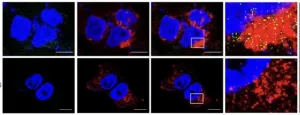
(Press-News.org) Shedding light on how the brain fine-tunes its wiring during learning, a new study finds that different dendritic segments of a single neuron follow distinct rules. The findings challenge the idea that neurons follow a single learning strategy and offer a new perspective on how the brain learns and adapts behavior. The brain's remarkable ability to learn and adapt is rooted in its capacity to modify the connections within its neural circuits – a phenomenon known as synaptic plasticity, in which specific synapses are altered to reshape neural activity and support behavioral change. Neurons, unlike most other cell types, are characterized by their intricate, tree-like dendritic arbors, which extend from the cell body and serve as the primary site for receiving signals from other neurons via synaptic inputs. These dendrites are not uniform; instead, they are organized into distinct compartments with specialized anatomical and biophysical properties which likely influence how various patterns of neural activity trigger the biochemical processes that underlie synaptic plasticity. However, how the brain determines which synapses should be modified during learning and whether individual neurons apply the same plasticity rules uniformly across their structurally and functionally distinct dendritic compartments remains unknown.
To explore how synapses function and adapt during learning, William Wright and colleagues used advanced imaging to observe single synapses in the motor cortex of mice as the animals learned new motor skills. Wright et al. trained mice on a motor task known to drive synaptic plasticity in layer 2/3 motor cortex neurons, observing clear behavioral signs of learning over two weeks. Then, to investigate how individual synapses adapt during this process, Wright et al. used in vivo two-photon imaging with molecular sensors that simultaneously tracked synaptic input (via glutamate release) and neuronal output (via calcium activity). The authors discovered that learning-related patterns of neural activity drive synaptic plasticity differently across dendritic compartments. In apical dendrites, synapses were strengthened when they were coactive with nearby neighbors, suggesting that plasticity here is governed by local interactions between adjacent inputs. In contrast, plasticity in basal dendrites was linked to the neuron's overall output—strengthening or weakening depending on how synapse activity aligned with global action potential firing. Suppressing a neuron's activity selectively impaired plasticity in basal, but not apical, dendrites. In a related Perspective, Ayelén Groisman and Johannes Letzkus discuss the study and its findings in greater detail.
END
Surprise: Synapses on single neurons follow distinct rules during learning
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2025-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fresh insights into why solid-state batteries fail could inform longer-lasting batteries
2025-04-17
Solid-state lithium batteries fail for the same reason over-bent paperclips snap – metal fatigue in the anode itself, according to a new study. The findings, which show that this fatigue follows well-documented mechanical behavior, provide a quantitative framework for predicting the cycle life of solid-state batteries, enabling new pathways for designing longer-lasting and safer energy storage systems. Solid-state lithium metal batteries (SSBs) promise both high energy and improved safety by combining a lithium ...
Curiosity rover identifies carbonates, providing evidence of a carbon cycle on ancient Mars
2025-04-17
NASA’s Curiosity rover has uncovered a hidden chemical archive of ancient Mars’ atmosphere, which suggests that large amounts of carbon dioxide have been locked into the planet’s crust, according to a new study. The findings provide in situ evidence that a carbon cycle once operated on ancient Mars and offer new insights into the planet’s past climate. The Martian landscape shows clear signs that liquid water once flowed across its surface, which would have required ...
Up to 17% of global cropland contaminated by toxic heavy metal pollution, study estimates
2025-04-17
Based on data from over 1000 regional studies combined with machine learning, researchers estimate that as many as 1.4 billion people live in areas with soil dangerously polluted by heavy metals like arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, chromium, copper, nickel, and lead. The study reveals a global risk, but also a previously unrecognized high-risk, metal-enriched zone in low-latitude Eurasia, in particular. The growth in demand for critical metals means toxic heavy metal pollution in soils is only likely to worsen. “We hope that the global soil pollution data presented in this report will ...
Curiosity rover finds large carbon deposits on Mars
2025-04-17
Research from NASA’s Curiosity rover has found evidence of a carbon cycle on ancient Mars, bringing scientists closer to an answer on whether the Red Planet was ever capable of supporting life.
Lead author Dr. Ben Tutolo, PhD, an associate professor with the Department of Earth, Energy and Environment in the Faculty of Science at the University of Calgary, is a participating scientist on the NASA Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity Rover team.
The team is working to understand climate transitions and habitability on ancient Mars as Curiosity explores Gale Crater.
The paper, published this week in the journal Science, reveals that ...
CHOP, Penn Medicine researchers use deep learning algorithm to pinpoint potential disease-causing variants in non-coding regions of the human genome
2025-04-17
Philadelphia, April 17, 2025 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (Penn Medicine) have successfully employed an algorithm to identify potential mutations which increase disease risk in the noncoding regions our DNA, which make up the vast majority of the human genome. The findings could serve as the basis for detecting disease-associated variants in a range of common diseases. The findings were published online today by the American Journal of Human Genetics.
While certain sections ...
Prevalence of obesity with and without confirmation of excess adiposity among US adults
2025-04-17
About The Study: Among U.S. adults ages 20 to 59, the prevalence of obesity by body mass index (BMI) only was nearly identical with the obesity prevalence after confirmation of excess adiposity. Approximately 98% of individuals identified as having obesity based on BMI had excess adiposity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Michael Fang, PhD, MHS, email mfang9@jh.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2025.2704)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Population attributable fraction of incident dementia associated with hearing loss
2025-04-17
About The Study: The results of this cohort study suggest that treating hearing loss might delay dementia for a large number of older adults. Public health interventions targeting clinically significant audiometric hearing loss might have broad benefits for dementia prevention. Future research quantifying population attributable fractions should carefully consider which measures are used to define hearing loss, as self-reporting may underestimate hearing-associated dementia risk.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding ...
New study reveals how cleft lip and cleft palate can arise
2025-04-17
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Cleft lip and cleft palate are among the most common birth defects, occurring in about one in 1,050 births in the United States. These defects, which appear when the tissues that form the lip or the roof of the mouth do not join completely, are believed to be caused by a mix of genetic and environmental factors.
In a new study, MIT biologists have discovered how a genetic variant often found in people with these facial malformations leads to the development of cleft lip and cleft palate.
Their findings suggest that the variant diminishes cells’ supply of transfer RNA, a molecule ...
Scientists hack cell entry to supercharge cancer drugs
2025-04-17
A new discovery could pave the way for more effective cancer treatment by helping certain drugs work better inside the body.
Scientists at Duke University School of Medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, and University of Arkansas have found a way to improve the uptake of a promising class of cancer-fighting drugs called PROTACs, which have struggled to enter cells due to their large size.
The new method works by taking advantage of a protein called CD36 that helps pull substances into cells. By designing drugs to use this CD36 pathway, researchers delivered 7.7 to 22.3 times more of the drug inside cancer cells, making ...
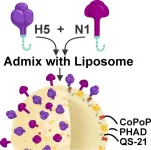
Study: Experimental bird flu vaccine excels in animal models
2025-04-17
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A vaccine under development at the University at Buffalo has demonstrated complete protection in mice against a deadly variant of the virus that causes bird flu.
The work, detailed in a study published today (April 17) in the journal Cell Biomaterials, focuses on the H5N1 variant known as 2.3.4.4b, which has caused widespread outbreaks in wild birds and poultry, in addition to infecting dairy cattle, domesticated cats, sea lions and other mammals.
In the study, scientists describe a process they’ve developed for creating doses with precise ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] Surprise: Synapses on single neurons follow distinct rules during learningSummary author: Walter Beckwith