(Press-News.org) A study led by researchers from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has used a novel approach to unravel the influence of the loss of Arctic sea ice on the planet's climate, isolating it from other factors related to climate change.
The study, published in the journal Communications Earth and Environment, shows that on decadal timescales, the loss of Arctic ice favours the climate of the south-west of the United States - and California in particular - becoming drier on average, especially in winter. This phenomenon would also affect the climate of Spain and Portugal, favouring conditions of higher humidity in winter, although in this case the observed effect is weaker.
'There is much scientific disagreement about the remote effects of Arctic sea ice loss. So far, many studies have focused on the long-term effects, on a scale of centuries. Others have investigated the response to sea ice loss with modelling setups that artificially impose heat to melt the sea ice, potentially affecting the simulated response. Some studies have been changing Antarctic and Arctic sea ice cover at the same time, making it difficult to discern their individual contributions. In our study, we have developed a methodology to assess the impact of Arctic ice loss without adding any heat fluxes, and we focused on the impacts developing within a few decades,' explains Ivana Cvijanovic, ISGlobal researcher and lead author of the study.
To reach these conclusions, the team used three models of varying complexity. In each of them, they ran two sets of simulations, one with the historical amount of sea ice in the Arctic and one with substantially decreased sea ice cover.
The disappearance of sea ice changes the surface albedo, i.e. the reflectivity of the Arctic Ocean, but also removes the insulation between the atmosphere and the ocean surface and affects salinity profiles. These local changes in turn drive a variety of atmospheric and oceanic teleconnections that can propagate far from the Arctic.
'It should be made clear that the conclusion is not necessarily that it will rain less in California and more in the Western Mediterranean in the coming years. In addition to the ice cover loss in the Arctic, there are many other factors responding to greenhouse gas emissions and affecting the climate (atmospheric and oceanic feedbacks and circulation changes, Antarctic sea ice loss, vegetation feedbacks, etc.). In any case, understanding the influence of this phenomenon separately will help us to refine global predictions,' says Desislava Petrova, ISGlobal researcher and last author of the study.
Despite all the different influences in our planet's climate system, it is interesting to note that the anomalies in the atmospheric circulation patterns of the last few decades show some striking similarities to the patterns simulated in our study - especially events such as the Californian drought of 2012-2016,' observes Ivana Cvijanovic.
Reference
Ivana Cvijanovic, Amelie Simon, Xavier Levine, Rachel White, Pablo Ortega, Markus Donat, Donald D. Lucas, John C. H. Chiang, Anne Seidenglanz, Dragana Bojovic, Arthur Ramos Amaral, Vladimir Lapin, Francisco Doblas-Reyes, Desislava Petrova, Arctic sea-ice loss drives a strong regional atmospheric response over the North Pacific and North Atlantic on decadal scales, Communications Earth Environment, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-025-02059-w
END
Arctic sea ice loss drives drier weather over California and wetter over Spain and Portugal
A new modelling study isolates the effect of Arctic sea ice melting from other factors
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nwd1 gene deletion triggers MASH-like pathology in mice: a new scientific breakthrough
2025-03-11
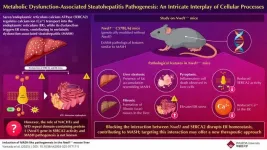
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is a liver disease that progresses without symptoms and is associated with significant global public health concerns. It is prevalent in 30% of the population worldwide and poses a risk of advancing to cirrhosis and liver cancer. MASH is marked by lipid droplet accumulation in the liver, progressing from steatosis to inflammation and cell damage, ultimately leading to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. A clear understanding of cellular processes in MASH pathogenesis is essential for developing ...
First burials: Neanderthal and Homo sapiens interactions in the Mid-Middle Palaeolithic Levant
2025-03-11
The first-ever published research on Tinshemet Cave reveals that Neanderthals and Homo sapiens in the mid-Middle Paleolithic Levant not only coexisted but actively interacted, sharing technology, lifestyles, and burial customs. These interactions fostered cultural exchange, social complexity, and behavioral innovations, such as formal burial practices and the symbolic use of ochre for decoration. The findings suggest that human connections, rather than isolation, were key drivers of technological and cultural advancements, highlighting the Levant as a crucial crossroads in early human history.
Link to the images: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/19p__omKCSSPkGBI3b8beF1QXqeRahGk1?usp=drive_link ...
Machine learning models fail to detect key health deteriorations, Virginia Tech research shows
2025-03-11
xIt would be greatly beneficial to physicians trying to save lives in intensive care units if they could be alerted when a patient’s condition rapidly deteriorates or shows vitals in highly abnormal ranges.
While current machine learning models are attempting to achieve that goal, a Virginia Tech study recently published in Communications Medicine shows that they are falling short with models for in-hospital mortality prediction, which refers to predicting the likelihood of a patient dying in the hospital, failing to recognize ...
Women with PVD often underdiagnosed & undertreated, highlighting need for more research
2025-03-11
Statement Highlights:
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD)—a condition affecting arteries, veins and the lymphatic systems throughout the body—has significant differences in incidence, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment and outcomes in women vs. men.
Women with PVD often experience subtle or atypical symptoms, which can lead to underdiagnosis or delay in diagnosis, and they are less likely to receive guideline-recommended treatments.
Targeted screening, tailored treatment strategies and increased representation of women in clinical trials are critical priorities to addressing these gaps ...
New Irresistible Materials CEO to drive commercialization and market adoption
2025-03-11
University of Birmingham spin-out Irresistible Materials Ltd (IM), a leader in the development of novel resist materials for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, has announced the appointment of Dinesh R. Bettadapur as its new chief executive officer (CEO) and board director.
Bettadapur brings a wealth of business experience and strategic vision to the company, having previously held leadership roles at ASML, Intel, and Lam Research, as well as multiple Silicon Valley startups where he enabled significant business growth leading to three successful exits.
In his new role, Bettadapur will lead IM’s business strategy and commercial engagements ...
Gold mining in the Peruvian Amazon has done more damage to peatlands in the last two years than in the previous three decades
2025-03-11
New research published in the academic journal Environmental Research Letters reveals that artisan gold mining in the southern Peruvian Amazon has caused more destruction to carbon-rich peatlands in the past two years than in the previous three decades combined, posing a serious threat to the environment and climate.
For decades, small-scale gold mining has thrived along the rivers of the Madre de Dios region, driven by gold frequently found in the surrounding soils. While the deforestation caused by mining has already resulted in significant carbon emissions, scientists have now discovered that the damage ...
Cheap and environmentally friendly – the next generation LEDs may soon be here
2025-03-11
Cost, technical performance and environmental impact – these are the three most important aspects for a new type of LED technology to have a broad commercial impact on society. This has been demonstrated by researchers at Linköping University in a study published in Nature Sustainability.
“Perovskite LEDs are cheaper and easier to manufacture than traditional LEDs, and they can also produce vibrant and intense colours if used in screens. I’d say that this is the next generation ...
Rare frog rediscovered after 130 years
2025-03-11
A team of researchers has rediscovered a frog species which has not been seen in more than 130 years. First described in 1902, Alsodes vittatus had evaded detection since then, despite multiple search efforts. The researchers discovered two populations of the frog at the southeastern end of the ancient Hacienda San Ignacio de Pemehue in La Araucanía Region, Chile. The rediscovery is an important milestone for South American herpetology and the conservation of biodiversity in the southern cone.
The frog Alsodes vittatus is an elusive creature – described in 1902, it managed to go undetected for more than a century. Now, after a decade of investigation, a research team ...
Earth's 'dirty mirror' effect is accelerating climate change
2025-03-11
Earth is absorbing more sunlight and trapping more heat than it releases into space, causing our planet to warm up at an increasing rate.
New research shows that cloudy areas over oceans are reflecting less sunlight to space than before, adding to heating from rising greenhouse gas levels and causing climate change to accelerate.
The study, published today (Tuesday, 11 March) in Environmental Research Letters, found this dimming effect was occurring in several regions, including cloudy areas off the coasts of California and Namibia, ...
Breakthrough in next-generation polio vaccines
2025-03-11
A more affordable, lower-risk polio vaccine is on the horizon, research led by the University of Leeds has found.
Researchers have taken a major step towards producing a more affordable and lower-risk polio vaccine using virus-like particles (VLPs). These particles mimic the outer protein shell of poliovirus, but are empty inside. This means there is no risk of infection, but the VLP still causes the immune system to respond.
Now, a research project led by Professor David Rowlands, Emeritus Professor of Molecular Virology at the University of Leeds, has tested the effectiveness of using different yeast, insect, mammalian and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
[Press-News.org] Arctic sea ice loss drives drier weather over California and wetter over Spain and PortugalA new modelling study isolates the effect of Arctic sea ice melting from other factors