(Press-News.org) Follow-up research from the Pediatric Study of Hepatitis C (PEDS-C) trial reveals that children treated with peginterferon alpha (pegIFNα) for hepatitis C (HCV) display significant changes in height, weight, body mass index (BMI), and body composition. Results appearing in the August issue of Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, indicate that most growth-related side effects are reversible with cessation of therapy. However, in many children the height-for-age score had not returned to baseline two years after stopping treatment.
In the U.S. an estimated 240,000 children have the HCV antibody and up to 100,000 have chronic HCV (Jonas, 2002). "While HCV in children is typically mild, some cases do progress to cirrhosis and liver cancer," explains lead author Maureen Jonas, Director of the Center for Childhood Liver Disease and Medical Director of the Liver Transplant Program at Boston Children's Hospital in Massachusetts. "Treatment of HCV with peginterferon and ribavirin is approved for young children and offers the most benefit while liver disease is mild. However, there are concerns about the potential side effects of peginterferon therapy in children, which is the focus of our current study."
Children between the ages of 5 to 18 years with chronic HCV were recruited for the Pediatric Study of Hepatitis C (PEDS-C), a multi-center trial of the safety of pegIFNα with and without ribavirin that took place from December 2004 through May 2006. For the present study, children were followed for an additional two years to determine if height, weight, or BMI were affected by treatment. Subjects were placed into three groups based on duration of pegIFNα therapy at 24, 48 or 72 weeks.
The study group included 107 children with a mean age of 11 years of age; 55% were male, 82% were Caucasian, and all were of normal height, weight, BMI, and body composition at baseline. While on therapy, researchers observed up to a 0.5 unit decrease in height, weight, and BMI z scores (standard deviation scores) in some participants on therapy. In the 48-week treatment group, 33% of children had a greater than 0.5 unit decrement in their height-for-age z score.
Results show that mean height-for-age z scores were slower to rebound than those for weight and BMI. The authors report that after two years following the end of treatment, mean height z scores were lower than baseline in most children who had been treated with peginterferon for 48 or 72 weeks. Physical activity and food intake among the children did not change during the study period.
"Our findings demonstrate significant effects on weight, BMI, and body composition in children treated with pegIFNα that are reversible upon cessation of treatment. A reduction in linear growth persisted even after treatment was discontinued," said Dr. Jonas. "Additional investigation of growth patterns is needed to determine long-term outcomes so that optimal timing of treatment can be determined for children with chronic HCV."
INFORMATION:
Full citation: "Peginterferon for Chronic Hepatitis C in Children affects Growth and Body Composition: Results from the Pediatric Study of Hepatitis C (PEDS-C) Trial." Maureen M. Jonas, William Balistreri, Regino P. Gonzalez-Peralta, Barbara Haber, Steven Lobritto, Parvathi Mohan, Jean P. Molleston, Karen F. Murray, Michael R.Narkewicz, Philip Rosenthal, Kathleen B. Schwarz, Bruce A. Barton, John A. Shepherd, Paul D. Mitchell and Christopher Duggan. Hepatology; (DOI: 10.1002/hep.25690); Print Issue Date: August, 2012.
URL: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.25690/abstract
Author Contact: To arrange an interview with Dr. Jonas, please contact Keri Stedman at keri.stedman@childrens.harvard.edu or at 617-919-3114.
This study is published in Hepatology. Media wishing to receive a PDF of this article may contact sciencenewsroom@wiley.com .
About the Journal:
Hepatology is the premier publication in the field of liver disease, publishing original, peer-reviewed articles concerning all aspects of liver structure, function and disease. Each month, the distinguished Editorial Board monitors and selects only the best articles on subjects such as immunology, chronic hepatitis, viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, genetic and metabolic liver diseases and their complications, liver cancer, and drug metabolism. Hepatology is published on is published by Wiley on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). For more information, please visit http://wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/hep.
About Wiley:
Founded in 1807, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. has been a valued source of information and understanding for more than 200 years, helping people around the world meet their needs and fulfill their aspirations. Wiley and its acquired companies have published the works of more than 450 Nobel laureates in all categories: Literature, Economics, Physiology or Medicine, Physics, Chemistry, and Peace.
Our core businesses publish scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly journals, encyclopedias, books, and online products and services; professional/trade books, subscription products, training materials, and online applications and Web sites; and educational materials for undergraduate and graduate students and lifelong learners. Wiley's global headquarters are located in Hoboken, New Jersey, with operations in the U.S., Europe, Asia, Canada, and Australia. The Company's Web site can be accessed at http://www.wiley.com. The Company is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbols JWa and JWb.
END
(Boston) – Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and Veterans Affairs (VA) Boston Healthcare System have demonstrated that the effects on white matter brain volume from long-term alcohol abuse are different for men and women. The study, which is published online in Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, also suggests that with abstinence, women recover their white matter brain volume more quickly than men.
The study was led by Susan Mosher Ruiz, PhD, postdoctoral research scientist in the Laboratory for Neuropsychology at BUSM and research ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Earthworms creep along the ground by alternately squeezing and stretching muscles along the length of their bodies, inching forward with each wave of contractions. Snails and sea cucumbers also use this mechanism, called peristalsis, to get around, and our own gastrointestinal tracts operate by a similar action, squeezing muscles along the esophagus to push food to the stomach.
Now researchers at MIT, Harvard University and Seoul National University have engineered a soft autonomous robot that moves via peristalsis, crawling across surfaces by contracting ...
NASA scientist Tom Hanisco is helping to fill a big gap in scientists' understanding of how much urban pollution -- and more precisely formaldehyde -- ultimately winds up in Earth's upper atmosphere where it can wreak havoc on Earth's protective ozone layer.
He and his team at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., have developed an automated, lightweight, laser-induced fluorescence device that measures the levels of this difficult-to-measure organic compound in the lower troposphere and then again at much higher altitudes. The primary objective is determining ...
Many of the long term goals people strive for — like losing weight — require us to use self-control and forgo immediate gratification. And yet, denying our immediate desires in order to reap future benefits is often very hard to do.
In a new article in the August issue of Current Directions in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, researchers Kentaro Fujita and Jessica Carnevale of The Ohio State University propose that the way people subjectively understand, or construe, events can influence self-control.
Research from psychological ...
NEW YORK, N.Y. (August 9, 2012) – Over 400 attendees from across the U.S. and around the world participated in the first national conference for families and professionals, "Treating the Whole Person with Autism: Comprehensive Care for Children and Adolescents with ASD."
Autism Speaks, the world's leading autism science and advocacy organization, organized and hosted the conference in collaboration with educational partners at Nationwide Children's Hospital (NCH), The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and the Health ...
VIDEO:
Researchers Alyssa Stark and Tim Sullivan test the adhesion of a geckos feet in water. Their findings may help improve the adhesion of bandages, sutures and similar items in moist...
Click here for more information.
Akron, Ohio, August 9, 2012 — Scientists already know that the tiny hairs on geckos' toe pads enable them to cling, like Velcro, to vertical surfaces. Now, University of Akron researchers are unfolding clues to the reptiles' gripping power in wet conditions ...
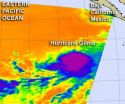
High, cold cloud tops with bitter cold temperatures are indicators that there's a lot of strength in the uplift of air within a tropical cyclone. NASA's Aqua satellite passed by Hurricane Gilma and saw a concentrated area of very cold cloud tops.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Gilma on August 9 at 5:53 a.m. EDT. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms and heaviest rainfall were wrapped around the storm's center. Cloud top temperatures in that area were as cold ...
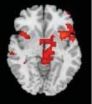
In patients with hoarding disorder, parts of a decision-making brain circuit under-activated when dealing with others' possessions, but over-activated when deciding whether to keep or discard their own things, a National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)-funded study has found. NIMH is part of the National Institutes of Health.
Brain scans revealed the abnormal activation in areas of the anterior cingulate cortex and insula known to process error monitoring, weighing the value of things, assessing risks, unpleasant feelings, and emotional decisions.
NIMH grantee David ...
For years, many scientists had thought that plate tectonics existed nowhere in our solar system but on Earth. Now, a UCLA scientist has discovered that the geological phenomenon, which involves the movement of huge crustal plates beneath a planet's surface, also exists on Mars.
"Mars is at a primitive stage of plate tectonics. It gives us a glimpse of how the early Earth may have looked and may help us understand how plate tectonics began on Earth," said An Yin, a UCLA professor of Earth and space sciences and the sole author of the new research.
Yin made the discovery ...
The possibility of an inexpensive, convenient test for Alzheimer's disease has been on the horizon for several years, but previous research leads have been hard to duplicate.
In a study to be published in the August 28 issue of the journal Neurology, scientists have taken a step toward developing a blood test for Alzheimer's, finding a group of markers that hold up in statistical analyses in three independent groups of patients.
"Reliability and failure to replicate initial results have been the biggest challenge in this field," says lead author William Hu, MD, PhD, ...