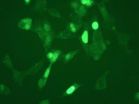
(Press-News.org) A new advance in X-ray imaging has revealed the dramatic three-dimensional shape of gold nanocrystals, and is likely to shine a light on the structure of other nano-scale materials.
Described today in Nature Communications, the new technique improves the quality of nanomaterial images, made using X-ray diffraction, by accurately correcting distortions in the X-ray light.
Dr Jesse Clark, lead author of the study from the London Centre for Nanotechnology said: "With nanomaterials playing an increasingly important role in many applications, there is a real need to be able to obtain very high quality three dimensional images of these samples.
"Up until now we have been limited by the quality of our X-rays. Here we have demonstrated that with imperfect X-ray sources we can still obtain very high quality images of nanomaterials."
Up until now, most nanomaterial imaging has been done using electron microscopy. X-ray imaging is an attractive alternative as X-rays penetrate further into the material than electrons and can be used in ambient or controlled environments.
However, making lenses that focus X-rays is very difficult. As an alternative, scientists use the indirect method of coherent diffraction imaging (CDI), where the diffraction pattern of the sample is measured (without lenses) and inverted to an image by computer.
Nobel Prize winner Lawrence Bragg suggested this method in 1939 but had no way to determine the missing phases of the diffraction, which are today provided by computer algorithms.
CDI can be performed very well at the latest synchrotron X-ray sources such as the UK's Diamond Light Source which have much higher coherent flux than earlier machines. CDI is gaining momentum in the study of nanomaterials, but, until now, has suffered from poor image quality, with broken or non-uniform density. This had been attributed to imperfect coherence of the X-ray light used.
The dramatic three-dimensional images of gold nanocrystals presented in this study demonstrate that this distortion can be corrected by appropriate modelling of the coherence function.
Professor Ian Robinson, London Centre for Nanotechnology and author of the paper said: "The corrected images are far more interpretable that ever obtained previously and will likely lead to new understanding of structure of nanoscale materials."
The method should also work for free-electron-laser, electron- and atom-based diffractive imaging.
###
Notes for Editors
1. For more information or to speak to Dr Jesse Clark or Professor Ian Robinson please contact Clare Ryan in the UCL Media Relations Office on tel: +44 (0)20 3108 3846, mobile: +44 07747 565 056, out of hours +44 (0)7917 271 364, e-mail: clare.ryan@ucl.ac.uk
2. 'High-resolution three-dimensional partially coherent diffraction imaging' is published online in the journal Nature Communications. Copies of the paper are available from UCL Media Relations.
About UCL (University College London)
Founded in 1826, UCL was the first English university established after Oxford and Cambridge, the first to admit students regardless of race, class, religion or gender, and the first to provide systematic teaching of law, architecture and medicine. We are among the world's top universities, as reflected by performance in a range of international rankings and tables. UCL currently has 24,000 students from almost 140 countries, and more than 9,500 employees. Our annual income is over £800 million.
www.ucl.ac.uk | Follow us on Twitter @uclnews
Advance in X-ray imaging shines light on nanomaterials
2012-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Food hypersensitivity and otolaryngologic conditions in young children
2012-08-07
Alexandria, VA — Cow's milk protein allergy (CMPA), although difficult to diagnose in young children, shows a causative relationship to otolaryngic symptoms. A new study in the August journal, Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery suggests an elimination diet may help manage such conditions in children under two and reduce the need for more serious upper airway tests and interventions.
"Early recognition of CMPA in association with upper airway disease may subsequently reduce the economic burden and number of procedures required in affected infants," report the authors.
The ...
Why do infants get sick so often?
2012-08-07
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Researchers at the University of Michigan Health System are helping to quell parents' worry about why infants seem to get sick so often.
It's been believed that, like walking and talking, fighting viral infections is something children will develop when they get older. But a U-M study suggests the natural ability to fight infection is there early on.
Scientists learned key cell signals inhibit the growth of essential immune cells early in life. Blocking this signaling could lead to improving an infant's response to infection, according to the study ...
Treatment target for diabetes, Wolfram syndrome
2012-08-07
AUDIO:
Wolfram syndrome is a rare disorder that causes insulin-dependent diabetes, kidney problems and vision and hearing loss, among other things. Now researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St....
Click here for more information.
Inflammation and cell stress play important roles in the death of insulin-secreting cells and are major factors in diabetes. Cell stress also plays a role in Wolfram syndrome, a rare, genetic disorder that afflicts children with ...
Frequent traveller: Dysentery-causing bacteria spreading from Europe to Australia
2012-08-07
Researchers have found that a strain of dysentery-causing bacterium that originated from Europe centuries ago is spreading rapidly to Australia and some developing countries
First author, Dr Kathryn Holt from the University of Melbourne said that the bacterium strain Shingella. sonnei is easily transmitted due to the high levels of drug resistance in developed countries.
"Contrary to standard guidelines, drug treatment and better sanitation alone will not be sufficient for controlling this strain. Vaccine development will be crucial." she said
Dr Holt has pioneered ...
Using wastewater as fertilizer
2012-08-07
Phosphorus is a vital element not only for plants but also for all living organisms. In recent times, however, farmers have been faced with a growing shortage of this essential mineral, and the price of phosphate-based fertilizers has been steadily increasing. It is therefore high time to start looking for alternatives. This is not an easy task, because phosphorus cannot be replaced by any other substance. But researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB in Stuttgart have found a solution that makes use of locally available resources ...
Making it easier to learn to read
2012-08-07
This press release is available in German.
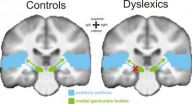
To participate successfully in life, it is important to be able to read and write. Nevertheless, many children and adults have difficulties in acquiring these skills and the reason is not always obvious. They suffer from dyslexia which can have a variety of symptoms. Thanks to research carried out by Begoña Díaz and her colleagues at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, a major step forward has been made in understanding the cause of dyslexia. The scientists have discovered an important ...
Lower risk of serious side-effects in trials of new targeted drugs
2012-08-07
Patients in early clinical trials of new-style targeted cancer therapies appear to have a much lower risk of the most serious side-effects than with traditional chemotherapy, according to a new analysis.
Researchers at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust analysed data from 36 Phase I trials run by the organisations' joint Drug Development Unit.
The study, published today in August's Annals of Oncology, found the overall risk to patients of suffering a life-threatening side-effect was around seven times less than for traditional ...
Study questions value of calcium and vitamin D supplements
2012-08-07
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Aug. 7, 2012 – Prescribing calcium and vitamin D supplements for men at risk of bone loss from hormonal treatment for prostate cancer seems like good medicine.
But new research from epidemiologists at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center showed that this type of supplementation did not prevent bone loss and, in fact, may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and aggressive prostate cancer. The study was published online in the July issue of the journal The Oncologist.
"It wouldn't be so bad if there simply was no obvious benefit," said Gary ...
Children's healthy diets lead to healthier IQ
2012-08-07
Children fed healthy diets in early age may have a slightly higher IQ, while those on heavier junk food diets may have a slightly reduced IQ, according to new research from the University of Adelaide.
The study - led by University of Adelaide Public Health researcher Dr Lisa Smithers - looked at the link between the eating habits of children at six months, 15 months and two years, and their IQ at eight years of age.
The study of more than 7000 children compared a range of dietary patterns, including traditional and contemporary home-prepared food, ready-prepared baby ...
What makes Paris look like Paris? Carnegie Mellon software finds stylistic core
2012-08-07
PITTSBURGH—Paris is one of those cities that has a look all its own, something that goes beyond landmarks such as the Eiffel Tower or Notre Dame. Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and INRIA/Ecole Normale Supérieure in Paris have developed visual data mining software that can automatically detect these sometimes subtle features, such as street signs, streetlamps and balcony railings, that give Paris and other cities a distinctive look.
The software analyzed more than 250 million visual elements gleaned from 40,000 Google Street View images of Paris, London, New ...