department of Geography at King’s College London and co-supervised by Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML) and ...