(Press-News.org) Two new landmark studies show how a seeming tangle of DNA is actually organized into a structure that coordinates thousands of genes to form a sperm cell. The work, published March 3 as two papers in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, could improve treatment for fertility problems and developmental disorders.
“We are finding the 3D structure of the genome,” said Satoshi Namekawa, professor of microbiology and molecular genetics at the University of California, Davis and senior author on one of the papers. “This is really showing us how the genomic architecture guides development.”
Although DNA is a long, stringy molecule, in living cells it is folded and looped like a ball of yarn. This means that genes can be physically close to the “enhancer” DNA switches that turn them on and off even if they are far apart in the DNA sequence.
To understand how genes are turned on and off to make different cell types, you have to figure out how the DNA is folded – and which genes and enhancers are paired together.
The memories of cells
In a mouse or human embryo, the cells that will one day produce sperm or eggs are already earmarked for that future purpose, Namekawa said.
These primordial germ cells are initially “bipotent” — able to become either sperm or eggs. But while the embryo is still snug in the womb, its bipotent cells commit to one path or another and once they cross that threshold, they cannot go back.
“Cells have a sort of memory,” Namekawa said. “But we don’t know how that memory works. We are trying to understand how this male fate is acquired.”
Namekawa and his students used a technique called “Hi-C” to identify the proximity junctions where far-flung parts of the genome are paired up next to one another. Using a computer to analyze those paired locations, Namekawa was able to see how the entire string of DNA is looped and folded.
Bookmarking the genome
In the new studies, UC Davis postdoctoral fellow Yuka Kitamura identified two proteins in germ cells that establish this cellular memory. The first, called SCML2, disconnects junctions and allows the DNA to unfold and loosen, preparing it to be reorganized in the next stage of sperm cell development.
Another protein, CTCF, attaches to locations of super-enhancer DNA and pairs them up with genes that they will later turn on during sperm development. This sets up a new structure that cements the cell’s future fate as a sperm cell.
The companion paper shows that well before the germ cells enter meiosis, CTCF and other proteins bookmark thousands of locations in the genome. This paper was led by postdoctoral fellow Chongil Yi and Bradley Cairns, professor and chair of oncological sciences at the University of Utah School of Medicine and an investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. It was published in collaboration with Namekawa and Kitamura.
These discoveries could have important medical implications, including diagnostic tests for causes of infertility linked to genome folding.
The discoveries could also help scientists working on stem cell therapies, since coaxing a stem cell to become a neuron or heart cell requires shifting it from one genetic program to another – each defined by a particular 3D genome structure.
“We are uncovering the language of cell memory and cell fate,” Namekawa said. “It’s really exciting.”
The work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
END
3D genome structure guides sperm development
Knowing how the genome folds to turn genes on and off could improve our understanding of fertility and developmental disorders
2025-03-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Certain genetic alterations may contribute to the primary resistance of colorectal and pancreatic cancers to KRAS G12C inhibitors
2025-03-03
Bottom Line: Colorectal cancer and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma that harbored the KRAS G12C mutation often carried other genetic alterations that can be associated with resistance to KRAS G12C inhibitors, despite no prior treatment with this therapy, according to recent results from a large multidatabase analysis.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Hao Xie, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center
Background: “The KRAS pathway plays a crucial role in cell biology by regulating ...
Melting Antarctic ice sheets will slow Earth’s strongest ocean current
2025-03-03
Melting ice sheets are slowing the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), the world’s strongest ocean current, researchers have found.
This melting has implications for global climate indicators, including sea level rise, ocean warming and viability of marine ecosystems.
The researchers, from the University of Melbourne and NORCE Norway Research Centre, have shown the current slowing by around 20 per cent by 2050 in a high carbon emissions scenario.
This influx of fresh water into the Southern Ocean is expected to change ...
Hallucinogen use linked to 2.6-fold increase in risk of death for people needing emergency care
2025-03-03
People seeking emergency care for hallucinogen use were at 2.6-fold higher risk of death within 5 years than the general population, according to a new study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241191.
The use of hallucinogens, such as ketamine, psychedelics, psilocybin, LSD, ayahuasca, and MDMA (Ecstasy), has rapidly increased since the mid-2010s, especially in Canada and the United States. In the US, the percentage of people reporting they used hallucinogens more than doubled from 3.8% in 2016 to 8.9% in 2021. “In Canada, an estimated 5.9% of people used a psychedelic ...
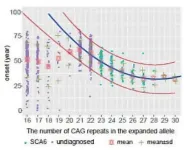
Pathogenicity threshold of SCA6 causative gene CACNA1A was identified
2025-03-03
Niigata, Japan - The Department of Neurology at Niigata University and National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry(NCNP) has identified pathogenic thresholds for the CAG repeat units (RU) of the CACNA1A gene that causes SCA6. They investigated the SCA6 causative gene in 2,768 patients. They carefully examined the relationship between RU, age of onset, and family history. First, in cases with 18 or fewer RU, the proportion of family history was low. For 19 or more RU, the proportion of family history ...
Mysterious interstellar icy objects
2025-03-03
Niigata, Japan - Organic molecules that serve as the building blocks of life are believed to form in space, but their exact formation sites and delivery mechanisms to planets remain a major mystery in astronomy and planetary science. One of the key elements in solving this mystery is the presence of ice in interstellar environments. In cold, dense, and shielded regions of the galaxy, atoms and molecules adhere to the surfaces of submicron-sized solid particles (dust), leading to the formation of interstellar ices. This process is similar to how snow forms in Earth’s clouds.
Astronomers from Niigata University and ...
Chronic diseases misdiagnosed as psychosomatic can lead to long term damage to physical and mental wellbeing, study finds
2025-03-03
A ‘chasm of misunderstanding and miscommunication’ is often experienced between clinicians and patients, leading to autoimmune diseases such as lupus and vasculitis being wrongly diagnosed as psychiatric or psychosomatic conditions, with a profound and lasting impact on patients, researchers have found.
A study involving over 3,000 participants – both patients and clinicians – found that these misdiagnoses (sometimes termed “in your head” by patients) were often associated with long term impacts on patients’ physical health and wellbeing and damaged trust in healthcare services.
The researchers are calling for greater awareness ...
Omalizumab treats multi-food allergy better than oral immunotherapy
2025-03-02
A clinical trial has found that the medication omalizumab, marketed as Xolair, treated multi-food allergy more effectively than oral immunotherapy (OIT) in people with allergic reactions to very small amounts of common food allergens. OIT, the most common approach to treating food allergy in the United States, involves eating gradually increasing doses of a food allergen to reduce the allergic response to it. Thirty-six percent of study participants who received an extended course of omalizumab could tolerate 2 grams or more of peanut protein, or about eight peanuts, and two other ...
Sleep apnea linked to increased risk of Parkinson’s, but CPAP may reduce risk
2025-03-02
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 2, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Sleep apnea linked to increased risk of Parkinson’s, but CPAP may reduce risk
Risk reduced if treatment started within two years of diagnosis
MINNEAPOLIS – People with obstructive sleep apnea have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease, but if started early enough, continuous positive airway pressure ...
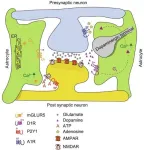
New insights into drug addiction: The role of astrocytic G protein-coupled receptors
2025-03-02
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the complex mechanisms of drug addiction, highlighting the crucial role of astrocytic G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). This research offers fresh perspectives on understanding and potentially treating substance-use disorders (SUDs).
For a long time, neuroscience research on drug addiction mainly focused on neuronal mechanisms. However, emerging evidence shows that astrocytes, the most abundant glial cells in the central nervous system, also play a significant part. Astrocytes ...
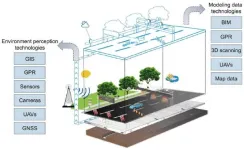
Digital twin technology: Transforming road engineering and its lifecycle applications
2025-03-02
A recent study published in the journal Engineering delves into the potential of digital twin (DT) technology in revolutionizing road engineering and its lifecycle applications. As road infrastructure worldwide faces the challenge of digitalization, DT has emerged as a promising solution.
The research, conducted by a team of scholars from Tongji University and Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), systematically reviews DT-enabling technologies, including model creation, condition sensing, data processing, and interaction. The development of DT in road engineering has been ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] 3D genome structure guides sperm developmentKnowing how the genome folds to turn genes on and off could improve our understanding of fertility and developmental disorders