(Press-News.org) Ann Arbor, March 11, 2025 – An analysis of the global burden and temporal trends of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias (ADODs) reveals significant cross-country inequalities associated with a series of sociodemographic development-related risk factors, such as education, income, fertility, and health expenditure. The new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, calls for the development of targeted prevention and control strategies in different countries.
The burden of ADODs has risen globally over the past three decades. The authors of this first systematic and comprehensive global study analyzing data from 1990 to 2021, including data from the Global Burden of Disease 2021 study and the World Bank, found that there are significant disparities in numbers, rates, and age-standardized rates of disability-adjusted life years across 204 countries and territories.
Lead investigator Ya Fang, MD, PhD, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, China, says, "ADODs currently pose a major global public health challenge. They stand as a leading cause of functional loss and dependence among older individuals worldwide. Yet, to date, there are no definitive treatments capable of fully resolving ADODs. Furthermore, research exploring the relationship between sociodemographic development-related factors and health inequalities associated with ADODs is currently limited. Therefore, we aimed to establish this connection by assessing the impact of sociodemographic development indicators such as education, income, fertility, and health expenditure on ADODs health metrics."
The study found that approximately two-thirds of individuals with ADODs worldwide now live in low- and low-middle income countries, and as populations grow, the number of cases with ADODs in these countries is expected to rise faster than in high-income countries. Therefore, the disease burden of ADODs is believed to be greater in low- and middle-income countries, where individuals are more likely to face poverty and limited access to healthcare. However, even in countries with high sociodemographic development levels, such as Luxembourg, Switzerland, and the United States, despite having relatively comprehensive healthcare systems, the disease burden of ADODs remains high because of the specific distribution of ADOD risk factors in these countries, such as obesity, poor diet, and diabetes.
Another noteworthy finding is that females exhibited a notably higher burden of ADODs than males across all age groups, corroborating previous research that identifies female sex as a risk factor for accelerated cognitive decline. Gender differences in disease may be influenced by reproductive capacity, sex hormones, genetic predisposition, and epigenetics. Females are especially sensitive to hormonal fluctuations, particularly during premenstrual, perinatal, and menopausal periods. Estradiol and progesterone fluctuations during pregnancy impact maternal brain structure and function, such that the reproductive history of women may affect brain aging and disease risk.
Dr. Fang concludes, "This study integrated the Global Burden of Disease 2021 and World Bank data, and to the authors' knowledge is the first systematic and comprehensive study on cross-country inequality associated with a series of sociodemographic development-related factors. Other significant strengths of this study are its long observation period, wide geographical range, and extensive data coverage. Based on the results, it is necessary to further control risk factors of ADODs by promoting a healthy diet and regular exercise for preventing the development of ADODs in developed countries. However, enhancing basic healthcare, improving medical resource access and affordability, and raising ADOD awareness among the public in developing countries are also vital."
END
Socioeconomic factors fuel global inequalities in Alzheimer's disease burden, study finds
An analysis in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine exposes significant disparities across 204 countries and territories
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Foraging footballers suggest how we come together to act as one
2025-03-11
What do albatrosses searching for food, stock market fluctuations, and the dispersal patterns of seeds in the wind have in common?
They all exhibit a type of movement pattern called Lévy walk, which is characterized by a flurry of short, localized movements interspersed with occasional, long leaps. For living organisms, this is an optimal strategy for balancing the exploitation of nearby resources with the exploration of new opportunities when the distribution of resources is sparse and unknown.
Originally described in the context of particles drifting through liquid, Lévy walk has been found to accurately describe a very wide range of phenomena, from cold atom dynamics to ...
SSA: Semantic Structure Aware Inference for Weakly Pixel-Wise Dense Predictions without Cost
2025-03-11
CAM is proposed to highlight the class-related activation regions for an image classification network, where feature positions related to the specific object class are activated and have higher scores while other regions are suppressed and have lower scores. For specific visual tasks, CAM can be used to infer the object bounding boxes in weakly-supervised object location(WSOL) and generate pseudo-masks of training images in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS). Therefore, obtaining the high-quality CAM is very important to improve the recognition performance of weakly supervised pixel-wise ...
New test helps doctors predict a dangerous side effect of cancer treatment
2025-03-11
Fukuoka, Japan — Medical researchers in Japan have discovered a way to predict a potentially life-threatening side effect of cancer immunotherapy before it occurs. By analyzing cerebrospinal fluid collected pre-treatment, researchers at Kyushu University identified specific proteins associated with a damaging immune response that can affect the central nervous system after therapy. Their findings, published in Leukemia on 11 March, 2025, could make immunotherapy cancer treatment safer by helping doctors identify high-risk patients in advance, ...
UC Study: Long sentences for juveniles make reentry into society more difficult
2025-03-11
Juveniles grow up hearing a multitude of adages about life, such as: “True friends are forever,” “Fake it ’til you make it,” and “Change is a good thing.”
However, these adages — and other life advice about behavior in society — are difficult to process for juveniles who were incarcerated at a young age and served long sentences, says J.Z. Bennett, a criminologist at the University of Cincinnati whose research focuses on prison reform.
“Spending decades in prison removes individuals from social structures and sources of informal social control, such as education, employment, marriage and parenting,” he writes ...
Death by feral cat: DNA shows cats to be culprits in killing of native animals
2025-03-11
Conservation scientists from UNSW Sydney have used DNA technology to identify feral cats as the primary predators responsible for the deaths of reintroduced native animals at two conservation sites in South Australia.
The finding fits in with research data that suggests feral cats have killed more native animals than any other feral predators in Australia, and are believed to be responsible for two thirds of mammal extinctions since European settlement.
But in a study published recently in the ...
Plant Physiology is Searching for its Next Editor-in-Chief
2025-03-10
After taking the helm of Plant Physiology 2022, Yunde Zhao's celebrated term as Editor-in-Chief of the journal, during which he introduced changes that saw the journal flourish, will come to a close on December 31, 2026. The American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB) is seeking a prominent plant scientist to assume the duties and responsibilities of Editor-in-Chief of Plant Physiology effective January 1, 2027. ASPB’s EIC Search Committee is charged with evaluating candidates for the position and invites members of the plant science community to participate in the process by nominating someone who they ...
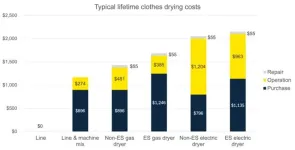
Clothes dryers and the bottom line: Switching to air drying can save hundreds
2025-03-10
Researchers from the University of Michigan are hoping their new study will inspire some Americans to rethink their relationship with laundry. Because, no matter how you spin it, clothes dryers use a lot of comparatively costly energy when air works for free.
Household dryers in the U.S. consume about 3% of our residential energy budget, about six times that used by washing machines. Collectively, dryers cost more than $7 billion to power each year in this country, and generating that energy emits the equivalent of more than ...
New insights into tRNA-derived small RNAs offer hope for digestive tract disease diagnosis and treatment
2025-03-10
This new article published in Genes & Diseases highlights the critical role of tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) in digestive tract diseases, positioning these molecules as potential biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and targeted therapies. The comprehensive review explores the biogenesis, classification, and biological functions of tsRNAs, shedding light on their influence over cellular processes such as translation regulation, epigenetic modification, and protein interactions.
Recent findings emphasize the significance of tsRNAs in both tumor and non-tumor digestive diseases, demonstrating their ability to regulate cell proliferation, ...
Emotive marketing for sustainable consumption?
2025-03-10
Does triggering certain emotions increase willingness to pay for sustainably produced food? In social media, emotional messages are often used to influence users' consumer behaviour. An international research team including the University of Göttingen investigated the short- and medium-term effects of such content on consumers' willingness to pay for bars of chocolate. They found that in the short term, provoking certain emotions increases willingness to pay, but the effect weakens after a very short time. The results were published in the journal Q Open.
Food ...
Prostate cancer is not a death knell, study shows
2025-03-10
Prostate cancer statistics can look scary: 34,250 U.S. deaths in 2024. 1.4 million new cases worldwide in 2022.
Dr. Bruce Montgomery, a UW Medicine oncologist, hopes that patients won’t see these numbers and just throw up their hands in fear or resignation.
“Being diagnosed with prostate cancer is not a death knell,” said Montgomery, senior author of a literature and trial review that appeared in JAMA today. Montgomery is the clinical director of Genitourinary Oncology at Fred Hutch Cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Socioeconomic factors fuel global inequalities in Alzheimer's disease burden, study findsAn analysis in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine exposes significant disparities across 204 countries and territories