(Press-News.org) DALLAS, March 27, 2025 — More than 56 million people globally live with heart failure (HF), which prevents the body from getting enough of the oxygen-rich blood it needs to work properly.[1]
While there is no cure for HF, many people with this condition can live full, enjoyable lives and disease progression can be slowed with the right treatment. Research shows that outcomes for patients with HF improve when health care professionals and hospitals provide guideline-directed medical therapies.
A new Heart Failure Center Certification is an effort from the American Heart Association, a global force for changing the future of health of all, to help reduce the more than 5 million years lived with disability due to HF around the world.[2] The hospital-based, continuous quality improvement program is being launched in 13 countries bringing this gold standard in HF care to communities outside the U.S. for the first time.
Heart Failure Center Certification will recognize hospitals dedicated to improving HF care in their communities. By promoting evidence-based treatments and seamless transitions from hospital to outpatient care, the certification strives to enhance patient outcomes and reduce hospital readmissions.
“Aligned with the American Heart Association’s vision of changing the future of health for all, this certification aims to reduce death and disability from cardiovascular diseases by enabling more facilities across the globe to deliver comprehensive, evidence-based heart failure care,” said : D.P. Suresh, M.D., FAHA, American Heart Association volunteer, incoming co-chair of the American Heart Association's International Committee and executive medical director of Florence Wormald Heart and Vascular Institute at St. Elizabeth Physicians. “The science is clear: hospitals and the patients they serve benefit from a coordinated heart failure program.”
Certification standards are developed independently and overseen by mission-driven organizations with the clinical background required to focus on patient-centered quality health care, safety and value.
Learn more at heart.org/HeartFailureCertification.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available on the right column of release link
Guiding heart failure teams to optimal patient care
Abstract 12163: Initiation of Guideline Directed Medical Therapy at Hospital Discharge Improves Outcomes in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction | Circulation
Abstract 17028: Characteristics and Short-Term Outcome of Patients in the Program “Get With the Guidelines” - One Vietnamese Center Registry | Circulation
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. Dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities, the organization has been a leading source of health information for more than one hundred years. Supported by more than 35 million volunteers globally, we fund groundbreaking research, advocate for the public’s health, and provide critical resources to save and improve lives affected by cardiovascular disease and stroke. By driving breakthroughs and implementing proven solutions in science, policy, and care, we work tirelessly to advance health and transform lives every day. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
[1] Burden, Trends, and Inequalities of Heart Failure Globally, 1990 to 2019. doi:10.1161/JAHA.122.027852.
[2] Burden, Trends, and Inequalities of Heart Failure Globally, 1990 to 2019 doi:10.1161/JAHA.122.027852; Significance of ischemic heart disease in patients with heart failure and preserved, midrange, and reduced ejection fraction Circ Heart Fail 2017;10:e003875; Fonarow G, et al. Characteristics, Treatments, and Outcomes of Patients With Preserved Systolic Function Hospitalized for Heart Failure: A Report From the OPTIMIZE-HF Registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:768–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2007.04.064; Lloyd-Jones D, et al. Lifetime Risk for Developing Congestive Heart Failure: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2022;106(24). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000039105.49749.6F.
END
Elevating global heart failure care with new certification
American Heart Association’s international Heart Failure Center Certification will recognize hospitals dedicated to optimizing HF treatment, reducing readmissions
2025-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The MIT Press releases 2025 Direct to Open (D2O) Impact Report
2025-03-27
The MIT Press is proud to release our 2025 Impact Report for Direct to Open (D2O), our sustainable framework for open access monographs that shifts publishing from a solely market-based purchase model where individuals and libraries buy single eBooks, to a collaborative, library-supported open access model.
The continued growth in the reach of open access publishing couldn’t be more timely. In 2025, access to truth and facts are under attack, and democratizing access to trustworthy, peer-reviewed information has never been more important. In the face of so many forces working against the spread of knowledge, Direct to Open continues to be a critical tool.
To date, ...
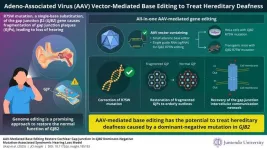
New study reveals the curative potential of genome editing approach for genetic deafness
2025-03-27
Congenital hearing loss refers to impaired auditory function that occurs due to genetic causes. GJB2 is the gene responsible for approximately half of all cases of hereditary hearing loss. Connexin 26 (CX26), which is encoded by GJB2, helps in the formation of intercellular gap junctions—channels that allow for the movement of ions and chemical messenger molecules between adjacent cells, where it regulates auditory function.
GJB2 mutations often lead to fragmentation of gap junctions and gap junction plaques (GJPs) which are composed ...
AAAS elects Keck School of Medicine of USC molecular biologist Yali Dou as 2025 fellow
2025-03-27
Molecular biologist Yali Dou, PhD, holder of the Marion and Harry Keiper Chair in Cancer Research and professor of medicine and cancer biology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, has been elected a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). She is one of seven USC faculty members in the 2025 cohort of new fellows.
The AAAS is the world’s oldest and largest general science organization and the publisher of Science, a top peer-reviewed academic journal. Election as a fellow is a lifetime honor — one of the AAAS’s ...
Damaging cluster of UK winter storms driven by swirling polar vortex miles above Earth
2025-03-27
University of Leeds news
Embargoed until 10:00 GMT, 27 March
Damaging cluster of UK winter storms driven by swirling polar vortex miles above Earth
Powerful winter storms which led to deaths and power outages in the UK and Ireland were made more likely by an intense swirling vortex of winds miles above the Arctic, say scientists.
A team of researchers led by the University of Leeds has pinpointed a new reason for winter storm clusters such as the trio named Dudley, Eunice and Franklin, which hit the nation within the space of a week in February 2022.
The findings which are published today in the journal ...
Losing forest carbon stocks could put climate goals out of reach
2025-03-27
In the past, intact forests absorbed 7.8 billion tonnes of CO₂ annually – about a fifth of all human emissions – but their carbon storage is increasingly at risk from climate change and human activities such as deforestation. A new study from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) shows that failing to account for the potentially decreasing ability of forests to absorb CO₂ could make reaching the Paris agreement targets significantly harder, if not impossible, and much more costly.
“Delaying action leads to disproportionately higher costs,” explains Michael Windisch, ...
From weight to wellness: New database transforms obesity research
2025-03-27
A new medical database automatically compiles the medical records of obese patients and those suffering from obesity-related diseases in a uniquely comprehensive and reliable manner. The initiative, led by Kobe University, offers valuable insights for health promotion and drug development.
“Obesity is at the root of many diseases,” says OGAWA Wataru, an endocrinologist at Kobe University. Obesity has been linked to the development of diabetes, hypertension, gout, coronary heart disease, stroke and many other diseases. Monitoring, treating and preventing obesity and the diseases it can cause is therefore not only good for ...
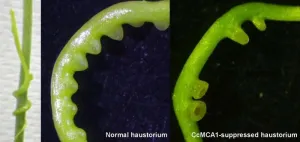
Nature’s viny vampire: Discovering what drives parasitic Cuscuta campestris
2025-03-27
The parasitic vine Cuscuta campestris grows by latching onto the stems and leaves of plants and inserting organs called haustorium into the host plant tissues to draw nutrients. The haustorium is formed when ion channels in the cell membrane are stimulated during coiling and induce a reaction within the cell.
Further, Cuscuta campestris has many types of ion channels, but which ones were linked to the development of haustorium were previously unknown.
“For the first time, the genes involved in sensing ...
How calcium may have unlocked the origins of life’s molecular asymmetry
2025-03-27
A new study led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Institute of Science Tokyo has uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping life’s earliest molecular structures. Their findings suggest that calcium ions can selectively influence how primitive polymers form, shedding light on a long-standing mystery: how life’s molecules came to prefer a single “handedness” (chirality).
Like our left and right hands, many molecules exist in two mirror-image forms. Yet life on Earth has a striking preference: ...
Study finds long Covid patients feel pressure to prove their illness is real
2025-03-27
People living with Long Covid often feel dismissed, disbelieved and unsupported by their healthcare providers, according to a new study from the University of Surrey.
The study, which was published in the Journal of Health Psychology, looked at how patients with Long Covid experience their illness. The study found that many patients feel they have to prove their illness is physical to be taken seriously and, as a result, often reject psychological support, fearing it implies their symptoms are "all in the mind".
Professor ...
Smartwatches may help control diabetes through exercise
2025-03-27
Wearable mobile health technology could help people with Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) to stick to exercise regimes that help them to keep the condition under control, a new study reveals.
Researchers studied the behaviour of recently-diagnosed T2D patients in Canada and the UK as they followed a home-based physical activity programme – some of whom wore a smartwatch paired with a health app on their smartphone.
They discovered that MOTIVATE-T2D participants were more likely to start and maintain purposeful exercise at if they had the support of wearable technology- the study successfully recruited 125 participants with an 82% ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] Elevating global heart failure care with new certificationAmerican Heart Association’s international Heart Failure Center Certification will recognize hospitals dedicated to optimizing HF treatment, reducing readmissions