Age matters: Kidney disorder indicator gains precision
New formula for hyperfiltration and glomerular filtration rate takes natural decline into account
2025-01-06
(Press-News.org)
Annual health checkups regularly include urine tests that serve several purposes, including checking for symptoms of kidney disease. The presence of albumin in the urine is one indicator as is glomerular filtration rate. In diabetic nephropathy, albuminuria first appears, leading to excessive filtration and eventually a decrease in GFR.
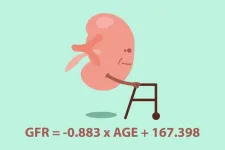
In the elderly, however, excessive filtration cannot be detected due to age-related GFR decline. To accurately assess GFR, Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have come up with a new calculation method.
The group led by Dr. Akihiro Tsuda, a lecturer at the Graduate School of Medicine, assessed 180 kidney transplant donor candidates to define a new formula for determining the threshold value for hyperfiltration based on age and GFR values.
Among other findings, the conventional method of correcting for body surface area in obese patients was determined to be inaccurate as excessive filtration cannot be detected. The researchers suggest calculating GFR without the correction but by taking into account the decline in the filtration rate due to aging.
“Since hyperfiltration is a precursor to diabetic nephropathy, we hope that using this new formula will more accurately diagnose the condition, leading to early detection and treatment,” stated Dr. Tsuda.
The findings were published in Hypertension Research.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-04
A new set of guidelines has been developed to assist with the diagnosis and expert management of serious blood cancers in pregnancy.
About 12.5 pregnancies per 100,000 are affected by blood cancers such as acute leukaemia and aggressive lymphomas, and their incidence has been rising.
Between 1994 and 2013, they increased by 2.7 per cent a year, due to factors including women having children later, improved diagnostic techniques, and increased health system engagement.
An Australian working group has now published a new position statement in the latest edition of The Lancet Haematology, based on current evidence and expert consensus.
It ...
2025-01-03
Biologists at Indiana University Bloomington have shown that the surfaces of plant leaves are coated with a diverse array of RNA molecules. The finding suggests that the RNA present on the leaf surface may play a role in shaping the microbial communities that inhabit them, potentially influencing plant health and interactions within their environment, according to a new study.
The study, Diverse plant RNAs coat Arabidopsis leaves and are distinct from apoplastic RNAs, was published Jan. 3, 2025 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The first authors are Lucía ...
2025-01-03
Urban sprawl is not just unsightly. It could also be impeding intergenerational mobility for low-income residents and reinforcing racial inequality, according to a series of recent studies led by a University of Utah geographer.
One analysis of tract-level Census data co-authored with a former economics graduate student in the U’s College of Social & Behavioral Science found that people who grew up in high-sprawl neighborhoods have less earning potential than those who grew in denser neighborhoods.
“For adults, jobs are harder to access in more sprawling neighborhoods,” said Kelsey Carlston, now an assistant professor of economics at Gonzaga University. “If we ...
2025-01-03
Raymond Y. Huang, MD, Ph.D., of the Department of Radiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is the corresponding author of a paper published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, “Comparative Analysis of Intracranial Response Assessment Criteria in Patients With Melanoma Brain Metastases Treated With Combination Nivolumab + Ipilimumab in CheckMate 204.”
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Our study examines how different imaging criteria can be used to assess brain tumor responses ...
2025-01-03
Go faster, farther, more efficiently.
That’s the goal driving spacecraft propulsion engineers like Chen Cui, a new assistant professor at the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science. Cui is exploring ways to improve electric propulsion thrusters — a key technology for future space missions.
“In order to ensure the technology remains viable for long-term missions, we need to optimize EP integration with spacecraft systems,” Cui said.
Working with his former adviser, University of Southern California professor Joseph Wang, ...
2025-01-03
A new study from UCLA Health adds to the growing body of evidence on the cognitive benefits of speaking multiple languages, finding that multilingualism not only enhances general cognitive abilities but also may help reduce certain symptoms and bolster control of daily thoughts and actions in children with and without autism.
The study, published in the journal Autism Research, found parents of autistic and non-autistic children in multilingual households reported their children had stronger overall executive ...
2025-01-03
Link to full release:
https://www.washington.edu/news/2025/01/03/galaxy-carbon-conveyer-belt/
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
For immediate release
Friday, Jan. 3, 2025
The carbon in our bodies probably left the galaxy and came back on cosmic ‘conveyer belt’
Life on Earth could not exist without carbon. But carbon itself could not exist without stars. Nearly all elements except hydrogen and ...
2025-01-03
Since its discovery in the 1990s, “programmed cell death protein 1,” or PD-1, has been regarded as a leading target in cancer treatments. A “checkpoint” receptor that often resides on the surface of immune system cells, the PD-1 molecule works as a type of off switch that keeps immune cells from attacking other cells.
After its discovery, which revolutionized oncology and earned a 2018 Nobel Prize, researchers developed new drugs to block PD-1 and unleash the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Yet treatments leveraging PD-1 are only effective in a small fraction of cancer patients, highlighting ...
2025-01-03
A NASA X-ray imager is heading to the Moon as part of NASA's Artemis campaign, where it will capture the first global images of the magnetic field that shields Earth from solar radiation.
The Lunar Environment Heliospheric X-ray Imager, or LEXI, instrument is one of 10 payloads aboard the next lunar delivery through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, set to launch from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida no earlier than mid-January, with Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Lander. The instrument will support ...
2025-01-03
Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) have attracted extensive attention due to their high safety, abundant reserves, and environmental friendliness. Iodine with high abundance in seawater (55 μg L−1) is highly promising to fabricate zinc-iodine batteries due to high theoretical capacity (211 mAh g−1) and appropriate redox potential (0.54 V). However, the low electrical conductivity of iodine hinders the redox conversion for the efficient energy storage process with zinc. Additionally, the formed soluble polyiodides are prone to migirate to Zn anode, leading to capacity degration and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Age matters: Kidney disorder indicator gains precision
New formula for hyperfiltration and glomerular filtration rate takes natural decline into account