(Press-News.org) By pooling the resources and expertise from alliance members, the initiative addresses common challenges in VR adoption for education, such as high development costs and lack of in-house technical expertise. The module provides a device-agnostic, 3D and 2D-accessible VR experience, enabling immersive learning opportunities for students and executives worldwide. As part of the module, a 20-minute pilot scenario allows users to engage in crisis management exercises, honing their soft skills through interactions with a digital counterpart (avatar). By uniting under a shared mission, individual alliance members’ investment was reduced by more than 85 percent compared to pursuing the project independently.
The VR module was built in partnership with Cornerstone, and key milestones included:
Development and training on a no-code VR authoring tool that enables project members to independently create and expand their own scenarios in the future
Collaborative fine-tuning of learning objectives and avatar performances
Iterative feedback rounds leading to a polished and impactful learning experience
Starting in 2025, the partner schools will conduct institutional pilots that will be accompanied by a shared evaluation framework. Feedback will inform future VR module iterations and potential content expansion. With plans to commercialize these modules, alliance members aim to solidify FOME’s position as a leader in management education innovation. “Through this collaboration, we are not only equipping students with critical soft skills, but also setting new standards for experiential learning in business education,” said FOME alliance chair Professor Steve Muylle, Vlerick Business School. “As the FOME Alliance explores additional opportunities to co-develop and license VR content, this initiative exemplifies the potential of alliances to shape the future of education.”
“The idiom, “practice makes perfect” is difficult to apply day to day in business and academia, because educators or managers are limited in their time and ability to support scaling practical applications, until now,” said Stephen Fromkin, Head of Immersive, Content Strategy & Partnerships at Cornerstone Immerse. “Immersive learning experiences and AI-response experiences help individuals practice, build confidence, and develop skills faster in real-world-like training modules. The FOME Alliance is prioritizing the accessibility and scale of proficiency across their coalition with this initiative and we’re very excited to support them in this mission.”
About FOME
The FOME Alliance comprises 13 of the world’s top business schools. It aims to transform management education through digital tools and pedagogical innovations. Created in 2018, FOME is a global leader in developing and delivering immersive and highly engaging online and hybrid business education experiences. For more information about FOME, please visit https://fomealliance.com/.
About ESMT Berlin
ESMT Berlin is a leading global business school with its campus in the heart of Berlin. Founded by 25 global companies, ESMT offers master, MBA, and PhD programs, as well as executive education on its campus in Berlin, in locations around the world, online, and in online blended format. Focusing on leadership, innovation, and analytics, its diverse faculty publishes outstanding research in top academic journals. Additionally, the international business school provides an interdisciplinary platform for discourse between politics, business, and academia. ESMT is a non-profit private institution of higher education with the right to grant PhDs and is accredited by AACSB, AMBA, EQUIS, and ZEvA. It is committed to diversity, equity, and inclusion across all its activities and communities. esmt.berlin
END
FOME alliance pioneers VR innovation in management education
2025-03-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Evidence expanding that 40Hz gamma stimulation promotes brain health
2025-03-03
A decade after scientists in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT first began testing whether sensory stimulation of the brain’s 40Hz “gamma” frequency rhythms could treat Alzheimer’s disease in mice, a growing evidence base supporting the idea that it can improve brain health—in humans as well as animals—has emerged from the work of labs all over the world. A new review article in PLOS Biology describes the state of research so far and presents some of the fundamental and clinical questions at the forefront of the non-invasive gamma stimulation now.
“As ...
Teaching kids how to become better citizens
2025-03-03
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In our polarized society, a new study offers hope for the future: Even young children can learn to discuss and argue about meaningful problems in a respectful and productive way.
Researchers at The Ohio State University found success in a social studies curriculum for fourth graders based on teaching what they called “civic competencies.”
Over the course of a school year, findings showed that the students participating in the curriculum significantly improved their argumentation skills and disciplinary thinking.
“This will give them the ability to collaborate, communicate effectively and consider multiple perspectives”, ...
Pusan National University researchers develop a novel 3D adipose tissue bioprinting method
2025-03-03
The adipose tissue, which serves as an endocrine organ, releases various molecules that regulate the repair of other damaged tissues, including the skin. Hence, adipose tissues can potentially be reengineered to regenerate the damaged organs. Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting technology has revolutionized regenerative medicine by enabling the generation of engineered and functional 3D organs or tissues, including adipose tissues. However, the currently used tissue biofabrication methods cannot replicate ...
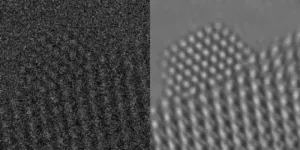
Scientists use AI to better understand nanoparticles
2025-03-03
A team of scientists has developed a method to illuminate the dynamic behavior of nanoparticles, which are foundational components in the creation of pharmaceuticals, electronics, and industrial and energy-conversion materials. The advance, reported in the journal Science, combines artificial intelligence with electron microscopy to render visuals of how these tiny bits of matter respond to stimuli.
“Nanoparticle-based catalytic systems have a tremendous impact on society,” explains Carlos Fernandez-Granda, director of NYU’s Center for Data Science and a professor of mathematics and data science, one of the paper’s authors. “It is estimated that 90 percent ...
We feed gut microbes sugar, they make a compound we need
2025-03-03
Gut microbes that were thought to feed exclusively on dietary fiber also get fed sugar from our guts, from which they produce short-chain fatty acids that are crucial to many body functions. The Kobe University discovery of this symbiotic relationship also points the way to developing novel therapeutics.
Gut microbes produce many substances that our body needs but cannot produce itself. Among them are short-chain fatty acids that are the primary energy source for the cells lining our guts but have other important roles, too, and ...
One of the largest psychotherapy trials in the world has implications for transforming mental health care during pregnancy and after birth
2025-03-03
Approximately one in five of pregnant and postpartum individuals experience depression and anxiety, yet less than 10 per cent receive proper treatment.
To address this problem, a team of interdisciplinary researchers from Canada and the United States investigated if talk therapy can be effectively delivered by non-mental health specialists and telemedicine to increase access. In a paper published today in Nature Medicine, they share results from the Scaling Up Maternal Mental health care by Increasing access to Treatment (SUMMIT) Trial, which reveals promising strategies to provide the necessary support and treatment more effectively and inclusively ...
It’s not just what you say – it’s also how you say it
2025-03-03
EVANSTON, Ill. --- You’ve probably heard the phrase, “It’s not what you say, it’s how you say it,” and now, science backs it up. A first-of-its-kind study from Northwestern University’s School of Communication, the University of Pittsburgh and the University of Wisconsin-Madison reveals a region of the brain, long known for early auditory processing, plays a far greater role in interpreting speech than previously understood.
The multidisciplinary study being published Monday, March ...
Sleep patterns may reveal comatose patients with hidden consciousness
2025-03-03
NEW YORK, NY (March 3, 2025)--Several studies in the past decade have revealed that up to a quarter of unresponsive patients with recent brain injuries may possess a degree of consciousness that’s normally hidden from their families and physicians.
New research from Columbia University and NewYork-Presbyterian may soon help physicians identify unresponsive brain-injury patients with hidden consciousness who are likely to achieve long-term recovery by looking for brain waves that are indicative of normal sleep patterns.
“We’re at an exciting crossroad in neurocritical care where we know that many patients appear to be unconscious, but some are recovering without ...
3D genome structure guides sperm development
2025-03-03
Two new landmark studies show how a seeming tangle of DNA is actually organized into a structure that coordinates thousands of genes to form a sperm cell. The work, published March 3 as two papers in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, could improve treatment for fertility problems and developmental disorders.
“We are finding the 3D structure of the genome,” said Satoshi Namekawa, professor of microbiology and molecular genetics at the University of California, Davis and senior author on one of the papers. “This is really showing us how the genomic architecture guides development.”
Although DNA is a long, stringy molecule, in living ...
Certain genetic alterations may contribute to the primary resistance of colorectal and pancreatic cancers to KRAS G12C inhibitors
2025-03-03
Bottom Line: Colorectal cancer and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma that harbored the KRAS G12C mutation often carried other genetic alterations that can be associated with resistance to KRAS G12C inhibitors, despite no prior treatment with this therapy, according to recent results from a large multidatabase analysis.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Hao Xie, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center
Background: “The KRAS pathway plays a crucial role in cell biology by regulating ...