(Press-News.org) Cardiac deaths increase significantly during compound heatwaves—heatwaves where temperatures are elevated both during the day and overnight—according to a new study in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. The study also found that some types of heart disease are more sensitive to heatwaves than others and that different types of heatwaves may impact heart health in distinct, nonlinear ways.
The research highlights the special risks of compound heatwaves and potential nonlinear relationships between different heatwave types and cardiac mortality. It finds that previous studies using traditional binary definitions—without accounting for different types of heatwaves and their cumulative heat load—may have underestimated this risk by as much as 54%. The findings could help improve clinical guidelines for cardiovascular patients and could also be used to improve public health adaptations to climate change, researchers said.
“Compound heatwaves impose a significantly higher risk to cardiac health than either daytime-only or nighttime-only heatwaves,” said coauthor Renjie Chen, PhD, of Fudan University. “Traditional heatwave definitions fail to capture the full scope of these risks.”
Previous research has found a link between short-term exposure to heatwaves and an increase in heart disease mortality using conventional binary definitions, but the shape of the risk curve and the role of different heatwave patterns were not well understood.
For the new study, researchers analyzed data for nearly 2.4 million heart disease deaths across mainland China over six years. They compared deaths across daytime-only, nighttime-only, and day-night compound heatwaves and introduced a new metric for measuring heatwave impact called Excess Cumulative Temperatures in Heatwaves, or ECT-HW.
“Unlike traditional binary indicators, ECT-HW captures the full spectrum of heatwave characteristics, including intensity, duration and timing within the season,” Chen explained. This provides more precise risk assessment, especially for high-intensity, high-duration and compound heatwaves.
Researchers found that the mortality risk associated with compound heatwaves increased steadily with exposure, without a clear threshold. Daytime-only and nighttime-only heatwaves displayed nonlinear patterns, with effects emerging only beyond specific thresholds and plateauing at moderate intensities.
They also found that risk was not equal across different heart disease subtypes. Sudden cardiac arrest, acute myocardial infarction and heart failure were especially sensitive to compound heatwaves, while pulmonary heart disease only showed elevated risk under high-intensity exposures.
Conventional studies of heatwave deaths that look only at whether a heatwave is present or not significantly underestimate mortality risks, they said.
The findings have several clinical and public health implications, Chen said.
Since different types of heatwaves affect cardiac conditions differently, prevention measures should consider heatwave type and intensity. In addition, given their higher impact, compound heatwaves should be explicitly considered in risk assessment and early warning systems for cardiovascular patients.
The findings also highlight the importance of urban heat mitigation strategies, such as cooling shelters and improved housing infrastructure to protect vulnerable populations.
“As climate change accelerates, the shifting and emerging heatwave exposure pattern demands better metrics and targeted interventions,” Chen said. “Given the increasing frequency and intensity of compound heatwaves due to climate change, our findings highlight the need for disease-specific prevention strategies and revised public health guidelines to better protect at-risk populations.”
Next, the team is planning follow-up research, including studies to project the future burden of heatwave-related cardiac mortality under different climate change scenarios.
The study, “Nonlinear Relation between Cardiac Mortality and Excess Temperature in Heatwaves: Exposure Response in 2.39 Million Patients,” was published in JACC.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at www.ACC.org.
The ACC’s JACC Journals rank among the top cardiovascular journals in the world for scientific impact. The flagship journal, the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) — and specialty journals consisting of JACC: Advances, JACC: Asia, JACC: Basic to Translational Science, JACC: CardioOncology, JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, JACC: Case Reports, JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology and JACC: Heart Failure — pride themselves on publishing the top peer-reviewed research on all aspects of cardiovascular disease. Learn more at JACC.org.
###
END
DALLAS, April 1, 2025 — A New York City-based physician scientist who explores ways to improve health by looking at the ways in which cells and molecules impact disease and an epidemiologist from Baltimore who has devoted her career to identifying ways to improve screening, diagnosis and patient care for people with diabetes are the most recent American Heart Association Merit Award recipients. Over the next five years, each researcher will receive a total of $1 million in funding from the Association, a global force changing the future of health for all.
The American Heart Association’s Merit Award is one of ...
A study of the use of AI by a Russian-backed propaganda outlet shows how AI allows propagandists to increase their production capacity without any loss in persuasive power. In December 2023, journalists at the BBC and Clemson University’s Media Forensics Hub published an investigation revealing that the site DCWeekly.org was a Russian propaganda outlet, part of a broader network disseminating pro-Kremlin and anti-Ukrainian narratives. Morgan Wack and colleagues found that prior to September 20, 2023, much of the content on the site was simply lifted from other right-leaning outlets. After that date, however, the stories were generally rewritten by AI, allowing the site to use a broader ...
Polysiloxane materials, such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based elastomers, exhibit a self-healing capability by the introduction of silanolate (Si–O–) groups. This ability stems from their dynamic siloxane (Si–O–Si) bonds, which can break and reform to repair damage. Their self-healing properties could make them valuable in applications like protective coatings for use in various fields, such as optics, electronics, and aerospace.
To improve the properties of PDMS-based materials, they have been combined with inorganic fillers such as nanoparticles or nanosheets. Generally, the introduction of nanosheets into polymers leads to the formation of ...
New York, NY – April 1, 2025- A study published today in the American Journal of Gastroenterology reveals significant disparities in healthcare utilization among racial and ethnic groups with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in the United States. The research, funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), led by investigators from the University of Pennsylvania, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and the Crohn's & Colitis Foundation provides crucial insights into the challenges faced by underrepresented communities ...
DALLAS, April 1, 2025 — Sedentary behavior has become a national health crisis, with 1 in 4 U.S. adults sitting for more than eight hours a day, increasing their risk for heart disease, stroke, and mental health challenges, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. To help people move more, the American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health of all, invites communities nationwide to walk together on Wednesday, April 2.
Adopting healthier routines doesn’t have to be intimidating or overwhelming according to Eduardo Sanchez MD, MPH, FAHA, the ...
A pan-Canadian team has developed a new way to quickly find personalized treatments for young cancer patients, by growing their tumours in chicken eggs and analyzing their proteins.
The team, led by researchers from the University of British Columbia and BC Children’s Hospital Research Institute, is the first in Canada to combine these two techniques to identify and test a drug for a young patient's tumour in time for their treatment.
Their success in finding a new drug for the patient, described today in EMBO Molecular Medicine, shows how the study of proteins, known as proteomics, ...
Eye tracking plays a critical role in the latest virtual and augmented reality headsets and is an important technology in the entertainment industry, scientific research, medical and behavioral sciences, automotive driving assistance and industrial engineering. Tracking the movements of the human eye with high accuracy, however, is a daunting challenge.
Researchers at the University of Arizona Wyant College of Optical Sciences have now demonstrated an innovative approach that could revolutionize eye-tracking ...
It’s (going to be) electric.
But how soon? How quickly our society can maximize the benefit of electrification hinges on finding cheaper, higher performance batteries — a reality closer to hand through new research from Virginia Tech.
A team of chemists led by Feng Lin and Louis Madsen found a way to see into battery interfaces, which are tight, tricky spots buried deep inside the cell. The research findings were published on April 1 in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
“There are major, longstanding challenges at the interfaces,” ...
April 1, 2025
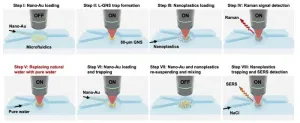
AMHERST, Mass. – While the threat that microplastics pose to human and ecological health has been richly documented and is well known, nanoplastics, which are smaller than one micrometer (1/50th the thickness of an average human hair), are far more reactive, far more mobile and vastly more capable of crossing biological membranes. Yet, because they are so tiny and so mobile, researchers don’t yet have an accurate understanding of just how toxic these particles are. The first step to understanding the toxicology of nanoplastics is to build a reliable, ...
Mpox has the potential to become a significant global health threat if taken too lightly, according to scientists at the University of Surrey.
In a letter published in Nature Medicine, researchers highlight how mpox – traditionally spread from animals to humans – is now showing clear signs of sustained human-to-human transmission.
Mpox is a viral infection caused by a virus that belongs to the same family as smallpox. The virus can cause a painful rash, fever, and swollen glands and, in some cases, lead to more serious illness. Mpox usually spreads through ...