Genome of blue stain fungus evolved to bypass tree defense in mountain pine beetle epidemic: UBC
2011-01-26
(Press-News.org) The genome of the fungus that helps mountain pine beetles infect and kill lodgepole pines has been decoded in a University of British Columbia study.
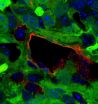
Also known as blue stain fungus for the stain it leaves in the wood of infected trees, Grosmannia clavigera is carried to the host trees by pine beetles and weakens the trees' natural defense system, allowing pine beetles to feed and reproduce in the tree bark. A successful beetle-fungus attack ultimately causes tree death.
Now, researchers from UBC and the BC Cancer Agency's Genome Sciences Centre have conducted a detailed genome analysis and identified genes in Grosmannia clavigera that are responsible for the fungus's ability to bypass the lodgepole pine's natural fungicide – and use it as a carbon source for fungal growth.
The study is published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"We found that the fungus cannot only survive, but thrive when exposed to the normally fungicidal resin chemicals of pines," says co-author Joerg Bohlmann, a Distinguished University Scholar and professor in the Michael Smith Laboratories at UBC. "In a way, it's like these genes give the fungus the ability to turn poison into nectar."
"Our study helps to clarify how the fungus has evolved to successfully infect lodgepole pine and gives us a better understanding of the intricate chemical interaction between the tree, beetle and fungus," says Bohlmann. "This new knowledge could inform strategies to prevent future outbreaks, such as selecting trees with improved resistance to pine beetles and their associated pathogens."
The current outbreak of mountain pine beetle has destroyed more than 16 million hectares of forest in B.C. – roughly twice the size of New Brunswick or more than 32 million football fields. It has crossed the Rocky Mountains, and is now in the boreal pine forests, moving east. The devastation of large areas of pine forest is anticipated to have major consequences for global carbon balance and sequestration.
###
The study was led by Bohlmann, Colette Breuil, a professor in the UBC Department of Wood Science and Scott DiGuistini, a doctoral student in the UBC Faculty of Forestry. It is funded by Genome BC, Genome Alberta, Genome Canada, as well as the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the B.C. Ministry of Forests.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-01-26
MADISON — Future queen or tireless toiler? A paper wasp's destiny may lie in the antennal drumbeats of its caretaker.
While feeding their colony's larvae, a paper wasp queen and other dominant females periodically beat their antennae in a rhythmic pattern against the nest chambers, a behavior known as antennal drumming.
The drumming behavior is clearly audible even to human listeners and has been observed for decades, prompting numerous hypotheses about its purpose, says Robert Jeanne, a professor emeritus of entomology at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Many have ...
2011-01-26
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– A new scientific study shows that debris coverage –– pebbles, rocks, and debris from surrounding mountains –– may be a missing link in the understanding of the decline of glaciers. Debris is distinct from soot and dust, according to the scientists.
Melting of glaciers in the Himalayan Mountains affects water supplies for hundreds of millions of people living in South and Central Asia. Experts have stated that global warming is a key element in the melting of glaciers worldwide.
Bodo Bookhagen, assistant professor in the Department of Geography ...
2011-01-26
Careful dating of new dinosaur fossils and volcanic ash around them by researchers from UC Davis and UC Berkeley casts doubt on the idea that dinosaurs appeared and opportunistically replaced other animals. Instead -- at least in one South American valley -- they seem to have existed side by side and gone through similar periods of extinction.
Geologists from Argentina and the United States announced earlier this month the discovery of a new dinosaur that roamed what is now South America 230 million years ago, at the beginning of the age of the dinosaurs. The newly discovered ...
2011-01-26
New research led by UC Davis scientists provides insight into why some body organs are more susceptible to cell death than others and could eventually lead to advances in treating or preventing heart attack or stroke.
In a paper published Jan. 21 in the journal Molecular Cell, the UC Davis team and their collaborators at the National Institutes of Health and Johns Hopkins University report that Bax, a factor known to promote cell death, is also involved in regulating the behavior of mitochondria, the structures that provide energy inside living cells.
Mitochondria constantly ...
2011-01-26
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Many of the genes that allow wheat to ward off Hessian flies are no longer effective in the southeastern United States, and care should be taken to ensure that resistance genes that so far haven't been utilized in commercial wheat lines are used prudently, according to U.S. Department of Agriculture and Purdue University scientists.
An analysis of wheat lines carrying resistance genes from dozens of locations throughout the Southeast showed that some give little or no resistance to the Hessian fly, a major pest of wheat that can cause millions of ...
2011-01-26
LA JOLLA, CA--Glioblastoma, the most common and lethal form of brain cancer and the disease that killed Massachusetts Senator Ted Kennedy, resists nearly all treatment efforts, even when attacked simultaneously on several fronts. One explanation can be found in the tumor cells' unexpected flexibility, discovered researchers at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies.
When faced with a life-threatening oxygen shortage, glioblastoma cells can shift gears and morph into blood vessels to ensure the continued supply of nutrients, reports a team led by Inder Verma, Ph.D., ...
2011-01-26
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue University researchers have reproduced portions of the female breast in a tiny slide-sized model dubbed "breast on-a-chip" that will be used to test nanomedical approaches for the detection and treatment of breast cancer.
The model mimics the branching mammary duct system, where most breast cancers begin, and will serve as an "engineered organ" to study the use of nanoparticles to detect and target tumor cells within the ducts.
Sophie Lelièvre, associate professor of basic medical sciences in the School of Veterinary Medicine, and ...
2011-01-26
Baltimore, Md. (January 24, 2011) – A research effort designed to prevent the introduction of viruses to blue crabs in a research hatchery could end up helping Chesapeake Bay watermen improve their bottom line by reducing the number of soft shell crabs perishing before reaching the market. The findings, published in the journal Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, shows that the transmission of a crab-specific virus in diseased and dying crabs likely occurs after the pre-molt (or 'peeler') crabs are removed from the wild and placed in soft-shell production facilities.
Crab ...
2011-01-26
MAYWOOD, Ill. -- The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) has released new medical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Loyola physician Pauline Camacho, MD, was part of a committee that developed the guidelines to manage this major public health issue.
These recommendations were developed to reduce the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures and improve the quality of life for patients. They explain new treatment options and suggest the use of the FRAX tool (a fracture risk assessment tool developed by the World ...
2011-01-26
They said it could be done and now they've done it. What's more, they did it with a GRIN. A team of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California, Berkeley, have carried out the first experimental demonstration of GRIN – for gradient index – plasmonics, a hybrid technology that opens the door to a wide range of exotic optics, including superfast computers based on light rather than electronic signals, ultra-powerful optical microscopes able to resolve DNA molecules with visible ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Genome of blue stain fungus evolved to bypass tree defense in mountain pine beetle epidemic: UBC