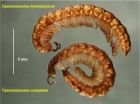
(Press-News.org) A mysterious line where two millipede species meet has been mapped in northwest Tasmania, Australia. Both species are common in their respective ranges, but the two millipedes cross very little into each other's territory. The 'mixing zone' where they meet is about 230 km long and less than 100 m wide where carefully studied.
The mapping was done over a two-year period by Dr Bob Mesibov, who is a millipede specialist and a research associate at the Queen Victoria Museum and Art Gallery in Launceston, Tasmania. His results have been published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
'I have no idea why the line is so sharp', said Dr Mesibov. 'The boundary runs up and down hills, crosses rivers and different bedrocks and soils, and ignores vegetation type and climate differences. Its position and its sharpness seem to be the result of an unexplained biological arrangement between the two millipede species.'
Biogeographers use the term 'parapatry' for the case where two species ranges meet but do not overlap, or overlap very little. Dr Mesibov said that parapatry has been reported before in other species of millipedes and in other terrestrial invertebrate animals, in Tasmania and elsewhere in the world. However, parapatric boundaries often parallel a geographical feature, such as a ridgeline, or a steep rainfall gradient.
'There does not seem to be an ecological or a geographic explanation for this particular boundary, or for any part of it. It is also longer than any other parapatric boundary I know about. At 230 km, it is 50% longer than the boundary between England and Scotland, and the 'border control' is a lot better than what we humans can do.'
The two millipede species, Tasmaniosoma compitale and T. hickmanorum, are in the same genus and thought to be closely related. They were first scientifically described in 2010, by the same author and again in ZooKeys. The parapatric boundary was mapped as a background study for later investigations of speciation in this group of millipedes, and of the mechanism of parapatry.
INFORMATION:
SOURCE
Mesibov R (2011) A remarkable case of mosaic parapatry in millipedes. In: Mesibov R, Short M (Eds) Proceedings of the 15th International Congress of Myriapodology, 18-22 July 2011, Brisbane, Australia. ZooKeys 156: 71. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.156.1893
PREVIOUS NEWS COVERAGE
http://www.abc.net.au/news/2011-08-02/020811-millipedes/2821498 [Australian TV news story, and accompanying online text]
RELATED BACKGROUND
Mesibov, R (2010) The millipede genus Tasmaniosoma Verhoeff, 1936 (Diplopoda: Polydesmida: Dalodesmidae) from Tasmania, Australia, with descriptions of 18 new species. ZooKeys 41: 31-80. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.41.420
Millipede border control better than ours
2011-12-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Go to work on a Christmas card
2011-12-27
If all the UK's discarded wrapping paper and Christmas cards were collected and fermented, they could make enough biofuel to run a double-decker bus to the moon and back more than 20 times, according to the researchers behind a new scientific study.
The study, by scientists at Imperial College London, demonstrates that industrial quantities of waste paper could be turned into high grade biofuel, to power motor vehicles, by fermenting the paper using microorganisms. The researchers hope that biofuels made from waste paper could ultimately provide one alternative to fossil ...
UK researchers present findings from Kentucky breast cancer patients with disease relapse
2011-12-27
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Dec. 23, 2011) — The University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center breast oncologist Dr. Suleiman Massarweh and his research team presented findings from their studies on relapse of breast cancer at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium this month.
The two studies aimed to characterize further risk factors for presentation with metastatic disease or risk of early metastatic relapse after initial therapy. Data for each study was collected from 1,089 patients at the UK Markey Cancer Center between January 2007 and May 2011.
The studies showed that patients ...
Cleveland Clinic researcher discovers genetic cause of thyroid cancer
2011-12-27
Friday, December 23, 2011, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers have discovered three genes that increase the risk of thyroid cancer, which is has the largest incidence increase in cancers among both men and women.
Research led by Charis Eng, M.D., Ph.D., Chair and founding Director of the Genomic Medicine Institute of Cleveland Clinic's Lerner Research Institute, included nearly 3,000 patients with Cowden syndrome (CS) or CS-like disease, which is related to an increased risk of breast and thyroid cancer.
Mutations in the PTEN gene are the foundation of Cowden ...
What are emotion expressions for?
2011-12-27
That cartoon scary face – wide eyes, ready to run – may have helped our primate ancestors survive in a dangerous wild, according to the authors of an article published in Current Directions in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The authors present a way that fear and other facial expressions might have evolved and then come to signal a person's feelings to the people around him.
The basic idea, according to Azim F. Shariff of the University of Oregon, is that the specific facial expressions associated with each particular emotion ...
Pions don't want to decay into faster-than-light neutrinos, study finds
2011-12-27
When an international collaboration of physicists came up with a result that punched a hole in Einstein's theory of special relativity and couldn't find any mistakes in their work, they asked the world to take a second look at their experiment.
Responding to the call was Ramanath Cowsik, PhD, professor of physics in Arts & Sciences and director of the McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis.
Online and in the December 24 issue of Physical Review Letters, Cowsik and his collaborators put their finger on what appears to be an insurmountable ...
A radar for ADAR: Altered gene tracks RNA editing in neurons
2011-12-27
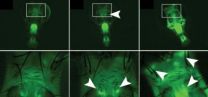
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To track what they can't see, pilots look to the green glow of the radar screen. Now biologists monitoring gene expression, individual variation, and disease have a glowing green indicator of their own: Brown University biologists have developed a "radar" for tracking ADAR, a crucial enzyme for editing RNA in the nervous system.
The advance gives scientists a way to view when and where ADAR is active in a living animal and how much of it is operating. In experiments in fruit flies described in the journal Nature Methods, the researchers ...
New synthetic molecules treat autoimmune disease in mice
2011-12-27
A team of Weizmann Institute scientists has turned the tables on an autoimmune disease. In such diseases, including Crohn's and rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's tissues. But the scientists managed to trick the immune systems of mice into targeting one of the body's players in autoimmune processes, an enzyme known as MMP9. The results of their research appear today in Nature Medicine.
Prof. Irit Sagi of the Biological Regulation Department and her research group have spent years looking for ways to home in on and block members of the ...
Faster, more accurate, more sensitive
2011-12-27
Lightning fast and yet highly sensitive: HHblits is a new software tool for protein research which promises to significantly improve the functional analysis of proteins. A team of computational biologists led by Dr. Johannes Söding of LMU's Genzentrum has developed a new sequence search method to identify proteins with similar sequences in databases that is faster and can discover twice as many evolutionarily related proteins as previous methods. From the functional and structural properties of the identified proteins conclusions can then be drawn on the properties of ...
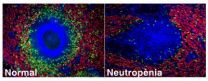
Discovered the existence of neutrophils in the spleen
2011-12-27
This release is available in Spanish.
Barcelona, 23rd of December 2011.- For the first time, it has been discovered that neutrophils exist in the spleen without there being an infection. This important finding made by the research group on the Biology of B Cells of IMIM (Hospital del Mar Research Institute) in collaboration with researchers from Mount Sinai in New York, has also made it possible to determine that these neutrophils have an immunoregulating role.
Neutrophils are the so-called cleaning cells, since they are the first cells to migrate to a place ...
Study links quality of mother-toddler relationship to teen obesity
2011-12-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The quality of the emotional relationship between a mother and her young child could affect the potential for that child to be obese during adolescence, a new study suggests.
Researchers analyzed national data detailing relationship characteristics between mothers and their children during their toddler years. The lower the quality of the relationship in terms of the child's emotional security and the mother's sensitivity, the higher the risk that a child would be obese at age 15 years, according to the analysis.
Among those toddlers who had the lowest-quality ...