(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA — Many imaging technologies and their contrast agents — chemicals used during scans to help detect tumors and other problems — involve exposure to radiation or heavy metals, which present potential health risks to patients and limit the ways they can be applied. In an effort to mitigate these drawbacks, new research from University of Pennsylvania engineers shows a way to coat an iron-based contrast agent so that it only interacts with the acidic environment of tumors, making it safer, cheaper and more effective than existing alternatives.
The research was conducted by associate professor Andrew Tsourkas and graduate student Samuel H. Crayton of the department of bioengineering in Penn's School of Engineering and Applied Science. It was published in the journal ACS Nano.
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is an increasingly common feature of medical care. Using a strong magnetic field to detect and influence the alignment of water molecules in the body, MRI can quickly produce pictures of wide range of bodily tissues, though the clarity of these pictures is sometimes insufficient for diagnoses. To improve the differentiation — or contrast — between tumors and healthy tissue, doctors can apply a contrast agent, such as nanoparticles containing iron oxide. The iron oxide can improve MRI images due to their ability to distort the magnetic field of the scanner; areas they are concentrated in stand out more clearly.
These nanoparticles, which have recently been approved in the United States for clinical use as contrast agents, are literally sugar-coated; an outer layer of dextran keeps the particles from binding or being absorbed by the body and potentially sickening the patient. This non-reactive coating allows the iron oxide to be flushed out after the imaging is complete, but it also means that the particles can't be targeted to a particular kind of tissue.
If the contrast agent could be engineered so it only sticks to tissue that is already diseased, such as tumors, it would solve both problems at once. Scientists have tried this approach by coating nanoparticles with proteins that bind only to receptors found on the exterior of tumors, but not all tumors are the same in this regard.
"One of the limitations of a receptor-based approach is that you just don't hit everything," Tsourkas said. "It's hard to recommend them as a screening tool when you know that the target receptors are only expressed in 30% of tumors."
"One of the reasons we like our approach is that it hits a lot of tumors; almost all tumors exhibit a change in the acidity of their microenvironment."
The Penn engineers took advantage of something known as the Warburg effect, a quirk of tumor metabolism, to get around the targeting problem. Most of the body's cells are aerobic; they primarily get their energy from oxygen. However, even when oxygen is plentiful, cancerous cells use an anaerobic process for their energy. Like overtaxed muscles, they turn glucose into lactic acid, but unlike normal muscles, tumors disrupt the blood flow around them and have a hard time clearing this acid away. This means that tumors almost always have a lower pH than surrounding healthy tissue.
Some imaging technologies, such as magnetic resonance spectroscopy, can also take advantage of tumors' low-pH microenvironments, but they require expensive specialized equipment that is not available in most clinical settings.
By using glycol chitosan — a sugar-based polymer that reacts to acids — the engineers allowed the nanocarriers to remain neutral when near healthy tissue, but to become ionized in low pH. The change in charge that occurs in the vicinity of acidic tumors causes the nanocarriers to be attracted to and retained at those sites.
This approach has another benefit: the more malignant a tumor is, the more it disrupts surrounding blood vessels and the more acidic its environment becomes. This means that the glycol chitosan-coated is a good detector of malignancy, opening up treatment options above and beyond diagnosis.
"You can take any nanoparticle and put this coating on it, so it's not limited to imaging by any means," said Tsourkas. "You could also use it to deliver drugs to tumor sites."
The researchers hope that, within seven to 10 years, glycol-chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles could improve the specificity of diagnostic screening. The ability to accurately detect sites of malignancy by MRI would be an immediate improvement to existing contrast agents for certain breast cancer scans.
"Gadolinium is used as a contrast agent in MRI breast cancer screenings for high-risk patients. These patients are recommended to get an MRI in addition to the usual mammogram, because the sensitivity of mammograms can be poor," said Tsourkas. "The sensitivity of an MRI is much higher, but the specificity is low: the screening detects a lot of tumors, but many of them are benign. Having a tool like ours would allow clinicians to better differentiate the benign and malignant tumors, especially since there has been shown to be a correlation between malignancy and pH."
###
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program.
Penn engineers develop more effective MRI contrast agent for cancer detection
2011-12-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Shearing triggers odd behavior in microscopic particles
2011-12-27
VIDEO:
This 12-second video shows the formation of particle strings at angles perpendicular to the direction of shear flow. Many scientists had predicted that the strings would form parallel to the...
Click here for more information.
Microscopic spheres form strings in surprising alignments when suspended in a viscous fluid and sheared between two plates — a finding that will affect the way scientists think about the properties of such wide-ranging substances as shampoo ...
A new way of approaching the early detection of Alzheimer's disease
2011-12-27
One of our genes is apolipoprotein E (APOE), which often appears with a variation which nobody would want to have: APOEε4, the main genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer's disease (the most common form in which this disorder manifests itself and which is caused by a combination of hereditary and environmental factors). It is estimated that at least 40% of the sporadic patients affected by this disease are carriers of APOEε4, but this also means that much more still remains to be studied. The researcher at the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) Xabier ...
Viagra against heart failure: Researchers at the RUB and from Rochester throw light on the mechanism
2011-12-27
How sildenafil, the active ingredient in Viagra, can alleviate heart problems is reported by Bochum's researchers in cooperation with colleagues from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester (Minnesota) in the journal Circulation. They studied dogs with diastolic heart failure, a condition in which the heart chamber does not sufficiently fill with blood. The scientists showed that sildenafil makes stiffened cardiac walls more elastic again. The drug activates an enzyme that causes the giant protein titin in the myocardial cells to relax. "We have developed a therapy in an animal model ...
A new sensor to detect lung cancer from exhaled breath
2011-12-27
Some illnesses such as lung and stomach cancer or liver diseases which, due to the difficulty of diagnosis, have symptoms that are often confused with routine disorders. Therefore, in most cases, the disease is only detected at an advanced stage. New methods for early detection are being investigated as an urgent need.
Tecnalia, through the Interreg project Medisen, is contributing to develop biosensors capable of detecting the presence of tumour markers of lung cancer in exhaled breath. This is possible because of the changes produced within the organism of an ill person, ...
More accurate than Santa Claus
2011-12-27
Every year for Christmas, the North American Air Defence Command NORAD posts an animation on their website, in which the exact flight path of Santa Claus' sled led by reindeer Rudolf is precisely located (http://www.noradsanta.org/en/). The path of navigation satellites, however, has to be determined much more accurately than Santa's flight path, when precise ground positioning is required. GPS is the best known system of this kind, the European system Galileo is planned to be decidedly more accurate.
On 10 December, seven weeks after the start of the first two Galileo ...
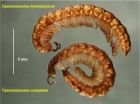
Millipede border control better than ours
2011-12-27
A mysterious line where two millipede species meet has been mapped in northwest Tasmania, Australia. Both species are common in their respective ranges, but the two millipedes cross very little into each other's territory. The 'mixing zone' where they meet is about 230 km long and less than 100 m wide where carefully studied.
The mapping was done over a two-year period by Dr Bob Mesibov, who is a millipede specialist and a research associate at the Queen Victoria Museum and Art Gallery in Launceston, Tasmania. His results have been published in the open access journal ...
Go to work on a Christmas card
2011-12-27
If all the UK's discarded wrapping paper and Christmas cards were collected and fermented, they could make enough biofuel to run a double-decker bus to the moon and back more than 20 times, according to the researchers behind a new scientific study.
The study, by scientists at Imperial College London, demonstrates that industrial quantities of waste paper could be turned into high grade biofuel, to power motor vehicles, by fermenting the paper using microorganisms. The researchers hope that biofuels made from waste paper could ultimately provide one alternative to fossil ...
UK researchers present findings from Kentucky breast cancer patients with disease relapse
2011-12-27
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Dec. 23, 2011) — The University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center breast oncologist Dr. Suleiman Massarweh and his research team presented findings from their studies on relapse of breast cancer at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium this month.
The two studies aimed to characterize further risk factors for presentation with metastatic disease or risk of early metastatic relapse after initial therapy. Data for each study was collected from 1,089 patients at the UK Markey Cancer Center between January 2007 and May 2011.
The studies showed that patients ...
Cleveland Clinic researcher discovers genetic cause of thyroid cancer
2011-12-27
Friday, December 23, 2011, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers have discovered three genes that increase the risk of thyroid cancer, which is has the largest incidence increase in cancers among both men and women.
Research led by Charis Eng, M.D., Ph.D., Chair and founding Director of the Genomic Medicine Institute of Cleveland Clinic's Lerner Research Institute, included nearly 3,000 patients with Cowden syndrome (CS) or CS-like disease, which is related to an increased risk of breast and thyroid cancer.
Mutations in the PTEN gene are the foundation of Cowden ...
What are emotion expressions for?
2011-12-27
That cartoon scary face – wide eyes, ready to run – may have helped our primate ancestors survive in a dangerous wild, according to the authors of an article published in Current Directions in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The authors present a way that fear and other facial expressions might have evolved and then come to signal a person's feelings to the people around him.
The basic idea, according to Azim F. Shariff of the University of Oregon, is that the specific facial expressions associated with each particular emotion ...