(Press-News.org) Banning smartphone and social media access alone fails to equip children for healthy use of technology, argues a group of international experts in The BMJ today.
They say the focus should shift to a rights based approach, underpinned by age appropriate design and education, that protects children from harm while developing skills to help them participate in a digital society.
Bans on smartphone and social media access have been advocated in many countries to protect children from harm despite lack of evidence on their effects, explain Victoria Goodyear and colleagues.
For example, a recent evaluation of school smartphone policies in England reported that restricted smartphone use in schools was not associated with benefits to adolescent mental health and wellbeing, physical activity and sleep, educational attainment, or classroom behaviour.
That study also found no evidence of school restrictions being associated with lower levels of overall phone or media use or problematic social media use.
While technology-free moments and spaces are important for children, the authors argue that blanket restrictions are “stop gap solutions that do little to support children’s longer term healthy engagement with digital spaces across school, home, and other contexts, and their successful transition into adolescence and adulthood in a technology filled world.”
Instead, they call for a rights based approach to smartphone and social media use, in line with the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child, which recommends ways of protecting children from harm while nurturing the healthy development of smartphone and social media use.
Recent international legislation, such as the European Union’s Digital Services Act and the UK Online Safety Act, also reflect a clear understanding of the need to ensure children’s uses of technology are compatible with their wellbeing.
Immediate priorities are to improve legislation for the tech industry grounded in children’s rights and create professional training and guidance for schools, teachers, and parents to help them be actively involved in the development of children’s healthy technology use and in shaping future policies and approaches, they write.
They acknowledge several potential challenges, but say in the longer term, this approach is likely to be more beneficial and sustainable as it is focused on building a safe ecosystem in a digital society.
“Ultimately, there is a need to shift debates, policies, and practices from a sole focus on restricting smartphone and social media access toward an emphasis on nurturing children’s skills for healthy technology use,” they conclude.
[Ends]
END
Smartphone bans alone fail to equip children for healthy use of technology
Focus should shift to a rights based approach, argue experts
2025-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discovery of novel small compounds that delay flowering in plants
2025-03-27
Ikoma, Japan—In an era where climate change threatens food security, scientists worldwide are searching for reliable ways to improve crop production. Extreme weather and shifting seasonal patterns can disrupt traditional agricultural cycles, making technologies that regulate the timing of plant growth invaluable for farmers worldwide.
Plant growth and development are dependent on many factors such as the environment, photoperiod, and genetics. Flowering is an important event in a plant’s life ...
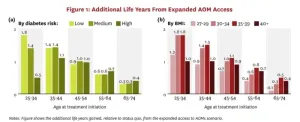
Expanding access to anti-obesity medications delivers 13% return on investment for society
2025-03-27
A new USC Schaeffer Center white paper finds expanded access to anti-obesity medications would lead to significant increases in life expectancy and disease-free years while generating a substantial societal return on investment, even after accounting for treatment costs.
More than 4 in 10 U.S. adults have obesity, which is linked to increased risk of over 200 diseases — including heart disease, diabetes, cancer and dementia — and costs society $260 billion annually to treat. Highly effective new anti-obesity medications can be a powerful tool against chronic disease, but fewer than one-third of health insurers cover them amid concerns about upfront ...
Genetic defense breakthrough: plants repurpose stomatal genes to fend off herbivores
2025-03-27
Ikoma, Japan—Throughout evolution, plants have continuously adapted to survive in changing environments. Apart from complex structural changes, plants have also developed various defense strategies against herbivores, including tougher protective layers, thorns, and chemical deterrents. Delving deeper into the evolution of defense mechanisms, a research team led by Assistant Professor Makoto Shirakawa from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), identified a surprising genetic adaptation in the Brassicales plant order. In these cruciferous ...
David B. Allison, Ph.D., Daniel W. Belsky, Ph.D., and Arlan Richardson, Ph.D., to receive 2025 Scientific Awards of Distinction from the American Federation for Aging Research
2025-03-27
New York, NY — The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR), is pleased to announce the 2025 recipients of three of its annual Scientific Awards of Distinction: David B. Allison, PhD, will receive the Irving S. Wright Award of Distinction; Daniel W. Belsky, PhD, will receive the Vincent Cristofalo Rising Star Award in Aging Research; and Arlan Richardson, PhD, will receive the George M. Martin Lifetime Achievement in Mentoring Award.
The Irving S. Wright Award of Distinction is named in honor of AFAR’s founder and recognizes exceptional contributions to basic ...
Pregnant women advised to avoid mentholated e-cigarettes
2025-03-27
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Vaping during pregnancy is becoming more common, but its impact on early human development is not well understood. A new study by scientists at the University of California, Riverside, now reports that the flavor chemical menthol used in electronic cigarettes could pose risks to a developing baby.
The study, published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, used human embryonic stem cells, or hESCs, to characterize early stages of embryonic development and examined how low concentrations of menthol affect important cellular processes.
The ...
Smart textiles and surfaces – How lightweight elastomer films are bringing tech to life
2025-03-27
Clothes that can mimic the feeling of being touched, touch displays that provide haptic feedback to users, or even ultralight loudspeakers. These are just some of the devices made possible using thin silicone films that can be precisely controlled so that they vibrate, flex, press or pull exactly as desired. And all done simply by applying an electrical voltage. The research teams at the Center for Mechatronics and Automation Technology in Saarbrücken (ZeMA) headed by Professors Stefan Seelecke and Paul Motzki (Saarland University) and John Heppe (htw saar – University of Applied Sciences ...
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers create innovative microparticles that unlock new insights into protein degradation and immune cell behavior
2025-03-27
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers have created a new method for studying protein degradation within immune cells that uses engineered microparticles to track and analyze degradation processes more effectively than traditional methods.
The work, which was published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, has important implications for treating diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s disease and autoimmune disorders.
“There is a lot we still don’t know about how cells ingest and eliminate tissue debris or pathogens — the process ...
Getting the ball rolling
2025-03-27
How gravity causes a perfectly spherical ball to roll down an inclined plane is part of elementary school physics canon. But the world is messier than a textbook.
Scientists in the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have sought to quantitatively describe the much more complex rolling physics of real-world objects. Led by L. Mahadevan, the Lola England de Valpine Professor of Applied Mathematics, Physics, and Organismic and Evolutionary Biology in SEAS and FAS, they combined theory, simulations, and experiments to understand what happens when an imperfect, ...
Breakthrough copper alloy achieves unprecedented high-temperature performance
2025-03-27
A team of researchers from Arizona State University, the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL), Lehigh University and Louisiana State University has developed a groundbreaking high-temperature copper alloy with exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength.
The research team’s findings on the new copper alloy, published in prestigious journal Science, introduce a novel bulk Cu-3Ta-0.5Li nanocrystalline alloy that exhibits remarkable resistance to coarsening and creep deformation, even at temperatures near its melting point.
“Our alloy design approach mimics the strengthening mechanisms found in Ni-based superalloys,” said Kiran Solanki, a professor at ...
Classroom talk plays a key part in the teaching of writing, study shows
2025-03-27
The way teachers manage classroom discussion with pupils plays a key role in the teaching of writing, a new study shows.
The research shows the importance of managing classroom discussion in a way that develops pupils’ understanding of the choices that writers make, and how those choices create particular effects for readers. This discussion helps pupils to think more about the choices that they make in their own writing.
The study reinforces the importance of dedicating time to discussion in secondary English lessons. It shows that time should be given to exploratory, speculative discussion that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
[Press-News.org] Smartphone bans alone fail to equip children for healthy use of technologyFocus should shift to a rights based approach, argue experts