Centrifugation liver support using regional mesylate anticoagulation is safe for liver failure patients with high risk of bleeding
2025-04-10
(Press-News.org) Background and objectives
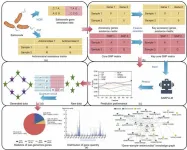
Patients with acute liver failure (ALF) or acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) are at high risk of bleeding with traditional artificial liver support systems. To address the bleeding risk in liver failure patients, the safety of regional mesylate anticoagulation (RMA) in centrifugation artificial liver support systems (cALSS) is proposed for study.
Methods
In this prospective single-arm study, ALF and ACLF patients were treated with cALSS using RMA. Coagulation function was monitored, and the predictors of mesylate dose were analyzed using the area under the curve (AUC). Blood ammonia, model for end-stage liver disease scores, and survival rates at 28 and 90 days were assessed.
Results
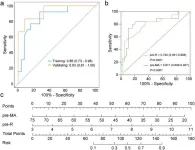
All 57 patients showed no new bleeding within 24 h post-cALSS. Most disseminated intravascular coagulation indicators improved at 0.5 h and 24 h post-cALSS. Thromboelastography showed hypocoagulability at 0.5 h post-cALSS. Univariate and multivariate analyses identified pre-R and pre-MA as key factors for R exceeding 10 m at 0.5 h post-cALSS, with odds ratios of 0.91 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.84–0.98) and 2.03 (95% CI: 1.05–3.90), respectively, P < 0.05. The predictive values were pre-MA ≤ 38 mm (AUC = 0.817, 95% CI [0.690–0.907], P < 0.001) and pre-R > 6.3 m (AUC = 0.790, 95% CI [0.661–0.888], P < 0.001). Patients showed improvements in blood ammonia and model for end-stage liver disease scores after the last session, especially those with high initial levels (>80 µmol/L and >30). The 28-day and 90-day survival rates of ALF patients were similar to those of ACLF patients.
Conclusions
cALSS with RMA is safe for liver failure patients with a high risk of bleeding. Adjusting the mesylate dose based on pre-R and pre-MA enhances safety.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2771-165X/JCTP-2024-00036
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Pathology.
Journal of Clinical and Translational Pathology (JCTP) is the official scientific journal of the Chinese American Pathologists Association (CAPA). It publishes high quality peer-reviewed original research, reviews, perspectives, commentaries, and letters that are pertinent to clinical and translational pathology, including but not limited to anatomic pathology and clinical pathology. Basic scientific research on pathogenesis of diseases as well as application of pathology-related diagnostic techniques or methodologies also fit the scope of the JCTP.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-10
April 10, 2025, ONTARIO — A yearlong campaign from the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) is celebrating the profound difference cancer research is making in the lives of Ontarians.
Cancer Research Changed My Life showcases the people behind research discoveries, bringing their personal stories to life through videos and first-person testimonials.
As the province’s cancer research institute, OICR brings together a community of scientists, cancer patients, clinicians and everyday Ontarians to solve cancer ...
2025-04-10
Washington, April 10, 2025—The American Educational Research Association (AERA) has announced the winners of its 2025 awards for excellence in education research.
“We are pleased to present the 2025 awards to this commendable and exemplary group of education scholars and champions,” said AERA Executive Director Felice J. Levine. “They have contributed tremendously to education research, across all career stages and fields, and continue to make a difference in the lives of students and educators.”
AERA will honor the recipients at the Awards Ceremony Luncheon at the 2025 Annual Meeting in Denver on ...
2025-04-10
A recent study published in Engineering presents a novel approach to predict Salmonella antimicrobial resistance, a growing concern for public health. The research, led by Le Zhang from Sichuan University, combines large language models (LLMs) and quantum computing to develop a predictive platform.
Salmonella is a common foodborne pathogen. The overuse of antimicrobials and genetic mutations have led to the rise of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella strains, making it crucial to predict resistance accurately for effective treatment. However, traditional methods like bacterial antimicrobial susceptibility tests (ASTs) are inefficient, ...
2025-04-10
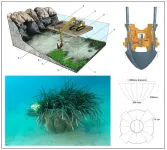
A study has resulted in the transplantation of 384 m² of Posidonia oceanica seagrass on the scale of an industrial project as part of maritime works in Monaco. This success challenges the idea that these ecosystems are "non-transplantable". This unprecedented experiment, conducted over a period of eight years, opens up new prospects for the preservation of seagrass meadows threatened by coastal urbanisation.
As part of the construction project for the "Mareterra" district in Monaco, the marine works involved the destruction of several hectares of Posidonia oceanica meadows, an underwater plant essential to the Mediterranean ...
2025-04-10
Everyone wants good quality healthcare, but what exactly is quality and how do you measure it?
Is it to do with the waiting time for home care services? Or how many nursing home residents have had medical supervision in the past year? Or whether the medication lists have been checked recently?
“These are important aspects that are all worth monitoring. The problem is that quality cannot be easily reduced to a quantifiable value,”said Randi Olsson Haave, an assistant professor and PhD research fellow at the Norwegian University of Science ...
2025-04-10
Beijing (China) and Berlin (Germany) April 10, 2025 - Tsinghua University Press (TUP), the leading university press in China, and ResearchGate, the professional network for researchers, has announced an expansion of its Journal Home partnership, which was the first of its kind with a Chinese publisher last year. This expansion more than doubles TUP’s coverage, now including 11 open access titles.
Since 1980, TUP has maintained a strong presence in China’s higher education, science, and technology sectors. The expanded partnership will increase the visibility of 10,000+ research articles, spanning nano research, AI, computing, ...
2025-04-10
Background
Therapy-related B-lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) following treatment for multiple myeloma is a rare occurrence. Despite its rarity and the lack of recognition by the World Health Organization as a distinct disease entity, previous publications indicate its possible emergence following myeloma treatment.
Case presentation
The patient is a 65-year-old gentleman with a history of IgG kappa multiple myeloma, status post multiple lines of therapy. The patient presented with a fever, and a complete blood count showed cytopenia. Bone marrow morphologic evaluation revealed numerous blasts. ...
2025-04-10
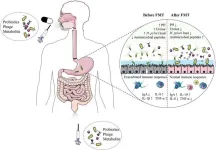
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a widespread bacterial infection associated with gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. While conventional antibiotic-based treatments have been the gold standard for eradication, their efficacy has been steadily declining due to the alarming rise in antibiotic resistance. This has spurred interest in alternative therapies, one of which is fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT).
FMT is a novel therapeutic approach that involves transferring microbiota from a healthy donor to a patient’s ...
2025-04-10
Large granular lymphocytic leukemias (LGLLs) are a heterogeneous group of rare chronic lymphoproliferative disorders characterized by the clonal proliferation of cytotoxic lymphocytes. Among them, T-cell LGLL (T-LGLL) and NK-cell LGLL (NK-LGLL) are the most prominent. Due to overlapping morphological, clinical, and immunophenotypic characteristics, distinguishing these disorders from related entities such as T-prolymphocytic leukemia (T-PLL), adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL), Sézary syndrome (SS), and aggressive NK-cell leukemia (ANKL) presents a significant diagnostic challenge. This review integrates recent molecular insights and updates from the WHO 5th edition ...
2025-04-10
Chemicals used as food preservatives, flavoring agents, dyes, pesticides, cosmetics, cleaners, and other industrial materials are being increasingly recognized as a health hazard. Their rampant use has led to an increase in the prevalence of various chemical toxicity-induced diseases, including hormonal disruption, cancer, neurological disorders, skin conditions, and occupational poisoning. Numerous chemicals are known to trigger “carcinogenesis” or cancer development by exerting genotoxic effects (direct or indirect interference with DNA replication and damage repair processes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Centrifugation liver support using regional mesylate anticoagulation is safe for liver failure patients with high risk of bleeding