(Press-News.org) A novel field experiment in Austria reveals that compounding climate conditions – namely drought, warming, and elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2 ) – could fundamentally reshape how water moves through soils in temperate grasslands. The findings provide new insights into post-drought soil water flow, in particular. Soil water, though a minuscule fraction of Earth's total water resources, plays a critical role in sustaining terrestrial life on Earth by regulating biogeochemical cycles, surface energy balance, and plant productivity. Soils also govern the fate of precipitation, directing it back to the atmosphere via evapotranspiration or into surface and groundwater systems, depending on soil water storage and flow properties, such as soil texture and structure. However, droughts – expected to become more frequent and severe under change – could disrupt these crucial processes. Atmospheric warming may increase evapotranspiration and soil water loss, while elevated atmospheric CO2 could reduce transpiration by narrowing plant stomata and conserving soil moisture. Thus, the combined effects of warming and elevated CO2 can produce complex, albeit poorly understood, hydrological outcomes. Grasslands, which cover 30-40% of Earth's land surface, depend heavily on shallow soil water, making them ideal for studying rootzone ecohydrological dynamics.
Jesse Radolinski et al. conducted a novel deuterium (²H) labeling field experiment in a temperate grassland in Austria to examine how elevated atmospheric CO2, warming, and recurring drought – individually and in combination – affect soil water. Radolinski et al. induced experimental drought conditions and then applied 2H-labeled rainfall under ambient and simulated future climate scenarios. According to the findings, elevated CO2 increased rootzone moisture, while warming reduced soil moisture, with soil water remaining well mixed under most conditions. However, combined summer drought, warming, and elevated CO2 drove grassland plants to conserve water by reducing transpiration, which restricted soil water flow to large, rapidly draining pores, limiting mixing with smaller pores. The findings suggest that future drought conditions could fundamentally alter soil water dynamics by limiting post-drought soil water flow and grassland vegetation water use.
END
Compounding drought and climate effects disrupt soil water dynamics in grasslands
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2025-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Multiyear “megadroughts” becoming longer and more severe under climate change
2025-01-16
Severe droughts are becoming hotter, longer, and increasingly devastating to ecosystems as climate change accelerates, according to a new study, which reports that temperate grasslands, including in parts of the United States, are facing the worst effects. The findings provide a global quantitative understanding of multiyear droughts (MYDs) – prolonged events lasting years or decades – and offer a benchmark for understanding their global trends and impacts. As droughts become more frequent ...
Australopithecines at South African cave site were not eating substantial amounts of meat
2025-01-16
Seven Australopithecus specimens uncovered at the Sterkfontein fossil site in South Africa were herbivorous hominins who did not eat substantial amounts of meat, according to a new study by Tina Lüdecke and colleagues. Lüdecke et al. analyzed organic nitrogen and carbonate carbon isotopes extracted from tooth enamel in the fossil specimens to determine the hominin diets. Some researchers have hypothesized that the incorporation of animal-based foods in early hominin diets led to increased brain size, smaller gut size ...
An AI model developed to design proteins simulates 500 million years of protein evolution in developing new fluorescent protein
2025-01-16
Guided by a multimodal generative language model called ESM3, Thomas Hayes and colleagues generated and synthesized a previously unknown bright fluorescent protein, with a genetic sequence so different from known fluorescent proteins that the researchers say its creation is equivalent to ESM3 simulating 500 million years of biological evolution. The model could provide a new way to “search” the space of protein possibilities with an eye to better understanding how naturally evolved proteins work, as well as developing novel proteins for uses in medicine, environmental remediation, and a host of other applications. ESM3 can reason over protein ...
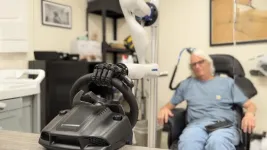
Fine-tuned brain-computer interface makes prosthetic limbs feel more real
2025-01-16
You can probably complete an amazing number of tasks with your hands without looking at them. But if you put on gloves that muffle your sense of touch, many of those simple tasks become frustrating. Take away proprioception — your ability to sense your body’s relative position and movement — and you might even end up breaking an object or injuring yourself.
“Most people don’t realize how often they rely on touch instead of vision — typing, walking, picking up a flimsy cup of water,” said Charles Greenspon, PhD, a neuroscientist at the University of Chicago. “If you can’t feel, you have ...
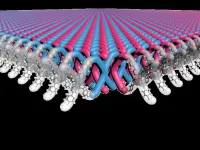
New chainmail-like material could be the future of armor
2025-01-16
EVANSTON, Il. --- In a remarkable feat of chemistry, a Northwestern University-led research team has developed the first two-dimensional (2D) mechanically interlocked material.
Resembling the interlocking links in chainmail, the nanoscale material exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength. With further work, it holds promise for use in high-performance, light-weight body armor and other uses that demand lightweight, flexible and tough materials.
Publishing on Friday (Jan. 17) in the journal ...
The megadroughts are upon us
2025-01-16
Increasingly common since 1980, persistent multi-year droughts will continue to advance with the warming climate, warns a study from the Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow, and Landscape Research (WSL), with Professor Francesca Pellicciotti from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) participating. This publicly available forty-year global quantitative inventory, now published in Science, seeks to inform policy regarding the environmental impact of human-induced climate change. It also detected previously ‘overlooked’ events.
Fifteen years of a persistent, devastating megadrought—the longest lasting in a thousand years—have nearly dried out ...
Eavesdropping on organs: Immune system controls blood sugar levels
2025-01-16
When we think about the immune system, we usually associate it with fighting infections. However, a study published in Science by the Champalimaud Foundation reveals a surprising new role. During periods of low energy—such as intermittent fasting or exercise—immune cells step in to regulate blood sugar levels, acting as the “postman” in a previously unknown three-way conversation between the nervous, immune and hormonal systems. These findings open up new approaches for managing conditions like diabetes, obesity, and cancer.
Rethinking the Immune ...
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors
2025-01-16
The trick to creating a better quantum sensor? Just give it a little squeeze.
For the first time ever, scientists have used a technique called “quantum squeezing” to improve the gas sensing performance of devices known as optical frequency comb lasers. These ultra-precise sensors are like fingerprint scanners for molecules of gas. Scientists have used them to spot methane leaks in the air above oil and gas operations and signs of COVID-19 infections in breath samples from humans.
Now, in a series of lab experiments, researchers have laid out a path for making those kinds of measurements even more sensitive and faster—doubling the speed of ...
New study reveals how climate change may alter hydrology of grassland ecosystems
2025-01-16
New research co-led by the University of Maryland reveals that drought and increased temperatures in a CO2-rich climate can dramatically alter how grasslands use and move water. The study provides the first experimental demonstration of the potential impacts of climate change on water movement through grassland ecosystems, which make up nearly 40% of Earth’s land area and play a critical role in Earth’s water cycle. The study appears in the January 17, 2025, issue of the journal Science.
“If we want to predict the effects of climate change ...
Polymer research shows potential replacement for common superglues with a reusable and biodegradable alternative
2025-01-16
EMBARGO: THIST CONTENT IS UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 2 PM U.S. EASTERN STANDARD TIME ON JANUARY 16, 2025. INTERESTED MEDIA MAY RECIVE A PREVIEW COPY OF THE JOURNAL ARTICLE IN ADVANCE OF THAT DATE OR CONDUCT INTERVIEWS, BUT THE INFORMATION MAY NOT BE PUBLISHED, BROADCAST, OR POSTED ONLINE UNTIL AFTER THE RELEASE WINDOW.
Researchers at Colorado State University and their partners have developed an adhesive polymer that is stronger than current commercially available options while also being biodegradable ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Compounding drought and climate effects disrupt soil water dynamics in grasslandsSummary author: Walter Beckwith