(Press-News.org) AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
Article URL: https://plos.io/4baFCW5
Article title: AI-determined similarity increases likability and trustworthiness of human voices
Author countries: Germany
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
END
AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
2025-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during
2025-03-05
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during the Pliocene or Miocene epochs
Article URL: https://plos.io/4gQHlB2
Article title: Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes of Theobroma cacao from northern Peru
Author countries: Perú
Funding: This study was supported by the Programa Nacional de Investigación Científica y Estudios Avanzados (PROCIENCIA) funded by the Project through the Contract N° 026-2016-FONDECYT “Círculo de Investigación ...
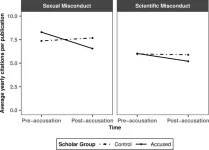
After sexual misconduct accusations, scholars’ work is cited less
2025-03-05
In a new analysis, scholars publicly accused of sexual misconduct experienced a significant decrease in the rate at which other scholars cited their published research. Giulia Maimone of the University of California, Los Angeles, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on March 5, 2025.
In academia, scholars cite other scholars’ publications as a widely agreed-upon way to reference existing research and promote scientific advancement. A scholar with a high number of citations may be considered particularly impactful in their field. Prior research ...
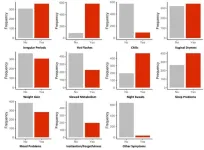
Menopause symptoms associated with future memory and neuropsychiatric problems
2025-03-05
Women who exhibit more menopausal symptoms are more likely to later have poorer cognitive function and mild behavioral impairments – both markers of dementia. That is the conclusion of a study of 896 postmenopausal females published March 5, 2025, in the open-access journal PLOS One by Zahinoor Ismail of University of Calgary, Canada, and colleagues.
Females are known to have a three-fold greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, and will be disproportionately ...
Findings may advance understanding of infertility in mothers
2025-03-05
Oxytocin, a hormone already known for its role in childbirth, milk release, and mother-infant bonding, may have a newfound purpose in mammalian reproduction. In times of maternal stress, the hormone can delay an embryo’s development for days to weeks after conception, a new study in rodents shows. According to the authors, the findings about so-called “diapause” may offer new insights into pregnancy and fertility issues faced by humans.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the study explored diapause, in which an embryo temporarily stops growing early in ...
Engineered cartilage from nasal septum cells helps treat complex knee injuries
2025-03-05
Injuries to the articular cartilage in different joints, including the knee, are painful and limit mobility. Therefore, researchers at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel are developing cartilage implants using cells from the patient’s nasal septum. A recent study shows that giving these cartilage implants more time to mature significantly improved clinical efficacy, even in patients with complex cartilage injuries. This suggests that the method could also be suitable for the treatment of degenerated cartilage in osteoarthritis.
An unlucky fall while skiing or playing ...
Damaged but not defeated: Bacteria use nano-spearguns to retaliate against attacks
2025-03-05
Some bacteria deploy tiny spearguns to retaliate against rival attacks. Researchers at the University of Basel mimicked attacks by poking bacteria with an ultra-sharp tip. Using this approach, they have uncovered that bacteria assemble their nanoweapons in response to cell envelope damage and rapidly strike back with high precision.
In the world of microbes, peaceful coexistence goes hand in hand with fierce competition for nutrients and space. Certain bacteria outcompete rivals and fend off attackers by injecting them with a lethal cocktail using tiny, ...
Among older women, hormone therapy linked to tau accumulation, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease
2025-03-05
A new study from Mass General Brigham researchers has found faster accumulation of tau—a key indicator of Alzheimer’s disease—in the brains of women over the age of 70 who took menopausal hormone therapy (HT) more than a decade before. Results, which are published in Science Advances, could help inform discussions between patients and clinicians about Alzheimer’s disease risk and HT treatment.
While the researchers did not see a significant difference in amyloid beta accumulation, they did find a significant difference in how fast regional tau accumulated in the brains of women over the age of 70, with women who had taken HT showing faster tau accumulation ...
Scientists catch water molecules flipping before splitting
2025-03-05
For the first time, Northwestern University scientists have watched water molecules in real-time as they prepared to give up electrons to form oxygen.
In the crucial moment before producing oxygen, the water molecules performed an unexpected trick: They flipped.
Because these acrobatics are energy intensive, the observations help explain why water splitting uses more energy than theoretical calculations suggest. The findings also could lead to new insights into increasing the efficiency of water splitting, a process that holds promise for generating clean hydrogen fuel and for producing breathable oxygen during future missions to Mars.
The study will be published Wednesday (March 5) ...
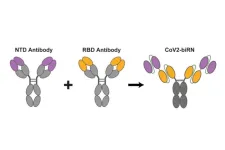
New antibodies show potential to defeat all SARS-CoV-2 variants
2025-03-05
The virus that causes COVID-19 has been very good at mutating to keep infecting people – so good that most antibody treatments developed during the pandemic are no longer effective. Now a team led by Stanford University researchers may have found a way to pin down the constantly evolving virus and develop longer-lasting treatments.
The researchers discovered a method to use two antibodies, one to serve as a type of anchor by attaching to an area of the virus that does not change very much and another to inhibit the virus’s ability ...
Mental health may be linked to how confident we are of our decisions
2025-03-05
A new study finds that a lower confidence in one’s judgement of decisions based on memory or perception is more likely to be apparent in individuals with anxiety and depression symptoms, whilst a higher confidence is more likely to be associated compulsivity, thus shedding light on the intricate link between cognition and mental health manifestations.
####
Article Title: Metacognitive biases in anxiety-depression and compulsivity extend across perception and memory
Author Countries: Germany, United Kingdom
Funding: TXFS is a Sir Henry Wellcome Postdoctoral Fellow (224051/Z/21/Z) based at the Max Planck UCL Centre for Computational Psychiatry ...