(Press-News.org) Wednesday, January 4, 2012 --
CHAPEL HILL – People with high cholesterol are at risk of heart attack and stroke because atherosclerotic plaques within their arteries can rupture triggering the formation of a blood clot called an occlusive thrombus that cuts off the blood supply to their heart or brain.
For years, scientists have studied the cause of this abnormal clotting. Now, a study led by researchers from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, has identified a molecular pathway that leads to this abnormal blood clotting and turned it off using a popular class of cholesterol-lowering drugs, statins.
The research was performed using humans, monkeys and mice with highly elevated blood lipid levels. It indicated that elevated levels of oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL) induces a molecule called "tissue factor" that triggers clotting. The study appears online in the January 3, 2012 issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
"Statins have been shown to have antithrombotic activity in several previous studies. However, I believe our study is the first to elucidate how statins reduce the activation of the blood clotting process independently of their lipid lowering activity, said senior study author Nigel Mackman, PhD, FAHA. Mackman is the John C. Parker Distinguished Professor of Hematology in the Department of Medicine and Director of the UNC McAllister Heart Institute.
Additionally, Mackman noted that statins "only target the 'bad and inducible tissue factor', not the good one used in normal clotting, and therefore should not be associated with the increased bleeding risk that is a typical side effect of anticoagulant drugs currently on the market."
Mackman has spent the last twenty-five years studying tissue factor, the number one initiator of clotting in the body. Tissue factor normally resides outside the blood vessels, only coming into contact with blood after an injury, such as cutting your finger. However, it is expressed at high levels under certain abnormal conditions, such as inside atherosclerotic plaques, and gets turned on in a special subset of blood cells called monocytes. Mackman wondered if this was the cause for the abnormal clotting seen in patients with high cholesterol.
To test his hypothesis, Mackman and his colleagues analyzed humans, monkeys and mice with high cholesterol. They found that all three groups have elevated levels of tissue factor in the circulation.
Then the researchers treated the mice and monkeys with simvastatin, a drug widely used to treat high blood cholesterol levels. They showed that simvastatin reduced levels of oxidized low density lipoprotein and circulating tissue factor which normalized coagulation without altering plasma cholesterol levels.
These results suggest that oxidized low density lipoproteins induce tissue factor expression on monocytes and this contributes to formation of an occlusive thrombus after plaque rupture.
"Though statin therapy is primarily prescribed to lower cholesterol, some added benefits are its anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic activities," said Mackman. "In terms of drug development, I think we should be trying to better understand the antithrombotic activities of statins so we can develop safer antithrombotic drugs that target the expression of inducible tissue factor."
INFORMATION:
The research was funded largely by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, a component of the National Institutes of Health. The majority of this work was performed by A. Phillip Owens III, PhD. Other study co-authors from Dr. Mackman's lab at UNC were Silvio Antoniak, PhD; Julie C. Williams; and Jianguo Wang, PhD.
Benefits of statin therapy may extend beyond lowering lipids
2012-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Patients Avoid Interruptions With Online Appointment Requests Through Santa Monica Cosmetic Dentist
2012-01-05
Father and son dental team, Drs. Roger Lent and Brett Lent, Santa Monica cosmetic dentists, are pleased to offer patients online appointment requesting availability. With their increased online availability, patients are now able to request an appointment with Lent Family Dental without altering their busy schedules.
With just the click of their mouse, patients can visit the practice's website for accessibility to online appointment requests. From the homepage for Lent Family Dental, patients can click on the available link for appointment requests. Once on the appointment ...
Prehistoric predators with supersized teeth had beefier arm bones
2012-01-05
The toothiest prehistoric predators also had beefier arm bones, according to results of a study published today in the journal Paleobiology.
Saber-toothed tigers may come to mind, but these extinct cats weren't the only animals with fearsome fangs.
Take the false saber-toothed cats--also known as nimravids--and their catlike cousins, a family of carnivores called the barbourofelids.
These mammal groups lived millions of years before cats came to be, and had knife-like canines along with well-built arm bones, said Julie Meachen, a paleontologist at the National Science ...
Hamilton Dentist Performs All Dental Work Including Cleanings for Patients
2012-01-05
Patients can rely on Dr. Scot Rosen, Hamilton dentist, for the completion of all of their dental health care needs. Dr. Rosen prides himself in completing all services and procedures to meet his patients' dental health care needs, including dental cleanings.
"It is important that my patients receive superior dental care, and it is my honor to be able to complete all of their needed dental work myself. From routine cleanings to more complex procedures, I pride myself in performing them all," said Dr. Scot Rosen, dentist in Trenton.
By performing available ...
Monaco Retains Title as the World's Most Prestigious Property Address
2012-01-05
Despite the depressing headlines throughout the world's press of late, property for sale in Monaco and the French Riviera is faring particularly well compared to many of its European neighbours.
Recent research has proven that despite restrictive measures enforced by most governments, Europe is still leading the field in the sale of exclusive real estate to wealthy investors. Indeed, Sotheby's auction house has revealed that sales in luxury property in Monaco and France has risen by 38% this last quarter compared to the previous quarter.
Those looking to purchase ...
Fish mimics octopus that mimics fish
2012-01-05
SAN FRANCISCO (January 4, 2012) — Nature's game of intimidation and imitation comes full circle in the waters of Indonesia, where scientists have recorded for the first time an association between the black-marble jawfish (Stalix cf. histrio) and the mimic octopus (Thaumoctopus mimicus).
Undescribed by scientists until 1998, the talented mimic octopus is known to impersonate toxic flatfish, lionfish, and even sea snakes by creatively configuring its limbs, adopting characteristic undulating movements, and displaying bold brown-and-white color patterns. Thanks to these ...
No more free rides for 'piggy-backing' viruses
2012-01-05
Scientists have determined the structure of the enzyme endomannosidase, significantly advancing our understanding of how a group of devastating human viruses including HIV and Hepatitis C hijack human enzymes to reproduce and cause disease.
The findings open the door to the development of new drugs to combat these deadly viruses that infect more than 180 million people worldwide.
The team of international scientists led by and Professor Gideon Davies from the University of York and Associate Professor Spencer Williams from the University of Melbourne, studied bacterial ...
Russian river water unexpected culprit behind Arctic freshening near US, Canada
2012-01-05
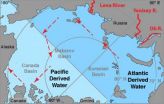
A hemispherewide phenomenon – and not just regional forces – has caused record-breaking amounts of freshwater to accumulate in the Arctic's Beaufort Sea.
Frigid freshwater flowing into the Arctic Ocean from three of Russia's mighty rivers was diverted hundreds of miles to a completely different part of the ocean in response to a decades-long shift in atmospheric pressure associated with the phenomenon called the Arctic Oscillation, according to findings published in the Jan. 5 issue of Nature.
The new findings show that a low pressure pattern created by the Arctic Oscillation ...
One in Four Brits Spend 40% of Take-Home Pay on Debt Payments, Reveals Debt Solutions Company, Debt Relief Orders
2012-01-05
The report from Moneysupermarket.com revealed that the average amount of non-mortgage debt paid off each month is GBP322 a month, around 25% of the average monthly net salary for a UK adult, while a shocking 8% claim to have spent over 80% of their wages repaying debt. And despite women having the reputation for being prolific shoppers, it is men that appear to have 15% more personal unsecured debt compared to their female counterparts - on average GBP7,944 compared to GBP6,739.
MoneySupermarket.com's head of loans and debt, Tim Moss, said: "With the cost of living ...
New fermented soy ingredient containing S-equol significantly reduced hot flash frequency
2012-01-05
Northridge, CALIF (Jan 4, 2012) – Daily doses of a soy germ-based nutritional supplement containing S-equol significantly improved menopausal symptoms, including significantly reducing hot flash frequency after 12 weeks according to a placebo-controlled study in postmenopausal Japanese women published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health.
"It is believed that S-equol, produced from the isoflavone daidzein during the fermentation of soy germ, interacts with specific estrogen receptors to promote the improvement in menopausal symptoms. Data from this study and ...
Results, Long-Term Breast Implants
2012-01-05
In 2006, the Food & Drug Administration approved two new models of silicone implants: one model was made by Mentor and the other by Allergan. This approval by the FDA proved controversial as many critics claimed there wasn't enough evidence of silicone implants being safe for the long term.
To study how the implants held up over long-term, the FDA required both Mentor and Allergan to perform a variety of follow-up studies--some studies won't even end until 2016. The study involved 40,000 participants for each model, totaling 80,000 in all.
Some studies included ...