(Press-News.org) Researchers in China have named a newly discovered fish species after the Studio Ghibli character San from Princess Mononoke based on its similar facial markings.
Published in the open-access journal ZooKeys, Branchiostegus sanae is a deepwater tilefish belonging to the family Branchiostegidae. It was discovered when scientists noticed unique cheek pattern on some deepwater tilefish individuals in online seafood markets.
The research team used genetic analysis to confirm the new-species status of the fish, and were inspired by its facial stripes to name it after the female protagonist, San, from Hayao Miyazaki’s animated film Princess Mononoke, choosing “sanae” as the specific epithet.
Additionally, the term “Mononoke” (もののけ) refers to supernatural spirits in Japanese folklore. This aligns with the common name used by Chinese fishermen for this species: “鬼马头鱼” (Ghost Horsehead Fish), a nod to its unusual cheek patterns.
Lead author of the study, Haochen Huang said: “Finding a new species in this group is a rare and fortunate event, especially one as distinctive as Branchiostegus sanae.
“In Princess Mononoke, San is a young woman raised by wolves after being abandoned by her human parents. She sees herself as a part of the forest and fights to protect it. The film delves into the complex relationship between humans and nature, promoting a message of harmonious coexistence between the two: something we hope to echo through this naming.”
As their name suggests, deepwater tilefish are found at great depths, with some species found 600 m below the surface. They are important food fish, commonly found in seafood markets in East and Southeast Asia.
The diversity of the group remains relatively low as only 31 species are described in the family Branchiostegidae, and 19 species in the genus Branchiostegus. Remarkably, from 1990 to 2024, only three new species of Branchiostegus have been described.
The study, led by researchers from the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Science, Zhejiang University and Ocean University of China, involved a combination of morphological analysis and genetic sequencing. Specimens were deposited in prestigious marine biological collections in China to facilitate future research.
Original study
Huang H, Chen J, Ke Z, Zhang C (2025) Branchiostegus sanae, a new species of deepwater tilefish (Eupercaria, Branchiostegidae) from the South China Sea. ZooKeys 1227: 129–142. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.1227.130512
END
New fish species with ‘face paint’ named after Studio Ghibli character
2025-02-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mechanical heart valve replacements have better long-term survival, study finds
2025-02-11
Patients aged between 50 to 70 years with a mechanical heart valve replacement had better long-term survival compared to those with a biological valve, new research led by the University of Bristol has found. The study is published in the European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.
The last two decades have seen an increase in the use of biological over mechanical heart valve replacements. However, while short-term clinical outcomes are known to be the same, long-term outcomes are still under debate.
Existing guidelines support the use of mechanical valves made of synthetic ...
Sandra Diaz and Eduardo Brondízio, scholars of human-nature interconnection, win the 2025 Tyler Prize with call for policies, business models and individuals to recognize humanity’s 'entanglement' wit
2025-02-11
FEBRUARY 11, 2025 – Argentine ecologist Sandra Díaz and Brazilian-American anthropologist Eduardo Brondízio are being awarded the 2025 Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement for their extraordinary work linking biodiversity to humankind, the Tyler Prize Executive Committee announced today.
Díaz and Brondízio are using the win to draw attention to humanity’s “entanglement” with nature in a joint call for policies, business models, and individuals to acknowledge their dependence and shared responsibility in the “fabric of life.”
“The ...
Kessler Foundation in partnership with Overlook Medical Center is first in NJ to implant novel spinal stimulator
2025-02-11
East Hanover & Summit, NJ – February 11, 2025 – The Tim and Caroline Reynolds Center for Spinal Stimulation at Kessler Foundation is proud to announce the implantation of a spinal cord epidural stimulator in an individual with paralysis, marking a significant advancement in spinal cord injury treatment and rehabilitation. The surgical procedure was funded by the Joseph and Cheryl Marino Family Foundation and performed by neurosurgeon Robert F. Heary, MD, at Overlook Medical Center in Summit, NJ, part of Atlantic Health System, home of the Atlantic Neuroscience Institute.
This groundbreaking procedure, ...
Study reveals how physical activity impacts sleep quality in older adults during COVID-19 pandemic
2025-02-11
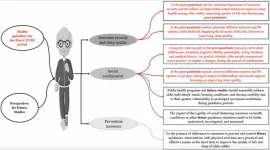
“[…] we found that PA may be associated with the sleep quality of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic and that reduced levels of PA during the COVID-19 pandemic period had a negative association with the quality of sleep of older adults in social isolation.”
BUFFALO, NY—February 11, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 15, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Association between physical activity practice and sleep quality of older people in social isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic and Health Guidelines and future studies ...
ADHD symptoms and later e-cigarette and tobacco use in youths
2025-02-11
About The Study: In this cohort study of U.S. youths, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms were associated with the onset of nicotine and tobacco use. The findings highlight the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment of ADHD to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of later nicotine and tobacco use.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sean Esteban McCabe, PhD, email plius@umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Prepandemic prevalence of dietary supplement use for immune benefits
2025-02-11
About The Study: This study has 3 findings in a prepandemic context. First, approximately 1 in 9 U.S. residents used a dietary supplement for perceived immune benefits (supplements to prevent colds or boost the immune system), and such usage varied by several sociodemographic and health characteristics. Second, label claims related to immune benefits consistently appeared on over half of dietary supplements taken for perceived immune benefits. Lastly, the prevalence of dietary supplement use for perceived immune benefits due to a doctor recommendation and dietary supplement use exclusively for perceived immune benefits were both generally ...
Born to heal: Why babies recover, but adults scar, after heart damage
2025-02-11
Study in experimental animals reveals fundamental differences in how immune system drives healing based on age
Newborn immune systems see, then eat dying cells, triggering production of bioactive lipids
Findings open the door to developing treatments that could ‘reprogram’ adult immune systems
CHICAGO --- Newborns with heart complications can rely on their newly developed immune systems to regenerate cardiac tissues, but adults aren’t so lucky. After a heart attack, most adults struggle to regenerate healthy heart tissue, leading ...
SNU researchers develop soft robot that crawls, climbs, and shape-shifts to move in new directions
2025-02-11
A new type of soft robot can crawl like a worm, climb cables, and suddenly snap into a completely different shape to move in a new direction—all controlled by a single air input. This breakthrough, developed by researchers at Seoul National University, introduces a fundamentally new way for soft robots to move and adapt to their surroundings.
A Leap Forward in Soft Robotics
Soft robots, made from flexible materials, are known for their ability to bend and stretch. However, until now, they struggled to precisely control motion and required complex ...
Mystery solved: New study reveals how DNA repair genes play a major role in Huntington's disease
2025-02-11
A new UCLA Health study has discovered in mouse models that genes associated with repairing mismatched DNA are critical in eliciting damages to neurons that are most vulnerable in Huntington's disease and triggering downstream pathologies and motor impairment, shedding light on disease mechanisms and potential new ways to develop therapies.
Huntington’s disease is one of the most common inherited neurodegenerative disorders that typically begins in adulthood and worsens over time. Patients begin to lose neurons in specific regions of the brain responsible for movement control, motor skill learning, language and ...
Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute announces launch of Center for Sepsis Epidemiology and Prevention Studies (SEPSIS)
2025-02-11
Boston, MA – The Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute is proud to announce the launch of the Center for Sepsis Epidemiology and Prevention Studies (SEPSIS). This pioneering center of excellence is dedicated to advancing understanding, prevention, and management of sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by a dysregulated immune response to infection.
The SEPSIS Center will be led by Dr. Chanu Rhee and Dr. Michael Klompas, internationally recognized leaders in sepsis surveillance, prevention, treatment, and policy. Both serve as faculty at Harvard Medical School and the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute and bring a wealth of expertise and a shared commitment ...