(Press-News.org) Berlin, Germany, June 8 2012: Results of a study presented today at EULAR 2012, the Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism, suggest that the newly developed RABBIT Risk Score, which calculates the risk of serious infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who are treated with anti-tumour necrosis factor drugs (anti-TNFs) or conventional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is a valid and effective tool for rheumatologists to predict risk of serious infection.
The German study used data from 2,603 patients enrolled in the RABBIT register at the start of treatment with anti-TNFs (n=1,327) or conventional DMARDs (n=1,276). The likelihood of serious infection based on individual risk profiles was calculated using the RABBIT risk score. The score was developed by the same group of researchers on a different patient sample.
There was good agreement between observed and expected rates of serious infections. In the anti-TNF group, expected number of infections was 31.5 versus actual number observed which was 33. For conventional DMARDs, the expected number of infections was 14.8 versus the actual number observed which was 13.
"The results of our study validate the RABBIT Risk Score as a useful tool to help identify RA patients at high risk of developing infections when treated with anti-TNFs or DMARDs," said Professor Angela Zink from the German Rheumatism Research Centre in Berlin, Germany. "This tool could help rheumatologists identify at-risk patients and avoid treatment combinations that have a higher risk of infectious complications. This could also help reducing costs associated with treating the infections."
In patients who had ≥1 risk factor, including chronic lung disease, chronic renal disease, and age above 60 years, the RABBIT Risk Score also successfully predicted infection (10.0 expected vs 9.0 observed in DMARD group, 6.4 expected vs 6 observed in anti-TNF group).
###Abstract Number: OP0144
* Strangfeld et al, Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(11):1914-20
NOTES TO EDITORS:
For further information on this study, or to request an interview with the study lead, please do not hesitate to contact the EULAR congress Press Office in Hall 6 on the 3rd floor of the Congress Centre during EULAR 2012 or on:
Email: eularpressoffice@cohnwolfe.com
Candice Debleu:
Onsite tel: +44 7894 386 425
About EULAR
The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) is the organisation which represents the patient, health professional and scientific societies of rheumatology of all the European nations
In line with The European Union of Medical Specialists (UEMS), EULAR defines rheumatology as including rheumatic diseases of the connective tissue, locomotor and musculoskeletal systems
EULAR aims to promote, stimulate and support the research, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of rheumatic diseases. With 45 scientific member societies, 36 PARE organisations and 10 health professionals associations, EULAR underscores the importance of combating rheumatic diseases not only by medical means, but also through a wider context of care for rheumatic patients and a thorough understanding of their social and other needs
Diseases of the bone and joints such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis cause disability in 4-5% of the adult population and are predicted to rise as people live longer
EULAR 2012 is set to be the biggest rheumatology event in Europe with over 15,000 scientists, physicians, allied health professionals, and related audiences in attendance from over 115 countries. Over the course of the congress, more than 275 oral and 1400 poster abstract presentations will be featured, with 1,010 invited speaker lectures taking place in 190 sessions
To find out more about the activities of EULAR, visit: www.eular.org
Rabbit risk score can help rheumatologists identify patients at high risk of infection
New study validates score as new tool
2012-06-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
13.7 million young adults stayed on or joined their parents' health plans in 2011
2012-06-08
June 8, 2012, New York, NY—In 2011, 13.7 million young adults ages 19 to 25 stayed on or joined their parents' health plans, including 6.6 million who would likely not have been able to do so before passage of the Affordable Care Act, according to a new Commonwealth Fund report.
However, not all young adults have parents with health plans they can join, and many still experience gaps in coverage and face medical bill problems and medical debt. Nearly two of five (39%) young adults ages 19 to 29 went without health insurance at some time in 2011, and more than one-third ...
Parcel2Go Helping Small Businesses to Beat Royal Mail Price Increase
2012-06-08
Small firms feeling the squeeze following the Royal Mail's decision to increase the price of first and second class stamps at the end of last month are being offered a helping hand by Bolton-based online parcel delivery firm Parcel2Go.
The company says businesses and individuals can try to beat the Royal Mail price increase by becoming Parcel2Go users and benefiting from the vast range of reliable and cost-effective UK express delivery solutions available through the website.
With just a few clicks of a mouse, customers can order delivery services from some of the ...
King Jackpot Makes Playing No Deposit Bingo a Breeze
2012-06-08
Any experienced bingo player can tell you that one of the keys to success in playing bingo online is choosing the right bingo website. Many bingo websites are all talk and no show, or do not give players the generous offers that they desire and deserve. One feature on bingo websites that every new player should look out for is no deposit required bingo.
This means that when players register, they are given free cash to be used towards trying bingo games on the website, without spending a penny of their own money! While players cannot withdraw this cash for personal ...
Bingo Newbies Learn Their Online Bingo Strategies With Bingo Cafe
2012-06-08
The difference between online bingo players and traditional bingo hall players is that the bingo lovers on the Internet like to play bingo at their own convenience - anytime, anywhere. Whether it is at the coffee shop or in the comfort of one's home, bingo games can be played online anywhere, as long as there is an Internet connection and a computer! What could be better than playing great bingo matches and winning money on the go? It is easy to see then why so many people are interested in trying their hand at online bingo. However, it can be difficult to know how and ...
Prompt Proofing Blog Post: Marketing Tips: Email Marketing Campaigns
2012-06-08
According to the Direct Marketing Association, email marketing campaigns produce an average return of more than $50 for each dollar spent. Given that email marketing is pretty cost effective anyway, this statistic does make it seem a no-brainer.
Certainly, we at Prompt Proofing have noticed that, whenever we send out a mass email, it generates new orders. These orders come from our existing customers, since they are the ones who have agreed to receive email from us. If people have not used your services, or purchased one of your products, for a while, you may well have ...
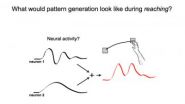
A different drummer: Stanford engineers discover neural rhythms drive physical movement
2012-06-05
Unlike their visual cousins, the neurons that control movement are not a predictable bunch. Scientists working to decode how such neurons convey information to muscles have been stymied when trying to establish a one-to-one relationship between a neuron's behavior and external factors such as muscle activity or movement velocity.
In an article published online June 3rd by the journal Nature, a team of electrical engineers and neuroscientists working at Stanford University propose a new theory of the brain activity behind arm movements. Their theory is a significant departure ...
Study suggests expanding the genetic alphabet may be easier than previously thought
2012-06-05
LA JOLLA, CA – A new study led by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute suggests that the replication process for DNA—the genetic instructions for living organisms that is composed of four bases (C, G, A and T)—is more open to unnatural letters than had previously been thought. An expanded "DNA alphabet" could carry more information than natural DNA, potentially coding for a much wider range of molecules and enabling a variety of powerful applications, from precise molecular probes and nanomachines to useful new life forms.
The new study, which appears in the June ...
Rhythmic firing of nerve cells involved in body's movements
2012-06-05
A new model for understanding how nerve cells in the brain control movement may help unlock the secrets of the motor cortex, a critical region that has long resisted scientists' efforts to understand it, researchers report June 3 in Nature.
Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis, Stanford University and Columbia University have shown that the motor cortex's effects on movement can be much more easily understood by looking at groups of motor cortex neurons instead of individual nerve cells. In the study, scientists identified rhythmic brain cell firing patterns ...
Lower income patients less likely to participate in cancer clinical trials
2012-06-05
MAYWOOD, Il. -- Lower-income cancer patients are less likely to participate in cancer clinical trials, according to a study co-authored by Loyola University Medical Center oncologist Kathy Albain, MD, FACP.
Patients with incomes of less than $50,000 per year were 27 percent less likely than higher-income patients to participate in clinical trials, and those with incomes less than $20,000 were 44 percent less likely to participate.
Fifty-three percent of patients with incomes less than $20,000 per year expressed concerns about their costs of participating in clinical trials. ...
New breast cancer drug halts tumor growth better than standard therapy
2012-06-05
DURHAM, N.C. – A new cancer treatment that links chemotherapy with an agent that homes in on specific breast cancer cells was significantly better than the current drug regimen at keeping patients' advanced tumors from progressing, according to results from a Phase III clinical trial led by Kimberly Blackwell, M.D., of the Duke Cancer Institute.
Participants with invasive breast cancer who took the investigational drug, called trastuzumab emtansine, or T-DM1, also had fewer and less harsh side effects than study participants who received a standard treatment.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Rabbit risk score can help rheumatologists identify patients at high risk of infectionNew study validates score as new tool