(Press-News.org) Marijuana is now legal in many places, but is it safe? Two new studies add to mounting evidence that people who use cannabis are more likely to suffer a heart attack than people who do not use the drug, even among younger and otherwise healthy adults. The findings are from a retrospective study of over 4.6 million people published in JACC Advances and a meta-analysis of 12 previously published studies being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
Marijuana use has risen in the United States, especially in states where it is legal to buy, sell and use the drug recreationally. In the retrospective study, researchers found that cannabis users younger than age 50 were over six times as likely to suffer a heart attack compared to non-users. The meta-analysis, which is the largest pooled study to date examining heart attacks and cannabis use, showed a 50% increased risk among those who used the drug.
“Asking about cannabis use should be part of clinicians’ workup to understand patients’ overall cardiovascular risk, similar to asking about smoking cigarettes,” said Ibrahim Kamel, MD, clinical instructor at the Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine and internal medicine resident at St. Elizabeth Medical Center in Boston and the study’s lead author. “At a policy level, a fair warning should be made so that the people who are consuming cannabis know that there are risks.”
Kamel and his team conducted the retrospective study using data from TriNetX, a global health research network that provides access to electronic medical records. Their findings indicate that over an average follow-up of over three years, cannabis users had more than a sixfold increased risk of heart attack, fourfold increased risk of ischemic stroke, twofold increased risk of heart failure and threefold increased risk of cardiovascular death, heart attack or stroke. All study participants were younger than age 50 and free of significant cardiovascular comorbidities at baseline, with blood pressure and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels within a healthy range and no diabetes, tobacco use or prior coronary artery disease.
For the meta-analysis, the researchers pooled data from 12 previously published research studies that collectively included over 75 million people. The studies were rated as being of moderate to good quality in terms of methodology. Of the 12 studies, 10 were conducted in the United States, one in Canada and one in India. Some of the studies did not include information about participants’ ages, but the average age was 41 years among those that did, suggesting that the pooled sample reflected a relatively young population.
Taken individually, seven of the studies found a significant positive association between cannabis use and heart attack incidence, while four showed no significant difference and one showed a slightly negative association. When the researchers pooled the data from all studies and analyzed it together, they found a significant positive association, with active cannabis users being 1.5 times as likely to suffer a heart attack compared with those who aren’t current users.
Cannabis use and heart attack incidence was assessed in a similar manner across the different studies. However, due to inconsistencies in the data available from each study, researchers were unable to account for several potential confounding factors including the duration and amount of cannabis use or the use of tobacco or other drugs.
“We should have some caution in interpreting the findings in that cannabis consumption is usually associated with other substances such as cocaine or other illicit drugs that are not accounted for,” Kamel said. “Patients should be forthcoming with their doctors and remember that we are their number one advocate and having the full story matters.”
While the mechanisms through which marijuana or its components may impact the cardiovascular system are not fully understood, the researchers hypothesize that it can affect heart rhythm regulation, heighten oxygen demand in the heart muscle and contribute to endothelial dysfunction, which makes it harder for the blood vessels to relax and expand, and can interrupt blood flow. One of the studies included in the meta-analysis found that the risk of heart attack peaked about one hour after marijuana consumption.
Since both studies were limited by their retrospective nature and the meta-analysis was limited by the challenges inherent in pooling data from multiple studies, researchers said that additional prospective studies would help to confirm the findings and determine which groups may face the highest risk.
A previous study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session in 2023 found that daily marijuana use was associated with an increased risk of developing coronary artery disease.
The meta-analysis will simultaneously publish in JACC Advances.
Kamel will present the study, “Risk of Myocardial Infarction in Cannabis Users: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis,” on Saturday, March 29, 2025, at 2:00 p.m. CT / 19:00 UTC in South Hall.
ACC.25 will take place March 29-31, 2025, in Chicago, bringing together cardiologists and cardiovascular specialists from around the world to share the newest discoveries in treatment and prevention. Follow @ACCinTouch, @ACCMediaCenter and #ACC25 for the latest news from the meeting.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at ACC.org.
###
END
Lifestyle and health factors that are linked with heart disease appear to have a greater impact on cardiovascular risk in women than men, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
While factors such as diet, exercise, smoking and blood pressure have long been linked with heart disease risk, the new study is the first to show that these associations are collectively stronger in women than men. According to the researchers, the ...
Enzymes found in landfills around the world may be able to break down plastic waste. Some 11 billion metric tons of plastic are projected to accumulate in the environment by 2050. Enzymatic and microbial degradation is a promising method of plastic recycling. Landfills, environments where plastics are an abundant resource, are crucibles of bacterial evolution. Liyan Song and colleagues collected plastic biocatalytic enzymes from landfills around the world, using metagenomics and machine learning. Samples came from China, Italy, Canada, Great Britain, Jamaica, and India and included refuse, leachate, sludge, and airborne particles. The authors identified 31,989 possible ...
PULLMAN, Wash. — For years, therapy dogs have ruled the world of animal-assisted services (AAS), offering stress relief to college students, hospital patients, and those in need of emotional support. But new research suggests that some cats might also have what it takes to join the ranks of therapy animals—bringing their purrs, gentle headbutts, and calm demeanor to the field.
A study in the journal Animals co-authored by Washington State University professor Patricia Pendry, in collaboration with researchers in Belgium, found that therapy cats share specific behavioral traits that may make them well-suited for AAS programs. The research team surveyed ...
Creamy, crumbly, mild, or sharp — cheese is a true crowd-pleaser. From everyday meals to gourmet delights, it’s a staple across the Western world. In 2023, the average European enjoyed 20.5 kilograms of cheese.
But it is no secret that, as a dairy product, heavy cheese consumption comes with a significant environmental impact. As such, extensive research is being conducted on how to produce plant-based cheeses. Unfortunately, finding an entirely plant-based cheese that satisfies cheese lovers in terms of both texture and taste has been difficult. And texture in particular has been challenging to get just right.
So, food researchers at the University ...
Mill Valley, CA – March 18, 2025 – The SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) dba Cure SYNGAP1, a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, has awarded a $65,000 grant to Dr. Julia Dallman, Associate Professor of Biology at the University of Miami College of Arts and Sciences, to investigate gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in SYNGAP1-related disorders (SRD) patients. Leveraging her extensive experience with zebrafish models, Dr. Dallman's research aims to identify therapies that alleviate severe GI issues, such as chronic ...
Unsubstituted π-electronic systems with expanded π-planes are highly desirable for improving charge-carrier transport in organic semiconductors. However, their poor solubility and high crystallinity pose major challenges in processing and assembly, despite their favourable electronic properties. The strategic arrangement of these molecular structures is crucial for achieving high-performance organic semiconductive materials.
In a significant breakthrough, a research team led by Professor Hiromitsu Maeda from Ritsumeikan University, including Associate Professor Yohei Haketa from ...
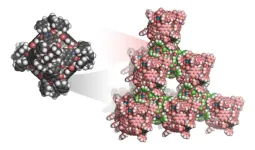
Researchers from Kyoto University have achieved a groundbreaking advancement in materials science by developing the world's first three-dimensional van der Waals open frameworks (WaaFs). This innovation challenges the conventional belief that van der Waals interactions are too weak for open framework materials, demonstrating their potential for stable and highly porous materials.
Published in Nature Chemistry, the study presents a strategy using octahedral metal-organic polyhedra (MOPs) as building blocks to construct WaaFs. These frameworks exhibit high thermal stability, exceptional porosity, and reversible assembly, opening new avenues for applications in gas storage, separation, ...
Global population datasets, crucial for decision-making by governments and institutions, may underestimate rural populations by as much as 53% to 84%, reveals an Aalto University study.
Governments, international bodies and researchers rely on global population data for resource allocation and infrastructure planning to disease epidemiology and disaster risk management. In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Aalto University in Finland show the profound and systematic extent to which these datasets underestimate ...
Modern humans descended from not one, but at least two ancestral populations that drifted apart and later reconnected, long before modern humans spread across the globe.
Using advanced analysis based on full genome sequences, researchers from the University of Cambridge have found evidence that modern humans are the result of a genetic mixing event between two ancient populations that diverged around 1.5 million years ago. About 300,000 years ago, these groups came back together, with one group contributing 80% of the genetic makeup of modern humans and the other contributing 20%.
For the last two decades, the prevailing view in human evolutionary genetics has been that Homo sapiens first ...
A first-of-its-kind artificial intelligence (AI)-based neural network can rapidly analyse and interpret millions of cells from a patient sample, predicting molecular changes in the tissue. It can potentially pinpoint where personalised treatments could be most effective for conditions such as cancer.
NicheCompass leverages the power of generative AI to create a visual database combining spatial genomic data on cell types, where they are found, and how they communicate. Created by researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the Institute of AI for Health ...