(Press-News.org)
A team of researchers at UCL and UCLH have identified the key brain regions that are essential for logical thinking and problem solving.
The findings, published in Brain, help to increase our understanding of how the human brain supports our ability to comprehend, draw conclusions, and deal with new and novel problems – otherwise known as reasoning skills.
To determine which brain areas are necessary for a certain ability, researchers study patients with brain lesions (an area of damage in the brain) caused by stroke or brain tumours. This approach, known as ‘lesion-deficit mapping’, is the most powerful method for localising function in the human brain.
Studying brain injuries can be difficult and time-consuming because researchers need a large number of patients with specific brain damage. This kind of damage can affect how a person thinks, feels, or moves. However, very few research centres have access to enough patients to conduct these studies effectively.
As a result, previous studies have mainly relied on functional imaging (fMRI) techniques in healthy individuals. However, these results can sometimes be misleading as they provide correlational rather than causal evidence.
The new study, led by researchers at the UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and Department of Neuropsychology at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, UCLH, used lesion-deficit mapping to investigate 247 patients with unilateral focal brain lesions in either the left or right frontal (front) or posterior (back) regions of the brain. An additional 81 healthy individuals served as controls.
To assess reasoning skills in these patients, the researchers developed two new tests.
These included a verbal analogical reasoning task (a type of puzzle where participants are asked to find relationships between words to solve problems), which included questions such as: “If Sarah is smarter than Diana and Sarah is smarter than Heather, is Diane smarter than Heather?”.
And a nonverbal deductive reasoning task (a type of puzzle where participants are asked to use pictures, shapes or numbers to figure out logical patterns and solve problems), with questions like: “Which set of numbers is 1,2,3 most similar to – 5,6,7 or 6,5,7?”.
The results showed that people with damage to the right frontal lobe had a much harder time on both tests compared to those with damage in other areas. They made about 15% more mistakes than the other patients and healthy individuals.
Lead author, Dr Joseph Mole (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and Department of Neuropsychology, UCLH) said: “Our study explores how the front right part of the brain helps people think and solve new problems.
“It also shows that our two new tests can help detect reasoning problems in individuals with brain damage, improving diagnosis and treatment.”
Senior author, Professor Lisa Cipolotti (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology and Department of Neuropsychology, UCLH) added: “By combining a detailed cognitive investigation in a large sample of brain damaged patients with advanced lesion mapping techniques - developed by Professor Parashkev Nachev and his team at the UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology - we have deepened our understanding of the complex and, so far, poorly understood, neural structures underlying human reasoning.
“Our findings show a close connection between the right frontal brain network involved in reasoning and the right frontal brain network essential for fluid intelligence (our ability to solve problems without prior experience). This suggests that a common area of the brain plays a critical role in both reasoning and fluid intelligence.”
The researchers believe that these findings have significant clinical implications, as the two new tests can help identify cognitive impairments that would otherwise go undetected.
With further validation and implementation, the team aim to make their new reasoning tests widely available in the NHS, addressing an unmet need for tools specifically designed for assessing right frontal lobe dysfunction.
The study was funded by Wellcome and the National Institute for Health and Care Research University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre (NIHR UCLH BRC) funding scheme. The researchers also received funding from The National Brain Appeal and the Guarantors of Brain.
END
Wildflowers growing on land previously used for buildings and factories can accumulate lead, arsenic and other metal contaminants from the soil, which are consumed by pollinators as they feed, a new study has found.
The metals have previously been shown to damage the health of pollinators, which ingest them in nectar as they feed, leading to reduced population sizes and death. Even low nectar metal levels can have long-term effects, by affecting bees’ learning and memory - which impacts their foraging ability.
Researchers have found that common plants including white clover and bindweed, which ...
The study, published in the journal Addiction and funded by Cancer Research UK, looked at survey data on vaping habits in England, Wales and Scotland before and after the UK Government announced plans to restrict vaping, including by banning disposable vapes, in January 2024.
The team found that the proportion of people vaping increased by nearly a quarter each year from January 2022 to January 2024, but stayed constant between January 2024 and January this year, including for young people.
After January 2024, they also found a substantial decline in the proportion of vapers mainly using disposable e-cigarettes. Among 16- to 24-year-olds, the proportion ...
TAMPA, Fla. (April 15, 2025) – The University of South Florida recently hosted the inaugural Invention Convention Florida at the University of South Florida, an event noted for showcasing the creativity and problem-solving of the next generation of changemakers. Moere than 150 K–12 student inventors from across the state visited USF’s Tampa campus on April 12 to present original solutions to real-world challenges ranging environmental issues to everyday inconveniences.
Invention Convention Florida, ...
Prescribed burns literally fight fire with more fire. Often referred to as a “beneficial fire,” they target areas at risk for wildfires and burn away material that could otherwise fuel a future blaze.
However, all fires, whether accidental or planned, produce smoke that can cause health and respiratory issues, especially in nearby communities. Burning fires release harmful chemicals, like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), that are carcinogenic – PAHs can cause cancer, lung damage, and lead to weakened immunity in those who inhale smoke.
Recently, in a study published in Atmospheric ...
Inactive ingredients in agricultural, pharmaceutical and other common products have typically been excluded from consideration as potential contaminants in drinking water. However, while these chemicals are inert in certain products, they still can pose hazards when combined with other materials during the drinking water treatment process.
A new study from researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis reveals how large this impact might be. Jean Brownell, a graduate student working with Kimberly Parker, associate professor of energy, environmental & chemical engineering, ...
UC Santa Cruz Assistant Professor of Environmental Studies Scott Winton has been wading through thick, smelly muck in the tropics for almost a decade. He wouldn’t have it any other way. As a wetland ecologist and biogeochemist, he’s been hard at work investigating an important and mysterious topic: peatlands.
Peatlands are a special type of wetland with enormous potential to either help or hurt global efforts to address climate change. If we want peatlands on our side, we’ll have to protect them. But that’s difficult to do, since we still don’t ...
CLEVELAND – A new study from University Hospitals Connor Whole Health found that it was feasible to conduct a hybrid music therapy intervention for patients with heart failure and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Participants reported positive effects on their mental health, and the pilot uncovered solutions to improve future research with this population. The findings from this study were recently published in BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.
Patients with chronic illnesses such as heart failure and COPD face significant challenges due ...
Heitor Medeiros, MD, and A. Sassan Sabouri, MD, of the Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, are the lead and corresponding authors, respectively, of a paper published in the British Journal of Anaesthesia (BJA).
How would you summarize your study?
Spinal anesthesia is widely used to numb patients during surgery, but its effects sometimes wear off too soon. Many anesthetists have experimented with adding extra drugs to extend pain relief. Dexmedetomidine demonstrated results in multiple randomized clinical trials suggesting it could prolong numbness ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
April 15, 2025
BATON ROUGE – The 2025 Bray Obesity Symposium welcomes all health physicians and researchers interested in the latest in metabolic health to register for the on-demand online offerings. The online-only content is available to access upon registration, and the symposium has been designated by the American Board of Obesity Medicine, or ABOM, as a Group One Primary Medicine Continuing Medical Education partner.
The symposium is an intensive Board Review Course in preparation for the ABOM’s certification exam, including materials ...
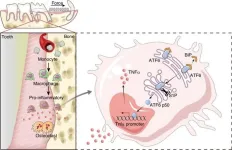
Orthodontic treatments often take years, but a breakthrough discovery could drastically shorten this period. Researchers have uncovered that ATF6, a protein activated in macrophages during corticotomy, accelerates tooth movement by promoting inflammation and boosting the production of TNFα, a key factor in bone remodeling. This finding paves the way for faster, more efficient orthodontic procedures, minimizing both treatment time and patient discomfort. The study highlights the potential for non-invasive therapies that could reshape the future of orthodontic care.
Corticotomy, a surgical procedure aimed at accelerating tooth movement, ...