(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this retrospective multi-institutional study, patients who underwent surgery immediately preceding the weekend had a significantly increased risk of complications, readmissions, and mortality compared with those treated after the weekend. Further study is needed to understand differences in care that may underpin these observations and ensure that patients receive high-quality care regardless of the day of the week.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Raj Satkunasivam, M.D., M.S., email raj.satkunasivam@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.58794)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.58794?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=030425
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Postoperative outcomes following preweekend surgery
JAMA Network Open
2025-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nearly 4 of 10 Americans report sports-related mistreatment
2025-03-04
Nearly 40% of adult Americans say they’ve experienced some type of sport-related mistreatment in their lives, a new study shows.
Mistreatment ranged from psychological and emotional to physical and sexual. But most people who reported mistreatment experienced more than one kind, the research found.
And one-third of those who never even played organized sports reported sports-related mistreatment.
“Many people talk about how they hated middle school or high school because of recess or gym class and the abuse or shame they felt playing sports in that environment,” said Chris Knoester, co-author of the study and professor of sociology ...
School absence patterns could ID children with chronic GI disorders, research suggests
2025-03-04
Children who frequently miss school because of abdominal complaints are far more likely to be suffering from disorders of the gut-brain axis such as irritable bowel syndrome than diseases that can be detected with medical tests, new UVA Health Children’s research has found. The discovery could improve care for children with these common GI disorders and might spare them from a barrage of unproductive tests.
UVA’s Stephen M. Borowitz, MD, and fourth-year medical student Seth M. Tersteeg looked at school absenteeism as reported by parents who brought their children to UVA Health Children’s Pediatric Gastroenterology Clinic. Children who had missed more ...
Mount Sinai researchers identify molecular glues that protect insulin-producing cells from damage related to diabetes
2025-03-04
Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York have discovered a novel approach to protecting insulin-producing beta cells from the damaging effects of glucolipotoxicity—a harmful condition linked to the progression of type 2 diabetes (T2D). These findings, published on March 2, 2025 in Nature Communications, could lead to promising treatments targeting beta cell dysfunction.
For patients, this research could lead to new treatments that protect the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, potentially ...
Study: Smartwatches could end the next pandemic
2025-03-04
Everyday smartwatches are extremely accurate in detecting viral infection long before symptoms appear — now, research shows how they could help stop a pandemic before it even begins.
Early detection of sickness is critical for preventing its spread — whether it’s COVID-19, influenza or the common cold. Yet, many illnesses are at their most contagious before people even know they’re sick. Research shows that 44 percent of COVID-19 infections were spread several days before the sufferer came down with symptoms.
Now, researchers at Aalto University, Stanford University and Texas A&M, have released a study that models how smartwatches ...
Equal distribution of wealth is bad for the climate
2025-03-04
Both the UN and several Nobel laureates have said that political and economic inequality is a driver of high carbon emissions.
The argument is that more democratic societies – where wealth, power and opportunities are more evenly distributed – are better at reducing their emissions.
But that is not true – quite the opposite.
“Some people hold that a rich power elite stands in the way of climate action, and that democracies can more easily implement measures such as banning emissions or raising taxes,” said Professor Indra de Soysa from the Norwegian ...
Evidence-based strategies improve colonoscopy bowel preparation quality, performance, and patient experience
2025-03-04
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
Tuesday, March 4, 2025 at 9:00 am Eastern Time
An advanced copy of the full recommendation is available upon request.
Media Contacts
American College of Gastroenterology
Becky Abel mediaonly@gi.org (301) 263-9000
American Gastroenterological Association
Annie Mehl communications@gastro.org (301) 272-0013
American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Andrea Lee alee@asge.org (630) 570-5601
North Bethesda, MD; Bethesda, MD; and Downers Grove, IL (March 4, 2025) ...
E. (Sarah) Du, Ph.D., named Senior Member, National Academy of Inventors
2025-03-04
E. (Sarah) Du, Ph.D., an associate professor in College of Engineering and Computer Science at Florida Atlantic University, has been selected as a Senior Member of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) for her significant contributions to innovation and invention.
The NAI is a member organization comprising United States and international universities, government agencies, and nonprofit research institutes. The NAI was founded to recognize and encourage inventors with U.S. patents, enhance the visibility of academic ...
Study establishes “ball and chain” mechanism inactivates key mammalian ion channel
2025-03-04
A new study has unveiled a precise picture of how an ion channel found in most mammalian cells regulates its own function with a “ball-and-chain” channel-plugging mechanism, according to investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine. The findings boost the understanding of ion channel biology and could lead to new drugs that target these channels to treat disorders such as epilepsy and hypertension.
Ion channels are protein structures embedded in cell membranes that allow charged molecules to flow into or out of the cell. They support essential biological functions, including signaling or communication between brain cells. The study, published ...
Dicamba drift: New use of an old herbicide disrupts pollinators
2025-03-04
March 4, 2025
Contact: Morgan Sherburne, 734-647-1844, morganls@umich.edu
Images of pollinators and plants
ANN ARBOR—An herbicide may "drift" from the agricultural fields where it's sprayed and harm weeds that grow at the edge of the fields, impacting pollinators.
A University of Michigan study examined the effects of the herbicide, called dicamba, and found that plants exposed to dicamba drift had a lowered abundance of pollinators, and that pollinator visits to flowers were reduced for some weeds, but not others. The study, led by U-M professor of ecology and evolutionary biology Regina Baucom, ...
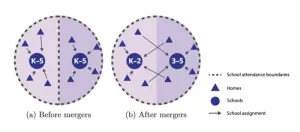
Merging schools to reduce segregation
2025-03-04
Racial segregation remains common in US schools, 70 years after federal legislation formally outlawing segregation by race. But previous research has demonstrated that integration can benefit students of all races and ethnicities. Students at integrated schools learn how to make connections with children from different backgrounds, developing empathy and mutual respect. Madison Landry and Nabeel Gillani explored whether merging schools could help integrate schools. One school could offer kindergarten through second grade for the current catchment areas of two elementary schools, while the remaining school could serve third through fifth graders for the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Postoperative outcomes following preweekend surgeryJAMA Network Open