(Press-News.org) WHAT:
A research team at the National Institutes of Health has found that bacteria that normally live in the skin may help protect the body from infection. As the largest organ of the body, the skin represents a major site of interaction with microbes in the environment.
Although immune cells in the skin protect against harmful organisms, until now, it has not been known if the millions of naturally occurring commensal bacteria in the skin—collectively known as the skin microbiota—also have a beneficial role. Using mouse models, the NIH team observed that commensals contribute to protective immunity by interacting with the immune cells in the skin. Their findings appear online on July 26th in Science.
The investigators colonized germ-free mice (mice bred with no naturally occurring microbes in the gut or skin) with the human skin commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis. The team observed that colonizing the mice with this one species of good bacteria enabled an immune cell in the mouse skin to produce a cell-signaling molecule needed to protect against harmful microbes. The researchers subsequently infected both colonized and non-colonized germ-free mice with a parasite. Mice that were not colonized with the bacteria did not mount an effective immune response to the parasite; mice that were colonized did.
In separate experiments, the team sought to determine if the presence or absence of commensals in the gut played a role in skin immunity. They observed that adding or eliminating beneficial bacteria in the gut did not affect the immune response at the skin. These findings indicate that microbiota found in different tissues—skin, gut, lung—have unique roles at each site and that maintaining good health requires the presence of several different sets of commensal communities.
This study provides new insights into the protective role of skin commensals, and demonstrates that skin health relies on the interaction of commensals and immune cells. Further research is needed, say the authors, to determine whether skin disorders such as eczema and psoriasis may be caused or exacerbated by an imbalance of skin commensals and potentially harmful microbes that influence the skin and its immune cells.
###
The study was led by investigators in the laboratories of Yasmine Belkaid, Ph.D., at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, in collaboration with Julie Segre, Ph.D., at the National Human Genome Research Institute, and Giorgio Trinchieri, M.D., and Heidi Kong, M.D., at the National Cancer Institute. All three Institutes are NIH components.
ARTICLE:
S Naik et al. Compartmentalized control of skin immunity by resident commensals. Science. DOI: 10.1126/science.1225152 (2012).
WHO:
Yasmine Belkaid, Ph.D., chief, Mucosal Immunology Section, Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and Julie Segre, Ph.D., senior investigator, Genetics and Molecular Biology Branch, National Human Genome Research Institute, are available for comment.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Julie Wu, (301) 402-1663, niaidnews@niaid.nih.gov, or Raymond MacDougall, (301) 402-0911, macdougallr@mail.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID Web site at http://www.niaid.nih.gov.
NHGRI is one of the 27 institutes and centers at the National Institutes of Health, an agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The NHGRI Division of Intramural Research develops and implements technology to understand, diagnose and treat genomic and genetic diseases. Additional information about NHGRI can be found at its website, www.genome.gov.
NCI leads the National Cancer Program and the NIH effort to dramatically reduce the burden of cancer and improve the lives of cancer patients and their families, through research into prevention and cancer biology, the development of new interventions, and the training and mentoring of new researchers. For more information about cancer, please visit the NCI Web site at http://www.cancer.gov or call NCI's Cancer Information Service at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/. END
NIH team describes protective role of skin microbiota
Commensal bacteria and immune cells work together to fight harmful microbes
2012-07-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Telephone therapy technique brings more Iraq and Afghanistan veterans into mental health treatment
2012-07-27
A brief therapeutic intervention called motivational interviewing, administered over the telephone, was significantly more effective than a simple "check-in" call in getting Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans with mental health diagnoses to begin treatment for their conditions, in a study led by a physician at the San Francisco VA Medical Center and the University of California, San Francisco.
Participants receiving telephone motivational interviewing also were significantly more likely to stay in therapy, and reported reductions in marijuana use and a decreased sense ...
Breast cancer patients who lack RB gene respond better to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
2012-07-27
PHILADELPHIA—Breast cancer patients whose tumors lacked the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene (RB) had an improved pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, researchers at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital and the Kimmel Cancer Center at Jefferson report in a retrospective study published in a recent online issue of Clinical Cancer Research.
Many breast cancer patients undergo neoadjuvant therapy to reduce the size or extent of the cancer before surgical intervention. Complete response of the tumor to such treatment signifies an improved overall prognosis. ...
Solving the mystery of how cigarette smoking weakens bones
2012-07-27
Almost 20 years after scientists first identified cigarette smoking as a risk factor for osteoporosis and bone fractures, a new study is shedding light on exactly how cigarette smoke weakens bones. The report, in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research, concludes that cigarette smoke makes people produce excessive amounts of two proteins that trigger a natural body process that breaks down bone.
Gary Guishan Xiao and colleagues point out that previous studies suggested toxins in cigarette smoke weakened bones by affecting the activity of osteoblasts, cells which build new bone, ...
Alcohol could intensify the effects of some drugs in the body
2012-07-27
Scientists are reporting another reason — besides possible liver damage, stomach bleeding and other side effects — to avoid drinking alcohol while taking certain medicines. Their report in ACS' journal Molecular Pharmaceutics describes laboratory experiments in which alcohol made several medications up to three times more available to the body, effectively tripling the original dose.
Christel Bergström and colleagues explain that beverage alcohol, or ethanol, can cause an increase in the amount of non-prescription and prescription drugs that are "available" to the body ...
A new genre of diagnostic tests for the era of personalized medicine
2012-07-27
A new genre of medical tests – which determine whether a medicine is right for a patient's genes – are paving the way for increased use of personalized medicine, according to the cover story in the current edition of Chemical & Engineering News. C&EN is the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society.
Celia Henry Arnaud, C&EN senior editor, points out that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved several precedent-setting cancer drugs that provide a glimpse of the "personalized" medical care that awaits patients ...
The first robot that mimics the water striders' jumping abilities
2012-07-27
The first bio-inspired microrobot capable of not just walking on water like the water strider – but continuously jumping up and down like a real water strider – now is a reality. Scientists reported development of the agile microrobot, which could use its jumping ability to avoid obstacles on reconnaissance or other missions, in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Qinmin Pan and colleagues explain that scientists have reported a number of advances toward tiny robots that can walk on water. Such robots could skim across lakes and other bodies of water to monitor water ...
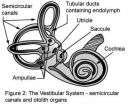
Decoding the secrets of balance
2012-07-27
If you have ever looked over the edge of a cliff and felt dizzy, you understand the challenges faced by people who suffer from symptoms of vestibular dysfunction such as vertigo and dizziness. There are over 70 million of them in North America. For people with vestibular loss, performing basic daily living activities that we take for granted (e.g. dressing, eating, getting in and out of bed, getting around inside as well as outside the home) becomes difficult since even small head movements are accompanied by dizziness and the risk of falling.
We've known for a while ...
Big horns trump smooth pickup lines every time
2012-07-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Elk and rhinoceros beetles aren't diabetic, but to grow big horns and attract mates it appears that the males are insulin-dependent.
Ian Dworkin, Michigan State University zoologist, was part of a team that for the first time ever showed why horns – from elk to rhinoceros beetles – and other decorative, mate-attracting structures are sensitive to changes in nutrition. As reported in the current issue of Science, the key ingredient for this growth is insulin, Dworkin said.
"Clearly elk antlers, peacock tail feathers and beetle horns are very different, ...
Rivers flowing into the sea offer vast potential as electricity source
2012-07-27
WASHINGTON, July 25, 2012 — The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series describes a process that could pave the way for a new genre of electric power-generating stations. These stations could supply electricity for more than a half billion people by tapping just one-tenth of the global potential of a little-known energy source that exists where rivers flow into the ocean.
Based on a report by Menachem Elimelech, Ph.D., and Ngai Yin Yip in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, ...
New research confirms efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression
2012-07-27
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – In one of the first studies to look at transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) in real-world clinical practice settings, researchers at Butler Hospital, along with colleagues across the U.S., confirmed that TMS is an effective treatment for patients with depression who are unable to find symptom relief through antidepressant medications. The study findings are published online in the June 11, 2012 edition of Depression and Anxiety in the Wiley Online Library.
Previous analysis of the efficacy of TMS has been provided through more than 30 published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Don’t Panic: ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’ has begun
A robust new telecom qubit in silicon
Vertebrate paleontology has a numbers problem. Computer vision can help
Reinforced enzyme expression drives high production of durable lactate-based polyester
In Rett syndrome, leaky brain blood vessels traced to microRNA
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
The Frontiers of Knowledge Award goes to Charles Manski for incorporating uncertainty into economic research and its application to public policy analysis
Walter Koroshetz joins Dana Foundation as senior advisor
Next-generation CAR-T designs that could transform cancer treatment
As health care goes digital, patients are being left behind
A clinicopathologic analysis of 740 endometrial polyps: risk of premalignant changes and malignancy
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
Women more likely to choose wine from female winemakers
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
[Press-News.org] NIH team describes protective role of skin microbiotaCommensal bacteria and immune cells work together to fight harmful microbes