(Press-News.org) Rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) diagnoses dropped during and shortly after Hurricanes Irma and Maria and the COVID-19 pandemic in Puerto Rico, according to a recent analysis. However, late-stage diagnoses eventually exceeded expectations, suggesting that limited access to cancer screening services due to these disasters likely hindered timely CRC diagnoses. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
During disasters, medical services may be delayed or inaccessible due to damaged infrastructure, overburdened health care facilities, or shortages of medical personnel. This can lead to late diagnoses, interruptions in treatment, and an overall worsening of survival and other health outcomes for patients.
To assess the impact of Hurricanes Irma and Maria and the COVID-19 lockdown restrictions on CRC diagnoses, investigators analyzed 2012–2021 data from the Puerto Rico Central Cancer Registry, which has been collecting information on all cancer cases diagnosed and treated in Puerto Rico since 1950.
The team led by investigators at the University of Puerto Rico found that from 2012–2021, a total of 18,537 residents received a first-time diagnosis of CRC. In the month the hurricanes struck, 161.4 CRC cases would have been expected in the absence of any interruption, but instead, only 82 cases were diagnosed.
After a slight upward trend, there was a second decline following the COVID-19 lockdown restrictions. In April 2020, the observed number of CRC cases was 50, but the expected number of cases without interruptions would have been 162.5.
By the end of the study, the estimated numbers of patients with early-stage CRC and those aged 50–75 years (the recommended screening age range) did not reach expected numbers. Meanwhile, numbers of patients with late-stage CRC and those outside the recommended screening age range (<50 years and ≥76 years) exceeded expected numbers.
“These findings suggest that limited health care access during these events may have delayed cancer detection and may have worsened health outcomes. This issue is especially critical in Puerto Rico, since the health care system already faces important challenges,” said co–lead author Tonatiuh Suárez-Ramos, MS. “Understanding these disruptions can help develop more adaptable and resilient strategies to ensure the continuity of essential care,” added co-lead author Yisel Pagán-Santana, DrPH.
Senior author Karen J. Ortiz-Ortiz, DrPH, stressed the urgent need for policies that strengthen health care systems in Puerto Rico and other regions that face similar challenges. “By evaluating the impact of events like hurricanes and the COVID-19 pandemic, we hope to start the conversation about long-term solutions to improve cancer care coordination, reduce health disparities, and ensure continued access to care,” she said. “Ultimately, our goal is to help people live longer, healthier lives by making health care systems more resilient and accessible, even in times of crisis.”
Additional information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. A free abstract of this article will be available via the CANCER Newsroom upon online publication. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com
Full Citation:
“Evaluating the Impact of Hurricanes and the COVID-19 Pandemic on Colorectal Cancer Incidence in Puerto Rico: An Interrupted Time-Series Analysis.” Tonatiuh Suárez-Ramos, Samantha Verganza, Yisel Pagán-Santana, Maira A. Castañeda-Avila, Carlos R. Torres-Cintrón, Eduardo J. Santiago-Rodríguez, and Karen J. Ortiz-Ortiz. CANCER; Published Online: April 14, 2025 (DOI: 10.1002/cncr.35793).
URL Upon Publication: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/cncr.35793
Author Contact: Ana Avilés, Communications Officer at the University of Puerto Rico Comprehensive Cancer Center, at anaviles@cccupr.org or +1 787-772-8300 ext. 1259.
About the Journal
CANCER is a peer-reviewed publication of the American Cancer Society integrating scientific information from worldwide sources for all oncologic specialties. The objective of CANCER is to provide an interdisciplinary forum for the exchange of information among oncologic disciplines concerned with the etiology, course, and treatment of human cancer. CANCER is published on behalf of the American Cancer Society by Wiley and can be accessed online. Follow CANCER on X @JournalCancer and Instagram @ACSJournalCancer, and stay up to date with the American Cancer Society Journals on LinkedIn.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Do disasters delay early cancer diagnoses?
Study reveals fewer colorectal cancer diagnoses during hurricanes and the COVID-19 pandemic but eventually elevated rates of late diagnoses.
2025-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rise and shine: Natural light lessens morning fatigue
2025-04-14
Sleep is a necessary part of people’s daily routine, but modern lifestyles and technology have ushered in an era of decreased rest time and subsequent fatigue. Further, the bedroom environment, such as light, sound, and temperature, is important for a good night's sleep, though this is often neglected in residential architecture.
In search of a conclusive remedy, common sleep studies use artificial light that is easy to control. Osaka Metropolitan University researchers, however, believe natural light could be more effective for re-creating actual living environments.
To test this, Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology student Xiaorui Wang and Professor ...
Nature’s plan for delaying pest resistance deciphered
2025-04-14
Farmers in dozens of countries have embraced crops genetically engineered to produce proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) bacteria that kill some key pests yet are safe for people and wildlife. Although this biotech approach reduces reliance on insecticide sprays thereby providing economic and environmental benefits, resistance to Bt crops has evolved in at least 11 species of pests. Thus, effective ways to combat such pest resistance are urgently needed.
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences identifies a natural strategy for thwarting pest resistance to Bt proteins. The researchers at the University of Arizona and ...
New guidance for managing obesity in children and adolescents
2025-04-14
A new guideline to help health care providers manage obesity in children and adolescents takes a patient-centred approach, emphasizing behavioural and psychological supports that focus on outcomes valued by patients and their families.
The guidelinehttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241456, based on the latest evidence, is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
It was developed by Obesity Canada through an extensive, 4-year-long collaboration involving adolescents and caregivers with lived obesity experience, methodologists, health care providers, and more than 50 multidisciplinary ...
High blood pressure? Eat more bananas
2025-04-14
New research from the University of Waterloo suggests increasing the ratio of dietary potassium to sodium intake may be more effective for lowering blood pressure than simply reducing sodium intake.
High blood pressure affects over 30 per cent of adults globally. It's the leading cause of coronary heart disease and stroke and may also lead to other afflictions like chronic kidney disease, heart failure, irregular heartbeats, and dementia.
"Usually, when we have high blood pressure, we are advised to eat less salt," said Anita Layton, professor of Applied Mathematics, ...
Weak evidence behind how we measure pain in babies
2025-04-14
A newly-published Cochrane review reveals significant gaps in the clinical rating scales used to assess pain in newborn babies, highlighting the urgent need for improved tools and global collaboration.
Despite the critical importance of accurately measuring pain in newborns, the review found that none of the available scales are backed by the high-quality evidence and methodological safeguards required to confirm their validity and reliability in clinical practice.
Neonatal pain assessment and management presents a challenge for clinical staff worldwide. Over 40 rating scales have been developed and adapted worldwide assessing ...
Novel breath test shows promise for diagnosing and monitoring bacterial infections
2025-04-13
This release has been removed upon request of the submitting institution. Please contact Luke Paskins, luke.paskins@beyondpr.com for more information. END ...
AI-guided lung ultrasound marks a major breakthrough in tuberculosis diagnosis
2025-04-13
(Monday, 14 April 2025, Vienna, Austria) A pioneering study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has demonstrated that an AI-powered lung ultrasound outperforms human experts by 9% in diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis (TB).1
The ULTR-AI suite analyses images from portable, smartphone-connected ultrasound devices, offering a sputum-free, rapid, and scalable alternative for TB detection. The results exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) benchmarks for pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis, marking a major opportunity for accessible and efficient TB triage.
Despite previous global declines, TB rates rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023.2 Early ...
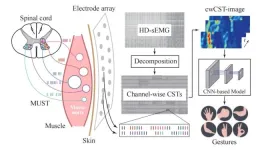
Towards hand gesture recognition using a channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model
2025-04-13
A research paper by scientists at Shanghai Jiao Tong University presented a novel channel-wise cumulative spike train image-driven model (cwCST-CNN) for hand gesture recognition.
The research paper, published on Mar. 21, 2025 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, leverage a custom convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract both local and global features for classifying hand gestures, by decomposing high-density surface EMG (HD-sEMG) signals into channel-wise cumulative spike trains (cw-CSTs) ...
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
2025-04-12
Parasitic infection and treatment linked to cancer-related gene activity in the cervix
New research has revealed that Schistosoma haematobium (S. haematobium), a parasitic infection affecting millions globally, can trigger cancer-related gene activity in the cervical lining, with changes becoming even more pronounced after treatment.1 Presented today at ESCMID Global 2025, this pivotal study sheds new light on how this often-overlooked parasitic disease may contribute to cervical cancer risk at the molecular level.
Schistosomiasis is a widespread parasitic disease, particularly prevalent in regions with poor access to clean water and sanitation.2 ...
Over 3 million children died from AMR-related infections in 2022, major study shows
2025-04-12
A landmark study presented today at ESCMID Global 2025 has revealed that over 3 million children worldwide lost their lives in 2022 due to antimicrobial resistance (AMR)-related infections.1
The study underscores the urgent need for both regional and global strategies to control paediatric AMR, particularly in high-burden areas such as South-East Asia and Africa. AMR poses a critical threat to children, who are highly vulnerable to infections.2 Access to new antibiotic formulations is often much more limited for children because of product development delays.
The study data found ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
[Press-News.org] Do disasters delay early cancer diagnoses?Study reveals fewer colorectal cancer diagnoses during hurricanes and the COVID-19 pandemic but eventually elevated rates of late diagnoses.