(Press-News.org) A new study is the first to examine the effectiveness of a widely used counseling approach to treating substance abuse among African-Americans. The study found that African-American women were more likely than men to continue a counseling approach to treating substance abuse, but their substance-abuse issues continued. The study led by LaTrice Montgomery, a doctoral student in the University of Cincinnati Department of Psychology, is published this month in "Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology," a journal of the American Psychological Association.
The study investigated the effectiveness of Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET) compared with the standard treatment, Counseling as Usual (CAU) – two clinical approaches to treating substance abuse – among African-Americans. The study, a secondary analysis of a clinical trial by the Clinical Trials Network of the National Institute of Drug Abuse, was a rare examination of both treatment retention rates and the effectiveness of MET in reducing drug abuse, specifically among African-Americans.
Motivation Enhancement Therapy is designed to address the ambivalence surrounding substance abuse treatment, whether abusers are at the stage where they're ready to live a substance-free life or whether they're against any treatment.
"The idea of MET is for counselors to help patients build motivation and strengthen commitment to behavior change," Montgomery says. "One technique that is commonly used in MET to facilitate this process is the use of decisional balance exercises which help patients examine the pros and cons of substance use."
"An example would be a patient discussing what he or she considers the 'pros' of substance use, such as drinking alcohol to reduce anxiety," explains Montgomery. "However, despite its ability to help reduce the patient's anxiety, the patient might also acknowledge that heavy drinking negatively influences their interpersonal relationships."
Montgomery added, "The task of the therapist in this situation would be to help the patient develop more reasons to change and identify more effective ways to reduce anxiety."
Previous research has suggested that the toll of substance abuse on African-Americans is greater than on other groups, not only in terms of health but also in the legal system.
The study compared the effectiveness of motivational enhancement therapy compared with counseling as usual over a 16-week period. The participants in the study were 194 African-Americans who were seeking outpatient substance abuse treatment at five different community-based treatment programs across the nation. The study included 146 African-American males (75.3 percent) and 48 females (24.7 percent), with the age of the participants averaging 37.5 years old. They were seeking treatment for issues such as cocaine abuse (25.8 percent), alcohol abuse (26.3 percent) and marijuana abuse (18 percent).
The study revealed higher retention rates among women in MET than in CAU. Men in MET and CAU did not differ in retention.
Among both genders, men and women in MET reported more days per week of substance abuse than participants in CAU.
"Previous studies have suggested that ethnic minorities in MET report more success in reducing substance abuse than non-ethnic minorities, but the studies combined several ethnic groups," explains Montgomery. "This research was examining the effectiveness of the treatment specifically for African-Americans."
"I think MET has a lot of value, in terms of being non-confrontational and non-judgmental as well as supporting self-efficacy," Montgomery says. "We found that the women stayed in MET treatment longer, but they didn't reduce their substance use. That's where my research is taking me now."
###
Secondary authors on the study are UC Psychology Professor Kathy Burlew, Duke University Biostatics and Bioinformatics Associate Professor Andrzej S. Kosinski and University of New Mexico Psychiatry Assistant Professor Alyssa Forcehimes.
Montgomery is currently serving a year-long clinical internship at the Yale University School of Medicine in the division of substance abuse. She is a 2011 recipient of the American Psychological Association's Dalmas A. Taylor Outstanding Student Research Award, which recognizes clinical psychology graduate students who have produced exemplary research on the clinical psychology of ethnic minorities.
Her advisor, Kathy Burlew, is the recipient of the APA's 2011 Kenneth and Mamie Clark Award for Outstanding Contributions to the Professional Development of Ethnic Minority Graduate Students.
http://www.uc.edu/profiles/profile.asp?id=13908
Last spring, Montgomery was honored as Most Outstanding Graduate Student by the UC Graduate Student Governance Association.
Montgomery was born and raised in Cincinnati, grew up in College Hill and is a graduate of Walnut Hills High School.
Research examines approaches to treating substance abuse among African-Americans
2011-10-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Links in the chain: Global carbon emissions and consumption
2011-10-19
Washington, D.C. — It is difficult to measure accurately each nation's contribution of carbon dioxide to the Earth's atmosphere. Carbon is extracted out of the ground as coal, gas, and oil, and these fuels are often exported to other countries where they are burned to generate the energy that is used to make products. In turn, these products may be traded to still other countries where they are consumed. A team led by Carnegie's Steven Davis, and including Ken Caldeira, tracked and quantified this supply chain of global carbon dioxide emissions. Their work will be published ...
2011 a banner year for young striped bass in Virginia
2011-10-19
Preliminary results from a 2011 survey conducted by researchers at the Virginia Institute of Marine Science (VIMS) suggest the production of a strong class of young-of-year striped bass in the Virginia portion of Chesapeake Bay. The 2011 year class represents the group of fish hatched this spring.
The results are good news for the recreational and commercial anglers who pursue this popular game fish because this year class is expected to grow to fishable size in 3 to 4 years. The results are also good news for Chesapeake Bay, where striped bass play an important ecological ...
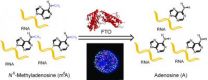
New research links common RNA modification to obesity
2011-10-19
An international research team has discovered that a pervasive human RNA modification provides the physiological underpinning of the genetic regulatory process that contributes to obesity and type II diabetes.
European researchers showed in 2007 that the FTO gene was the major gene associated with obesity and type II diabetes, but the details of its physiological and cellular functioning remained unknown.
Now, a team led by University of Chicago chemistry professor Chuan He has demonstrated experimentally the importance of a reversible RNA modification process mediated ...
NewBlueFX Announces Titler Pro Bundle With Sony Vegas Pro 11
2011-10-19
Innovative video effects creator and technology developer NewBlue, Inc. announces the inclusion of their new Titler Pro with Vegas Pro 11 from Sony, along with 13 other NewBlue plug-ins from 6 best-selling video plug-in collections. NewBlue Titler Pro (MSRP $299.95) is designed for the professional editor's schedule; to make it easy for editors to quickly create 2D & 3D graphics on a timeline.
Titler Pro title animations use the computer's GPU to blend sophisticated 3D modeling with 2D raster processing to generate imagery in real time. Titler Pro also boasts an ...
Farmland floods do not raise levels of potentially harmful flame retardants in milk
2011-10-19
WASHINGTON, Oct. 12, 2011 — As millions of acres of farmland in the U.S. Midwest and South recover from Mississippi River flooding, scientists report that river flooding can increase levels of potentially harmful flame retardants in farm soils. But the higher levels apparently do not find their way into the milk produced by cows that graze on these lands.
That's the reassuring message in the latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS) award-winning "Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions" podcast series.
Iain Lake, Ph.D., notes in the podcast that the flame ...
Muscling toward a longer life: Genetic aging pathway identified in flies
2011-10-19
Researchers at Emory University School of Medicine have identified a set of genes that act in muscles to modulate aging and resistance to stress in fruit flies.
Scientists have previously found mutations that extend fruit fly lifespan, but this group of genes is distinct because it acts specifically in muscles. The findings could help doctors better understand and treat muscle degeneration in human aging.
The results were published online this week by the journal Developmental Cell.
The senior author is Subhabrata Sanyal, PhD, assistant professor of cell biology at ...
"Impact of US Domestic Tonnage Regulations on Design, Maintenance and Manning" Topic of Free WorkBoat.com Webinar on October 26
2011-10-19
Designing a vessel to meet a tonnage parameter has proven to be the bane of designers, builders and owners since the earliest days of the maritime industry. Today, regulations initially established over 140 years ago in a surveyor's office in London can dramatically affect the construction of virtually every commercial vessel at work in the United States.
"Every boat needs to have a tonnage certificate for whatever its type of function and any modification to a vessel can result in ramifications to the tonnage certificate," said David Krapf, editor in chief ...
Amorphous diamond, a new super-hard form of carbon created under ultrahigh pressure
2011-10-19
An amorphous diamond – one that lacks the crystalline structure of diamond, but is every bit as hard – has been created by a Stanford-led team of researchers.
But what good is an amorphous diamond?
"Sometimes amorphous forms of a material can have advantages over crystalline forms," said Yu Lin, a Stanford graduate student involved in the research.
The biggest drawback with using diamond for purposes other than jewelry is that even though it is the hardest material known, its crystalline structure contains planes of weakness. Those planes are what allow diamond ...
Canadian Pharmacy Customers Save Big on Wellbutrin XL
2011-10-19
Canada Drug Pharmacy offers Wellbutrin XL at a cheaper price, much cheaper when compared to purchasing the same drug from traditional retail stores. As more and more people turn to the internet to shop online, they are also searching for ways to save money. One of the benefits of buying Canadian drugs from CanadaDrugPharmacy.com is that the price of prescription medications is cheaper than traditional brick and mortar pharmacies. Purchasing online is also convenient since the consumers don't have to leave their house to buy their medicine. Customers can now log-in to Canada ...
Chinese-Americans don't overborrow, MU study finds
2011-10-19
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Bad mortgage loans and rampant consumer debt were two of the primary causes for the recent economic recession in the U.S. Despite a national trend of debt problems, a University of Missouri researcher has found one American population that holds almost no consumer debt outside of typical home mortgages. Rui Yao, an assistant professor of personal financial planning in the College of Human Environmental Sciences at the University of Missouri, found that while 72 percent of Chinese-American households hold a mortgage, only five percent of those households ...