(Press-News.org) A fossil Pleistocene-age hominin jawbone discovered in Taiwan has now been identified as belonging to a Denisovan, according to a new paleoproteomic analysis of the remains. The findings provide direct molecular evidence that Denisovans occupied diverse climates, from the cold Siberian mountains to the warm, humid subtropical latitudes of Taiwan, and offer new morphological insights into this enigmatic hominin lineage. Recent research has revealed a surprising variety of ancient human relatives that lived in eastern Asia during the Pleistocene before modern humans arrived. One of the most important discoveries is the Denisovans, a distinct group identified through DNA from fossils in Denisova Cave, Siberia. Studies show that Denisovans were closely related to Neanderthals and interbred with both them and modern humans. However, outside Siberia, direct genetic evidence of Denisovans has only been found on the Tibetan Plateau. While other fossils found across eastern Asia have been proposed as being Denisovan, their classification remains uncertain without molecular confirmation. Here, Takumi Tsutaya and colleagues provide paleoproteomic evidence identifying a fossil hominin mandible (Penghu 1) recovered from the Penghu Channel off Taiwan as belonging to a male Denisovan. The Penghu remains, along with various animal fossils, were retrieved through commercial fishing dredging from the seafloor, which was once part of the Asian mainland during lower sea levels in the Pleistocene. Using ancient proteomic analysis, Tsutaya et al. extracted proteins from bone and dental enamel from the fossil and retrieved 4,241 amino acid residues, two of which were Denisovan-specific protein variants. According to the authors, these variants are rare in modern human populations but have a higher frequency in regions associated with Denisovan genetic introgression. What’s more, morphological analysis of the Penghu 1 remains reveals a robust jaw structure with large molars, and distinctive root structures, features that align with traits seen in the Tibetan Denisovan specimen, suggesting these traits were characteristic of the lineage and perhaps sex-specific.
END
Pleistocene-age Denisovan male identified in Taiwan
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2025-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
KATRIN experiment sets most precise upper limit on neutrino mass: 0.45 eV
2025-04-10
Researchers from the KATRIN (Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino) experiment report the most precise measurement of the upper mass limit of the neutrino to date, establishing it as 0.45 electron volts (eV) – less than one-millionth the mass of an electron. The findings tighten the constraints on one of the universe’s most elusive fundamental particles and push the boundaries of physics beyond the Standard Model. Neutrinos – electrically neutral elementary particles – are the most abundant particles in the universe and ...
How the cerebellum controls tongue movements to grab food
2025-04-10
By studying the skilled movements of marmoset tongues, researchers have discovered that Purkinje cells (P-cells) in a brain region called the cerebellum signal to stop protrusion as the tongue approaches its target, according to a study published April 10th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Reza Shadmehr from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, U.S., and colleagues.
We use our tongue to shape the air and generate sounds to communicate, and we use our tongue to evaluate food morsels and transport them through the oral cavity when eating. These skillful acts involve coordination of more ...
It’s not you—it’s cancer
2025-04-10
Cancer ravages both body and mind. If you’ve ever lost loved ones to the disease, you might recognize the physical and emotional changes cancer patients often endure during their final months. They seem drained of strength and spirit. Even people who’ve maintained a positive outlook throughout their lives can enter a state of despair. New research published in Science suggests apathy and lack of motivation are symptoms of a condition called cancer cachexia. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory ...
Drug pollution alters migration behavior in salmon
2025-04-10
In the largest study of its kind to date, a team of international researchers has investigated how pharmaceutical pollution affects the behaviour and migration of Atlantic salmon.
The study, led by the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, revealed that commonly detected environmental levels of clobazam – a medication often prescribed for sleep disorders – increased the river-to-sea migration success of juvenile salmon in the wild.
The researchers also discovered that clobazam shortened the time it took for juvenile salmon to navigate through two hydropower dams along their migration route – obstacles that typically ...
Scientists decode citrus greening resistance and develop AI-assisted treatment
2025-04-10
In a groundbreaking study published in Science, a research team led by Prof. YE Jian from the Institute of Microbiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has identified the first mechanism of citrus resistance to citrus greening disease, or huanglongbing (HLB).
Utilizing artificial intelligence (AI), the team has also developed antimicrobial peptides that offer a promising therapeutic approach to combat the disease. This discovery addresses a long-standing challenge in the agricultural community—the absence of naturally occurring HLB-resistant genes in citrus.
Citrus ...
Venom characteristics of a deadly snake can be predicted from local climate
2025-04-10
Local climate can be used to predict the venom characteristics of a deadly snake that is widespread in India, helping clinicians to provide targeted therapies for snake bite victims, according to a study publishing April 10 in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases by Kartik Sunagar and colleagues at the Indian Institute of Science.
Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) is found across the Indian subcontinent and is responsible for over 40% of snake ...
Brain pathway links inflammation to loss of motivation, energy in advanced cancer
2025-04-10
The fatigue and lack of motivation that many cancer patients experience near the end of life have been seen as the unavoidable consequences of their declining physical health and extreme weight loss. But new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis challenges that long-held assumption, showing instead that these behavioral changes stem from specific inflammation-sensing neurons in the brain.
In a study published April 11 in Science, the researchers report that they identified a direct connection between cancer-related inflammation ...
Researchers discover large dormant virus can be reactivated in model green alga
2025-04-10
Researchers had been studying the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii for decades without seeing evidence of an active virus within it — until a pair of Virginia Tech researchers waded into the conversation.
Maria Paula Erazo-Garcia and Frank Aylward not only found a virus in the alga but discovered the largest one ever recorded with a latent infection cycle, meaning it goes dormant in the host before being reactivated to cause disease.
“We’ve known about latent infections for a long time,” said Aylward, associate professor in the Department of Biological Sciences. ...
New phase of the immune response uncovered
2025-04-10
The research groups led by Wolfgang Kastenmüller and Georg Gasteiger employed innovative microscopy techniques to observe how specific immune cells, known as T-cells, are activated and proliferate during a viral infection. Their findings revealed novel mechanisms: the immune system amplifies its defense cells in a far more targeted way than previously believed.
T-Cells Proliferate and Specialize During the Immune Response
T-cells are crucial defense cells in the immune system. To effectively ...
Drawing board rather than salt shaker
2025-04-10
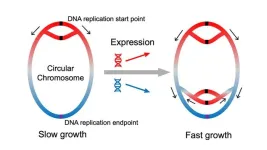
Bioinformaticians from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the university in Linköping (Sweden) have established that the genes in bacterial genomes are arranged in a meaningful order. In the renowned scientific journal Science, they describe that the genes are arranged by function: If they become increasingly important at faster growth, they are located near the origin of DNA replication. Accordingly, their position influences how their activity changes with the growth rate.
Are genes distributed randomly along the bacterial chromosome, as if scattered from a salt shaker? This opinion, which is held by a majority of researchers, has ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] Pleistocene-age Denisovan male identified in TaiwanSummary author: Walter Beckwith