(Press-News.org) Melting ice sheets are slowing the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), the world’s strongest ocean current, researchers have found.
This melting has implications for global climate indicators, including sea level rise, ocean warming and viability of marine ecosystems.
The researchers, from the University of Melbourne and NORCE Norway Research Centre, have shown the current slowing by around 20 per cent by 2050 in a high carbon emissions scenario.
This influx of fresh water into the Southern Ocean is expected to change the properties, such as density (salinity), of the ocean and its circulation patterns.
University of Melbourne researchers, fluid mechanist Associate Professor Bishakhdatta Gayen and climate scientist Dr Taimoor Sohail, and oceanographer Dr Andreas Klocker from the NORCE Norwegian Research Centre, analysed a high-resolution ocean and sea ice simulation of ocean currents, heat transport and other factors to diagnose the impact of changing temperature, saltiness and wind conditions.
Associate Professor Gayen said: “The ocean is extremely complex and finely balanced. If this current ‘engine’ breaks down, there could be severe consequences, including more climate variability, with greater extremes in certain regions, and accelerated global warming due to a reduction in the ocean’s capacity to act as a carbon sink.”
The ACC works as a barrier to invasive species, like rafts of southern bull kelp that ride the currents, or marine-borne animals like shrimp or molluscs, from other continents reaching Antarctica.
As the ACC slows and weakens, there is a higher likelihood such species will make their way onto the fragile Antarctic continent, with a potentially severe impact on the food web, which may, for example, change the available diet of Antarctic penguins.
More than four times stronger than the gulf stream, the ACC is a crucial part of the world’s “ocean conveyor belt”, which moves water around the globe – linking the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans – and is the main mechanism for the exchange of heat, carbon dioxide, chemicals and biology across these ocean basins.
The researchers used Australia’s fastest supercomputer and climate simulator, GADI, located at Access National Research Infrastructure in Canberra. The underlying model (ACCESS-OM2-01) has been developed over a number of years by Australian researchers from various universities.
The projections explored in this analysis were conducted by a research team based at UNSW, who found that the transport of ocean water from the surface to the deep may also slow in the future.
Dr Sohail said it is predicted that the slow-down will be similar under the lower emissions scenario, provided ice melting accelerates as predicted in other studies.
“The 2015 Paris Agreement aimed to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Many scientists agree that we have already reached this 1.5 degree target, and it is likely to get hotter, with flow-on impacts on Antarctic ice melting,” Dr Sohail said.
“Concerted efforts to limit global warming (by reducing carbon emissions) will limit Antarctic ice melting, averting the projected ACC slowdown.”
Published in Environmental Research Letters today, the research reveals that the impact of ice melting and ocean warming on the ACC is more complex than previously thought.
“The melting ice sheets dump vast quantities of fresh water into the salty ocean. This sudden change in ocean ‘salinity’ has a series of consequences – including the weakening of the sinking of surface ocean water to the deep (called the Antarctic Bottom Water), and, based on this study, a weakening of the strong ocean jet that surrounds Antarctica,” Associate Professor Gayen said.
The new research contrasts with previous studies that suggested the ACC may be accelerating due to steeper temperature differences in different latitudes of the ocean caused by climate change, he says.
“Ocean models have historically been unable to adequately resolve the small-scale processes that control current strength. This model resolves such processes, and shows a mechanism through which the ACC is projected to actually slow down in the future. However, further observational and modelling studies of this poorly-observed region are necessary to definitively discern the current’s response to climate change.”
END
Melting Antarctic ice sheets will slow Earth’s strongest ocean current
Melting ice sheets are slowing the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), the world’s strongest ocean current, researchers have found.
2025-03-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hallucinogen use linked to 2.6-fold increase in risk of death for people needing emergency care
2025-03-03
People seeking emergency care for hallucinogen use were at 2.6-fold higher risk of death within 5 years than the general population, according to a new study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241191.
The use of hallucinogens, such as ketamine, psychedelics, psilocybin, LSD, ayahuasca, and MDMA (Ecstasy), has rapidly increased since the mid-2010s, especially in Canada and the United States. In the US, the percentage of people reporting they used hallucinogens more than doubled from 3.8% in 2016 to 8.9% in 2021. “In Canada, an estimated 5.9% of people used a psychedelic ...
Pathogenicity threshold of SCA6 causative gene CACNA1A was identified
2025-03-03
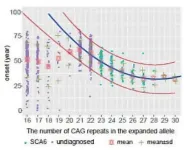
Niigata, Japan - The Department of Neurology at Niigata University and National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry(NCNP) has identified pathogenic thresholds for the CAG repeat units (RU) of the CACNA1A gene that causes SCA6. They investigated the SCA6 causative gene in 2,768 patients. They carefully examined the relationship between RU, age of onset, and family history. First, in cases with 18 or fewer RU, the proportion of family history was low. For 19 or more RU, the proportion of family history ...
Mysterious interstellar icy objects
2025-03-03
Niigata, Japan - Organic molecules that serve as the building blocks of life are believed to form in space, but their exact formation sites and delivery mechanisms to planets remain a major mystery in astronomy and planetary science. One of the key elements in solving this mystery is the presence of ice in interstellar environments. In cold, dense, and shielded regions of the galaxy, atoms and molecules adhere to the surfaces of submicron-sized solid particles (dust), leading to the formation of interstellar ices. This process is similar to how snow forms in Earth’s clouds.
Astronomers from Niigata University and ...
Chronic diseases misdiagnosed as psychosomatic can lead to long term damage to physical and mental wellbeing, study finds
2025-03-03
A ‘chasm of misunderstanding and miscommunication’ is often experienced between clinicians and patients, leading to autoimmune diseases such as lupus and vasculitis being wrongly diagnosed as psychiatric or psychosomatic conditions, with a profound and lasting impact on patients, researchers have found.
A study involving over 3,000 participants – both patients and clinicians – found that these misdiagnoses (sometimes termed “in your head” by patients) were often associated with long term impacts on patients’ physical health and wellbeing and damaged trust in healthcare services.
The researchers are calling for greater awareness ...
Omalizumab treats multi-food allergy better than oral immunotherapy
2025-03-02
A clinical trial has found that the medication omalizumab, marketed as Xolair, treated multi-food allergy more effectively than oral immunotherapy (OIT) in people with allergic reactions to very small amounts of common food allergens. OIT, the most common approach to treating food allergy in the United States, involves eating gradually increasing doses of a food allergen to reduce the allergic response to it. Thirty-six percent of study participants who received an extended course of omalizumab could tolerate 2 grams or more of peanut protein, or about eight peanuts, and two other ...
Sleep apnea linked to increased risk of Parkinson’s, but CPAP may reduce risk
2025-03-02
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 2, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Sleep apnea linked to increased risk of Parkinson’s, but CPAP may reduce risk
Risk reduced if treatment started within two years of diagnosis
MINNEAPOLIS – People with obstructive sleep apnea have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease, but if started early enough, continuous positive airway pressure ...
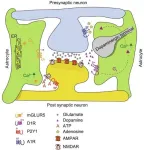
New insights into drug addiction: The role of astrocytic G protein-coupled receptors
2025-03-02
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the complex mechanisms of drug addiction, highlighting the crucial role of astrocytic G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). This research offers fresh perspectives on understanding and potentially treating substance-use disorders (SUDs).
For a long time, neuroscience research on drug addiction mainly focused on neuronal mechanisms. However, emerging evidence shows that astrocytes, the most abundant glial cells in the central nervous system, also play a significant part. Astrocytes ...
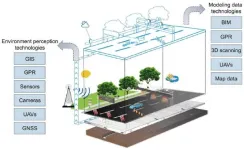
Digital twin technology: Transforming road engineering and its lifecycle applications
2025-03-02
A recent study published in the journal Engineering delves into the potential of digital twin (DT) technology in revolutionizing road engineering and its lifecycle applications. As road infrastructure worldwide faces the challenge of digitalization, DT has emerged as a promising solution.
The research, conducted by a team of scholars from Tongji University and Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), systematically reviews DT-enabling technologies, including model creation, condition sensing, data processing, and interaction. The development of DT in road engineering has been ...
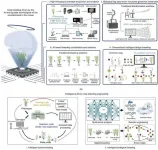
Next-generation AI and big data: Transforming crop breeding
2025-03-01
A new study published in Engineering explores how next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) and big data are revolutionizing crop breeding, with potential far-reaching implications for global food security.
Crop breeding has come a long way, evolving through distinct stages from domestication breeding to the current era of big data intelligent design breeding. The latest stage, “Breeding 4.0,” integrates biotechnology, big data, and AI. This convergence aims to achieve efficient, personalized breeding of new crop varieties, marking a significant shift from traditional “scientific” ...
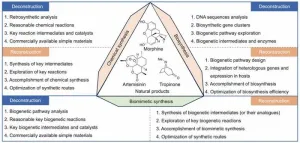
Biomimetic synthesis of natural products: Progress, challenges and prospects
2025-03-01
In a recent publication in Engineering, researchers from Jinan University in China and the University of Illinois Chicago in the US presented an in-depth perspective on the biomimetic synthesis of natural products. This research area, which bridges chemistry, biology, and pharmacy, has seen significant progress in recent years.
Natural products are crucial in drug discovery, providing essential scaffolds for developing new medications. However, obtaining sufficient quantities of these compounds for research and production is challenging due to resource limitations. Traditional chemical synthesis and biosynthesis methods also face their own set of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] Melting Antarctic ice sheets will slow Earth’s strongest ocean currentMelting ice sheets are slowing the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), the world’s strongest ocean current, researchers have found.