(Press-News.org)
Capturing carbon dioxide (CO₂) from industrial emissions is crucial in the fight against climate change. But current methods, like chemical absorption, are expensive and energy-intensive. Scientists have long eyed graphene—an atom-thin, ultra-strong material—as a promising alternative for gas separation, but making large-area, efficient graphene membranes has been a challenge.
Now, a team at EPFL, led by Professor Kumar Agrawal, has developed a scalable technique to create porous graphene membranes that selectively filter CO₂ from gas mixtures. Their approach slashes production costs while improving membrane quality and performance, paving the way for real-world applications in carbon capture and beyond.
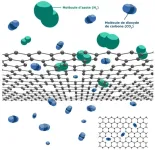
Graphene membranes are excellent at separating gases because they can be engineered with pores just the right size to let CO₂ through while blocking larger molecules like nitrogen. This makes them ideal for capturing CO₂ emissions from power plants and industrial processes. But there’s a catch: manufacturing these membranes at a meaningful scale has been difficult and costly.
Most existing methods rely on expensive copper foils to grow high-quality graphene needed for membranes and require delicate handling techniques that often introduce cracks, reducing membrane efficiency. The challenge has been to find a way to create large, high-quality graphene membranes in a cost-effective, reproducible manner.
The EPFL team tackled these challenges head-on. First, they developed a method to grow high-quality graphene on low-cost copper foils, dramatically cutting down material expenses. Then, they refined a chemical process using ozone (O₃) to etch tiny pores into the graphene, allowing for highly selective CO₂ filtration. Crucially, they improved how the gas interacts with the graphene, ensuring uniform pore formation over large areas—a key step toward industrial scalability.
To solve the issue of membrane fragility, the researchers also introduced a novel transfer technique. Instead of floating the delicate graphene film onto a support, which often leads to cracks, they designed a direct transfer process inside membrane module that eliminates handling issues and reduces failure rates to near zero.
Using their new approach, the researchers successfully created 50 cm² graphene membranes—far larger than what was previously feasible—with near-perfect integrity. The membranes demonstrated exceptional CO₂ selectivity and high gas permeance, meaning they efficiently let CO₂ through while blocking unwanted gases.
Moreover, by optimizing the oxidation process, they were able to increase the density of CO₂-selective pores, further enhancing performance. Computational simulations confirmed that improving gas flow across the membrane played a crucial role in achieving these results.
This breakthrough could change the game for carbon capture. Traditional CO₂ capture technologies rely on energy-intensive chemical processes, making them complex and expensive for widespread use. Graphene membranes, on the other hand, require no heat input, and operate using simple pressure-driven filtration, significantly reducing energy consumption.
Beyond carbon capture, this method could be applied to other gas separation needs, including hydrogen purification and oxygen production. With its scalable production process and cost-effective materials, EPFL’s innovation brings graphene membranes one step closer to commercial viability.
Reference
Jian Hao, Piotr Mieczyslaw Gebolis, Piotr Marcin Gach, Mojtaba Chevalier, Luc Sébastien Bondaz, Ceren Kocaman, Kuang-Jung Hsu, Kapil Bhorkar, Deep J. Babu, Kumar Varoon Agrawal. Scalable synthesis of CO₂-selective porous single-layer graphene membranes. Nature Chemical Engineering 11 April 2025. DOI: 10.1038/s44286-025-00203-z
END
Researchers have developed a simple and cost-effective blood test capable of detecting Parkinson’s disease long before symptoms emerge, comparing the current state of diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases to the fight against cancer 50 years ago—when most cases were identified too late for effective treatment. The test quantifies specific RNA fragments in the blood, focusing on a repetitive RNA sequence that accumulates in Parkinson’s patients and a parallel decline in mitochondrial RNA, which deteriorates as the disease progresses. By measuring the ratio between these biomarkers, the test offers a highly accurate, non-invasive, rapid and affordable diagnostic tool, ...
A novel paper led by Dr Ulrich Brose of the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the Friedrich Schiller University Jena is widening understanding of how species interact within ecosystems via the so-called “Internet of Nature.” Published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, the paper reveals that species not only exchange matter and energy but also share vital information that influences behaviour, interactions, and ecosystem dynamics – revealing previously hidden characteristics of natural ecosystems.
Traditionally, ecological studies have ...
Police officers are more than twice as likely to have traumatic brain injuries compared to the general population. Officers who incur these injuries while on duty face more than double the risk of developing complex post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
That’s according to a new survey-based study from the University of Exeter, published in The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, which found a connection between traumatic brain injuries and PTSD in police officers. Authors say the findings ...
SINGAPORE, 11 APRIL 2025—Duke-NUS Medical School has appointed Professor Patrick Tan as its next and fourth Dean, effective 1 January 2026, marking a new chapter for the School as it builds on its legacy of medical education, research and innovation. Prof Tan will serve as Dean-designate from 1 July 2025, succeeding Professor Thomas Coffman, the School’s longest-serving Dean since 2015. This leadership transition coincides with the School’s 20th anniversary, underscoring Duke-NUS’ commitment to advancing ...
Since cefixime and tellurite are known to inhibit most bacteria belonging to Enterobacterales, we found that addition of tellurite inhibited E. albertii growth in Luria Bertani broth but not in tryptic soy broth (TSB), and addition of phosphate and soy peptone enhanced E. albertii growth in TSB in presence of tellurite.
Subsequently, to find the positive factor present in TSB, E. albertii growth was examined in tryptone, soy peptone, glucose, or phosphate deficient tryptic soy agar plates. Phosphate, soy peptone, and/or ...
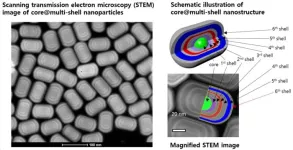
Dr. Ho Seong Jang and colleagues at the Extreme Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed an upconversion nanoparticle technology that introduces a core@multi-shell nanostructure, a multilayer structure in which multiple layers of shells surround a central core particle, and enables high color purity RGB light emission from a single nanoparticle by adjusting the infrared wavelength.
Luminescent materials are materials that light up on their own and are used in a variety of display devices, including TVs, tablets, monitors, and smartphones, to allow us to view a variety of images ...
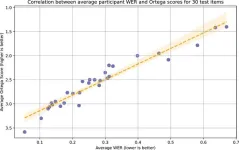
In today’s increasingly interconnected world, language learning has become essential for education, business, and cultural exchange. However, accurately measuring proficiency in language learners is a complex matter. One particularly valuable approach involves asking learners to listen to sentences and then repeat them back as accurately as possible. Known as elicited imitation (EI), this method reveals much more than mere memory and mimicking abilities. When sentences exceed our working memory capacity—typically beyond 8 to 10 syllables—successful repetition requires learners to quickly process and ...
The persistent higher rate of alcohol deaths in England since the pandemic in 2020 is an “acute crisis” requiring urgent action from government, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL and the University of Sheffield.
For the study, published in Lancet Public Health, researchers analysed Office for National Statistics (ONS) figures of deaths caused solely by alcohol in England. They found that death rates were stable between 2009 and 2019, but increased by a fifth in 2020, rising by a further 13.5% between 2020 and 2022.
The team estimated that 3,911 more people had died solely because of alcohol in England ...
Decarbonisation in the automotive and housing sectors is paramount if the UK’s legally binding commitment to achieving net zero by 2050 is to succeed, say researchers at University of Sheffield
Exploring the presence of socioeconomic inequalities in the uptake of low-carbon technologies (LCTs), such as solar panels and electric vehicles, has important policy implications for the decarbonisation in the UK
The new report advocates for interventions at an individual, as well as community-level, to help those from more disadvantaged backgrounds adopt technologies that ...
TAMPA, Fla. (Apr. 10, 2025) — A multi-institutional study led by Moffitt Cancer Center found that percutaneous hepatic perfusion using a melphalan hepatic delivery system may help patients with a rare eye cancer that has spread to their liver. This disease, known as metastatic uveal melanoma, is traditionally very hard to treat and usually has poor outcomes.
The phase 3 FOCUS trial, published in the Annals of Surgical Oncology, compared two treatments for metastatic uveal melanoma. One group of patients received the melphalan hepatic delivery system treatment, while the other group received standard of care treatment. Patients treated with the melphalan hepatic delivery ...