(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS — Some people living with chronic stress have a higher risk of stroke, according to a study published on March 5, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study looked at younger adults and found an association between stress and stroke, with no known cause, in female participants, but not male participants. This study does not prove that stress causes stroke; it only shows an association.
“Younger people often experience stress due to the demands and pressures associated with work, including long hours and job insecurity, as well as financial burdens,” said Nicolas Martinez-Majander, MD, PhD, of the Helsinki University Hospital in Finland. “Previous research has shown that chronic stress can negatively affect physical and mental health. Our study found it may increase the risk of stroke in younger women.”
For the study, researchers looked at 426 people aged 18 to 49 who had an ischemic stroke with no known cause. They were matched for age and sex with 426 people who did not have stroke. Ischemic stroke is when blood flow is blocked to part of the brain. It can lead to weakness, trouble speaking, vision problems or even death.
Participants completed a questionnaire about stress levels over a one-month period. Those with stroke were asked after their stroke to record stress levels in the month prior to their stroke. Participants were asked 10 questions, such as “In the last month, how often have you felt that you were unable to control the important things in your life?” Scores for each question ranged from zero to four, with four meaning “very often.” A total score of 0 to 13 represented low stress; 14 to 26, moderate stress; and 27 to 40, high stress. Those with stroke had an average score of 13 compared to those without stroke who had an average score of 10.
People with stroke were more likely to have at least moderate stress levels. Of those with stroke, 46% had moderate or high stress levels compared to 33% of those who did not have stroke.
After adjusting for factors that could affect risk of stroke such as education level, alcohol use and blood pressure, researchers found for female participants, moderate stress was associated with a 78% increased risk of stroke and high stress was associated with a 6% increased risk. Researchers did not find a link between stress and stroke in male participants.
“More research is needed to understand why women who feel stressed, but not men, may have a higher risk of stroke,” said Martinez-Majander. “In addition, we need to further explore why the risk of stroke in women was higher for moderate stress than high stress. Knowing more about how stress plays a role could help us to create better ways to prevent these strokes.”
A limitation of the study was that people experiencing higher levels of stress may have been less likely to enroll in the study, which could have affected the results.
The study was supported by the Helsinki and Uusimaa Hospital District, Academy of Finland, The Finnish Medical Foundation, The Sigrid Jusélius Foundation and Sahlgrenska University Hospital.
Discover more about stroke at BrainandLife.org, from the American Academy of Neurology. This resource also offers a magazine, podcast, and books that connect patients, caregivers and anyone interested in brain health with the most trusted information, straight from the world’s leading experts in brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, X, and Instagram.
The American Academy of Neurology is the leading voice in brain health. As the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals with more than 40,000 members, the AAN provides access to the latest news, science and research affecting neurology for patients, caregivers, physicians and professionals alike. The AAN’s mission is to enhance member career fulfillment and promote brain health for all. A neurologist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, care and treatment of brain, spinal cord and nervous system diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, concussion, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, headache and migraine.
Explore the latest in neurological disease and brain health, from the minds at the AAN at AAN.com or find us on Facebook, X, Instagram, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
END
Stressed out? It may increase the risk of stroke
2025-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nanoscale tweaks help alloy withstand high-speed impacts
2025-03-05
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led collaboration devised a new method for designing metals and alloys that can withstand extreme impacts, which could lead to the development of automobiles, aircraft and armor that can better endure high-speed impacts, extreme heat and stress.
The research, published in Communications Materials, introduces nanometer-scale speed bumps that suppress a fundamental transition that controls how metallic materials deform.
The project was led by Mostafa Hassani, assistant professor of mechanical ...
AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
2025-03-05
AI-generated voices which sound like you are perceived as more trustworthy and likeable, with implications for deep-fakes and manipulation
Article URL: https://plos.io/4baFCW5
Article title: AI-determined similarity increases likability and trustworthiness of human voices
Author countries: Germany
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during
2025-03-05
The cacao tree species (Theobroma cacao L.), from which we get chocolate, is likely about 7.5 million years old, with chloroplast genomes indicating that the current known diversity diversified during the Pliocene or Miocene epochs
Article URL: https://plos.io/4gQHlB2
Article title: Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes of Theobroma cacao from northern Peru
Author countries: Perú
Funding: This study was supported by the Programa Nacional de Investigación Científica y Estudios Avanzados (PROCIENCIA) funded by the Project through the Contract N° 026-2016-FONDECYT “Círculo de Investigación ...
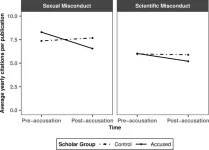
After sexual misconduct accusations, scholars’ work is cited less
2025-03-05
In a new analysis, scholars publicly accused of sexual misconduct experienced a significant decrease in the rate at which other scholars cited their published research. Giulia Maimone of the University of California, Los Angeles, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on March 5, 2025.
In academia, scholars cite other scholars’ publications as a widely agreed-upon way to reference existing research and promote scientific advancement. A scholar with a high number of citations may be considered particularly impactful in their field. Prior research ...
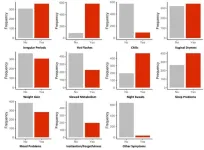
Menopause symptoms associated with future memory and neuropsychiatric problems
2025-03-05
Women who exhibit more menopausal symptoms are more likely to later have poorer cognitive function and mild behavioral impairments – both markers of dementia. That is the conclusion of a study of 896 postmenopausal females published March 5, 2025, in the open-access journal PLOS One by Zahinoor Ismail of University of Calgary, Canada, and colleagues.
Females are known to have a three-fold greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, and will be disproportionately ...
Findings may advance understanding of infertility in mothers
2025-03-05
Oxytocin, a hormone already known for its role in childbirth, milk release, and mother-infant bonding, may have a newfound purpose in mammalian reproduction. In times of maternal stress, the hormone can delay an embryo’s development for days to weeks after conception, a new study in rodents shows. According to the authors, the findings about so-called “diapause” may offer new insights into pregnancy and fertility issues faced by humans.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the study explored diapause, in which an embryo temporarily stops growing early in ...
Engineered cartilage from nasal septum cells helps treat complex knee injuries
2025-03-05
Injuries to the articular cartilage in different joints, including the knee, are painful and limit mobility. Therefore, researchers at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel are developing cartilage implants using cells from the patient’s nasal septum. A recent study shows that giving these cartilage implants more time to mature significantly improved clinical efficacy, even in patients with complex cartilage injuries. This suggests that the method could also be suitable for the treatment of degenerated cartilage in osteoarthritis.
An unlucky fall while skiing or playing ...
Damaged but not defeated: Bacteria use nano-spearguns to retaliate against attacks
2025-03-05
Some bacteria deploy tiny spearguns to retaliate against rival attacks. Researchers at the University of Basel mimicked attacks by poking bacteria with an ultra-sharp tip. Using this approach, they have uncovered that bacteria assemble their nanoweapons in response to cell envelope damage and rapidly strike back with high precision.
In the world of microbes, peaceful coexistence goes hand in hand with fierce competition for nutrients and space. Certain bacteria outcompete rivals and fend off attackers by injecting them with a lethal cocktail using tiny, ...
Among older women, hormone therapy linked to tau accumulation, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease
2025-03-05
A new study from Mass General Brigham researchers has found faster accumulation of tau—a key indicator of Alzheimer’s disease—in the brains of women over the age of 70 who took menopausal hormone therapy (HT) more than a decade before. Results, which are published in Science Advances, could help inform discussions between patients and clinicians about Alzheimer’s disease risk and HT treatment.
While the researchers did not see a significant difference in amyloid beta accumulation, they did find a significant difference in how fast regional tau accumulated in the brains of women over the age of 70, with women who had taken HT showing faster tau accumulation ...
Scientists catch water molecules flipping before splitting
2025-03-05
For the first time, Northwestern University scientists have watched water molecules in real-time as they prepared to give up electrons to form oxygen.
In the crucial moment before producing oxygen, the water molecules performed an unexpected trick: They flipped.
Because these acrobatics are energy intensive, the observations help explain why water splitting uses more energy than theoretical calculations suggest. The findings also could lead to new insights into increasing the efficiency of water splitting, a process that holds promise for generating clean hydrogen fuel and for producing breathable oxygen during future missions to Mars.
The study will be published Wednesday (March 5) ...